

Beowulf OE Video. Intro.
Beowulf Animated 1998 Part 1/6. What the English of Shakespeare, Beowulf, and King Arthur actually sounded like. Let's hop into a time machine and go back to the England of yore!

If this were a movie, no matter when we got out of the machine, we could walk up to people and start talking. It could be medieval times or the age of King Arthur's round table, and they'd just say, "Who art thou, varlet? " and we'd reply with something like, "We, uh, would-eth like-eth some beer-eth," and we'd all party. Yeah, no. I mean, of course they have to do that in movies, because we need to understand them. Shakespearean England First stop: the early 1600s. James Harbeck What Americans will sound like in 2050 Stop calling possessives 'possessive' Medieval England Next stop: the 1300s.
Whan that Aprill, with his shoures sooteThe droghte of March hath perced to the rooteAnd bathed every veyne in swich licour,Of which vertu engendred is the flour You can probably sort out what's being said, generally. Here's a bit of the text (the þ characters are how we used to write th): But wait, there's more. Old English Hwæt! Seamus Heaney on BEOWULF. And now this is ‘an inheritance’ – Upright, rudimentary, unshiftably planked In the long ago, yet willable forward Again and again and again.

The poem called Beowulf was composed some time between the middle of the seventh and the end of the tenth century of the first millennium, in the language that is today called Anglo-Saxon or Old English. It is a heroic narrative, more than three thousand lines long, concerning the deeds of a Scandinavian prince, also called Beowulf, and it stands as one of the foundation works of poetry in English. The fact that the English language has changed so much in the last thousand years means, however, that the poem is now generally read in translation and mostly in English courses at schools and universities.
The poem was written in England but the events it describes are set in Scandinavia, in a ‘once upon a time’ that is partly historical. We know about the poem more or less by chance, because it exists in one manuscript only. Fing. So. Beowulf (modern English translation) by Anonymous. Beowulf in Old English (Prologue) Old English / Anglo-Saxon. Old English was the West Germanic language spoken in the area now known as England between the 5th and 11th centuries.
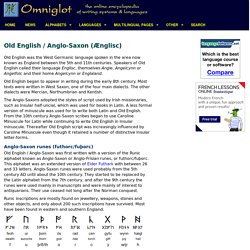
Speakers of Old English called their language Englisc, themselves Angle, Angelcynn or Angelfolc and their home Angelcynn or Englaland. Old English began to appear in writing during the early 8th century. Most texts were written in West Saxon, one of the four main dialects. The other dialects were Mercian, Northumbrian and Kentish. The Anglo-Saxons adopted the styles of script used by Irish missionaries, such as Insular half-uncial, which was used for books in Latin. Anglo-Saxon runes (futhorc/fuþorc) Old English / Anglo-Saxon was first written with a version of the Runic alphabet known as Anglo-Saxon or Anglo-Frisian runes, or futhorc/fuþorc.
Runic inscriptions are mostly found on jewellery, weapons, stones and other objects, and only about 200 such inscriptions have survived. Old English alphabet Notes Long vowels were marked with macrons. Old English pronunciation. Resources for the Study of Beowulf. Search websites about Beowulf: Why is Beowulf important?

Beowulf is the first English literary masterpiece and one of the earliest European epics written in the vernacular, or native language, instead of literary Latin. The story, accessibly retold by Beowulf for Beginners, survives in one fragile manuscript copied by two scribes near the end of the 10th or the first quarter of the 11th century. Until quite recently, most scholars thought that this surprisingly complex and poignant poem was written in the 8th century or earlier, but Kevin Kiernan stirred up controversy in 1981 with the publication of Beowulf and the Beowulf Manuscript (rev sub edition 1997) by asserting that the work was composed in the 11th century, and that the manuscript itself may have even been the author's working copy.
The manuscript was badly damaged by fire in 1731, and its charred edges crumbled over time, losing words on the outer margins of the leaves. Sir Robert Cotton(1571-1631) Why Read Beowulf? TOEBI. Scops. Because the scop was the product of a preliterate society, our records of his origins are imprecise.
The earliest records of the scop date from the fourth century. These references occur in early English poems which, although probably written in their extant forms after the invasion of these islands, date back in substance to the age when the Angles still dwelt in a continental home around the base of the Jutish peninsula (Chambers 28).Because scops sometimes travelled from place to place, they are often grouped with a larger class of itinerant entertainers ranging from the jugglers and bear-keepers to acting troupes and musicians who traversed Europe in search of patronage and wealth (Maclean 678) . This assumption is misleading because the scop was not simply a solo entertainer. His was not a performance to produce pleasure, but rather to produce power. How did English evolve? - Kate Gardoqui. This is a great story.

But really, I made it sound way more simple than it really is. You probably have some questions already, if you’re a critical sort of person. Anglorum - A Brief History of Anglo-Saxon England. The Anglo-Saxon settlement of England was no overnight affair.

The late-Roman army had many Germanic elements and from the fourth century they and their families had settled in Britain. It is, therefore, not surprising that after the withdrawal of the legions at the beginning of the fifth century individual towns looked to Germanic mercenaries to maintain their security. Vortigern, the post-Roman Kentish king, is often left to take the blame, but he was no doubt only one of several leaders who took this course. The fifth and sixth centuries saw increased Germanic settlement although the balance of local power fluctuated between Britons and Saxons. Christian Elements in Beowulf. Anglo-Saxon Paganism. Anglo-Saxon Paganism or Anglo-Saxon Heathenry is a modern religion based on the ancient pagan tribal religions of the Germanic tribes that moved into what is now England in the 5th century.

These tribes are generally thought to be the Angles, Jutes, and Saxons, although portions of other tribes such as the Frisians may have migrated also. It is therefore closely related to the ancient Norse pagan religion and shares many of the deities such as Odin (Woden) and Thor (Thunor). Modern Anglo-Saxon Paganism or Anglo-Saxon Heathenry was first revived by Garman Lord in 1976, and for years he remained its main mover and shaker.
After several false starts with groups such as the Witan Coven, he founded the Wínland Ríce which for several years remained the major Anglo-Saxon Pagan organization. Anglo-Saxon Paganism - David Raoul Wilson. Unavailable in your country. Unavailable in your country. Unavailable in your country. Unavailable in your country. Unavailable in your country. Unavailable in your country. Unavailable in your country. Unavailable in your country. Unavailable in your country. Unavailable in your country. Unavailable in your country. Unavailable in your country. Unavailable in your country. Tenth-century Studies: Essays in Commemoration of the Millennium of the ... Weale-MBE-02-AS.pdf.