

Important Link between the Brain and Immune System Found. When the ancient Egyptians prepared a mummy they would scoop out the brain through the nostrils and throw it away.
How Removing Half of Someone's Brain Can Improve Their Life. We may be biased, but we think the human brain is pretty special.
All this week, mentalfloss.com is celebrating this miracle organ with a heap of brain[y] stories, lists, and videos. It all leads up to Brain Surgery Live With mental_floss, a two-hour television event that will feature—yes—live brain surgery. Hosted by Bryant Gumbel, the special airs Sunday, October 25 at 9 p.m. EST on the National Geographic Channel. From the outside, Elena del Peral seems to be like any other high-achieving college senior.
But beneath her cap is one remarkable mind. Aphantasia. Aphantasia is the suggested name for a condition where one does not possess a functioning mind's eye and cannot visualize imagery.[1] The phenomenon was first described by Francis Galton in 1880,[2] but has remained largely unstudied since.
Interest in the phenomenon renewed after the publication of a study conducted by a team led by Prof. Adam Zeman of the University of Exeter,[3] which also coined the term aphantasia.[4] Research on the subject is still scarce, but further studies are planned.[5][6] History[edit] The phenomenon was first described by Francis Galton in 1880 in a statistical study about mental imagery.[2] Galton described it as a common phenomenon among his peers.[7] However, it remained largely unstudied until 2005, when Prof. In popular culture[edit] In April 2016 an essay by Blake Ross was published on Facebook, describing his own aphantasia and his recent realisation that not everyone experiences it. Related concepts[edit] This Nifty Infographic Is a Great Introduction to Neuroplasticity and Cognitive Therapy.
It's startling to think about how we've got a spaceship billions of miles away rendezvousing with Pluto, yet here on Earth there are major aspects of our own anatomy that we're almost completely ignorant about.
We've climbed Everest, sent men to the moon, and invented the Internet — but we still don't know how our brains work. The positive outlook is that many health, science, and research specialists believe we're on the precipice of some major neuroscientific breakthroughs. One example of a recent discovery with major implications is our further understanding of neuroplasticity. Simply put, we used to think our brain was what it was — unchangeable, unalterable. We were stuck with what nature gave us. 9 Nervy Facts About the Vagus Nerve. Neurocomic: A Graphic Novel About How the Brain Works. By Maria Popova From the caves of memory to the castles of deception, by way of naughty neurotransmitters and giddy ganglia.
Scientists are only just beginning to understand how the brain works — from what transpires in it while we sleep to how to optimize its memory to what love does to it to how music affects it — and the rest of us fall somewhere on the spectrum between fascinated and confused when it comes to the intricate inner workings of our master-controller.
From British indie press Nobrow — who also brought us Freud’s graphic biography, those lovely illustrated chronicles of the Space Race and aviation, as well as Blexbolex’s magnificent No Man’s Land — comes Neurocomic (public library | IndieBound), a graphic novel about how the brain works. This remarkable collaboration between Dr. Hana Roš (and dog knows I love few things more than a female neuroscientist) and neuroscience-PhD-turned-illustrator Dr. Etymology of Neuroscience Terms. Neuroscience. Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system.[1] Traditionally, neuroscience has been seen as a branch of biology.
However, it is currently an interdisciplinary science that collaborates with other fields such as chemistry, computer science, engineering, linguistics, mathematics, medicine and allied disciplines, philosophy, physics, and psychology. Facts about the human brain.
Brain function. Memory. Self. Willpower. Emotions. Sociobiology. Sociobiology is a field of scientific study which is based on the assumption that social behavior has resulted from evolution and attempts to explain and examine social behavior within that context.
Often considered a branch of biology and sociology, it also draws from ethology, anthropology, evolution, zoology, archaeology, population genetics, and other disciplines. Within the study of human societies, sociobiology is very closely allied to the fields of Darwinian anthropology, human behavioral ecology and evolutionary psychology. Sociobiology investigates social behaviors, such as mating patterns, territorial fights, pack hunting, and the hive society of social insects. It argues that just as selection pressure led to animals evolving useful ways of interacting with the natural environment, it led to the genetic evolution of advantageous social behavior. Definition[edit] The discipline seeks to explain behavior as a product of natural selection. Introductory example[edit] History[edit] Behavioral neuroscience. Behavioral neuroscience, also known as biological psychology,[1] biopsychology, or psychobiology[2] is the application of the principles of biology (in particular neurobiology), to the study of physiological, genetic, and developmental mechanisms of behavior in humans and non-human animals.
It typically investigates at the level of neurons, neurotransmitters, brain circuitry and the basic biological processes that underlie normal and abnormal behavior. Often, experiments in behavioral neuroscience involve non-human animal models (such as rats and mice, and non-human primates) which have implications for better understanding of human pathology and therefore contribute to evidence-based practice. History[edit] Behavioral neuroscience as a scientific discipline emerged from a variety of scientific and philosophical traditions in the 18th and 19th centuries.
In philosophy, people like René Descartes proposed physical models to explain animal and human behavior. Research methods[edit] Pineal Gland's Third Eye: One Of The Biggest Cover-ups in Human History. The pineal gland (also called the pineal body, epiphysis cerebri, epiphysis or the “third eye”) is a small endocrine gland in the vertebrate brain.
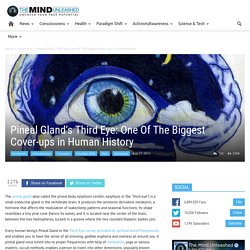
It produces the serotonin derivative melatonin, a hormone that affects the modulation of wake/sleep patterns and seasonal functions. Its shape resembles a tiny pine cone (hence its name), and it is located near the center of the brain, between the two hemispheres, tucked in a groove where the two rounded thalamic bodies join. Every human being’s Pineal Gland or the Third Eye can be activated to spiritual world frequencies and enables you to have the sense of all knowing, godlike euphoria and oneness all around you. A pineal gland once tuned into to proper frequencies with help of meditation, yoga or various esoteric, occult methods, enables a person to travel into other dimensions, popularly known as astral travel or astral projection or remote viewing.
The Secret : What they don’t want you to KNOW! Source. Brain Waves And The Deeper States Of Consciousness. Every part of your body vibrates to its own rhythm.

Your brain has a unique set of brain waves. In neuroscience, there are five distinct brain wave frequencies, namely Beta, Alpha, Theta, Delta and the lesser known Gamma. Learning mind control at the deeper states of consciousness opens you up to the world of your subconscious mind where you can create your reality at will and with exact precision. Each frequency, measured in cycles per second (Hz), has its own set of characteristics representing a specific level of brain activity and hence a unique state of consciousness.
Beta (12-30Hz): Beta brain waves are associated with normal waking consciousness and a heightened state of alertness, logic and critical reasoning. Alpha (7.5-12Hz): Alpha brain waves are present in deep relaxation with the eyes usually closed and while day-dreaming. The New Science of Addiction: Genetics and the Brain. The Split Brain Experiments. Lists of Nobel Prizes and Laureates The Split Brain Experiments Play the Split Brain Experiments About the game. Researcher: Dopamine Not About Pleasure (Anymore) John Salamone, professor of psychology, at his office. (Peter Morenus/UConn Photo) To John Salamone, professor of psychology and longtime researcher of the brain chemical dopamine, scientific research can be very slow-moving.
“It takes a long time for things to change in science,” he says. BrainMind.net. When hallucinations follow depth electrode or cortical stimulation, much of the material experienced is very dream-like (Gloor 1990, 1992; Halgren et al., 1978; Malh et al., 1964; Penfield & Perot 1963) and consists of recent perceptions, ideas, feelings, and other emotions which are similarly illusionary and dream-like.
Indeed, the right amygdala, hippocampus, and the right hemisphere in general (Broughton, 1982; Goldstein et al., 1972; Hodoba, 1986; Humphrey & Zangwill, 1961; Kerr & Foulkes, 1978; Meyer et al. 1987) also appear to be involved in the production of deam imagery as well as REM sleep (chapter 10). For example stimulation of the amygdala triggers and increases ponto-geniculo-occipital paradoxical activity during sleep (Calvo, et al. 1987), which in turn is associated with REM and dreaming.
The Right Hemisphere & Dreams. Forgotten Dreams. The Ten Most Revealing Psych Experiments. Psychology is the study of the human mind and mental processes in relation to human behaviors - human nature. Due to its subject matter, psychology is not considered a 'hard' science, even though psychologists do experiment and publish their findings in respected journals. Some of the experiments psychologists have conducted over the years reveal things about the way we humans think and behave that we might not want to embrace, but which can at least help keep us humble.
That's something. 1. The Dark Side of Oxytocin, the Hormone of Love - Ethnocentrism. Yes, you knew there had to be a catch. As oxytocin comes into sharper focus, its social radius of action turns out to have definite limits. The love and trust it promotes are not toward the world in general, just toward a person’s in-group. 10 Brilliant Social Psychology Studies. Ten of the most influential social psychology experiments. “I have been primarily interested in how and why ordinary people do unusual things, things that seem alien to their natures.Why do good people sometimes act evil? Why do smart people sometimes do dumb or irrational things?” Mythbusters: 5 Amazing Facts about the Brain « psychosycho.
Here’s 5 incredible facts about your brain that will put those common myths to rest – and give you an insight into that amazing and intricate mass in your head. 1. 10 Practical Uses For Psychological Research in Everyday Life. The Limits of Intelligence. Brain-based learning, ideas, and materials. Multitasking:This is your Brain on Media. The Schmidt Sting Pain Index: How Much Could You Take? Have you ever been stung by a bee? Want to know how much you have suffered on a scale of one to four? 10 Questions About the Pineal Gland That Add to the Mystery of Spirituality. Near death experience. Characteristics[edit]