

Treatment using matrix. A type of statistical analysis used to study high-energy physics and stock market fluctuations could yield a new angle of attack in the fight against the virus that causes AIDS.

A surgical strike on specific, steadfast sectors of HIV could lead to new drugs or vaccines, according to a new study. HIV has been so difficult to fight in part because it is such an adept mutant. It produces sloppy copies of itself as it replicates, leading to many variations that can withstand drugs and vaccines. And it can produce 100 billion new virus particles every day, as Ed Yong points out over at Discover, which leads to lots and lots of copies. Broad-spectrum drugs or vaccines can't do very much against a target that morphs so quickly. But not all the pieces of HIV mutate with such abandon, according to this new study. Researchers led by HIV research pioneer Bruce Walker and MIT chemical engineering professor Arup Chakraborty say this stalwart section of the virus can be turned against it.
HIV model picture. From MathBio When to Initiate HIV Therapy A summary and explanation of the paper written by Annah Jeffrey, Xiaohua Xia and Ian Craig Overview This project explores the application of control theory to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/AIDS models.
Mathematics provides a shortcut to timely, cost-effective interventions for HIV. Mathematical estimates of treatment outcomes can cut costs and provide faster delivery of preventative measures.

South Africa is home to the largest HIV epidemic in the world with a total of 5.6 million people living with HIV. Large-scale clinical trials evaluating combination methods of prevention and treatment are often prohibitively expensive and take years to complete. In the absence of such trials, mathematical models can help assess the effectiveness of different HIV intervention combinations, as demonstrated in a new study by Elisa Long and Robert Stavert from Yale University in the US. Their findings appear in the Journal of General Internal Medicine, published by Springer. Currently 60 percent of individuals in need of treatment for HIV in South Africa do not receive it.
The authors developed a mathematical model accounting for disease progression, mortality, morbidity and the heterosexual transmission of HIV to help forecast future trends in the disease. Random matrix theory-hiv variation. HIV-supercomputer-not from chimps. Theoretical biologist Bette Korber’s career has been devoted to classifying one of the most variable viruses ever identified By Regina McEnery Los Alamos, New Mexico, consists of a series of rust-colored mesas that form a picture-postcard setting: snow-capped Jemez Mountains in the distance and vast swathes of undisturbed wilderness that belie its history-making role in US defense.
Los Alamos is, of course, the place where 30 scientists gathered in 1943 to build the world’s first atomic bomb. Physicists recruited to work at the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) with nuclear physicist J. Robert Oppenheimer, scientific director of the Manhattan Project, worked feverishly in the race to develop a nuclear weapon before the Germans. Seven decades later, the LANL campus still looks a bit like a frontier outpost.
History. Google Updates Flu Model. Google has updated its Flu prediction model that uses search activity for information about flu to give accurate realtime estimates of the occurrence of the disease.
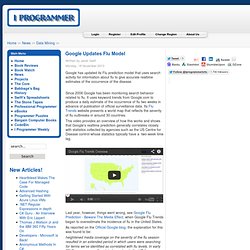
Since 2008 Google has been monitoring search behavior related to flu. It uses keyword trends from Google.com to produce a daily estimate of the occurrence of flu two weeks in advance of publication of official surveillance data. Its Flu Trends website presents a world map that reflects the severity of flu outbreaks in around 30 countries. This video provides an overview of how this works and shows that Google's realtime prediction generally correlates closely with statistics collected by agencies such as the US Centre for Disease control whose statistics typically have a two-week time lag. Last year, however, things went wrong, see Google Flu Prediction - Beware The Media Effect, when Google Flu Trends began to overestimate the incidence of flu in the United States. (click to open larger version) Zombies.pdf. Overview and assumptions of SIR model.
In order to model the progress of an epidemic in a large population, the population diversity must be reduced to a few key characteristics which are relevant to the infection under consideration.
For example, for most common childhood diseases that confer long-lasting immunity, it makes sense to divide the population into those who are susceptible to the disease, those who are infected and those who have recovered and are immune. These subdivisions of the population are called compartments. The SIR model[edit] The SIR model labels these three compartments S = number susceptible, I =number infectious, and R =number recovered (immune). This is a good and simple model for many infectious diseases including measles, mumps and rubella. The letters also represent the number of people in each compartment at a particular time. The SIR model is dynamic in three senses[edit] Blue=Susceptible, Green=Infected, and Red=Recovered Transition rates[edit] The SIR model without vital dynamics[edit] . . Then: INtro to SIR ppt. Harvard sir model.