

Bottazzi
Artist visual
Why Emotions Are Attention-getters. TO UNDERSTAND IS TO PERCEIVE PATTERNS. First map of the human brain reveals a simple, grid-like structure between neurons. In an astonishing new study, scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH), have imaged human and monkey brains and found… well, the image above says it all.
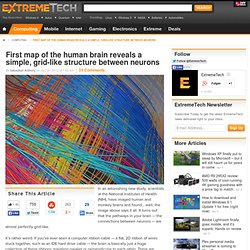
It turns out that the pathways in your brain — the connections between neurons — are almost perfectly grid-like. It’s rather weird: If you’ve ever seen a computer ribbon cable — a flat, 2D ribbon of wires stuck together, such as an IDE hard drive cable — the brain is basically just a huge collection of these ribbons, traveling parallel or perpendicular to each other. There are almost zero diagonals, nor single neurons that stray from the neuronal highways. The human brain is just one big grid of neurons — a lot like the streets of Manhattan, minus Broadway, and then projected into three dimensions. This new imagery comes from a souped-up MRI scanner that uses diffusion spectrum imaging to detect the movement of water molecules within axons (the long connections made by neurons).
“Before, we had just driving directions. Brain Waves. The human brain is more complex than your scientists suspect.
They are busily mapping where certain functions occur, and how parts of the brain activate in syncronicity. They know that parts of the brain, near the stem, are older than, for instance, the forebrain, and that a human can survive remarkably well with only half a brain, as long as that half is either the right or left, intact. But what your scientists do not know is that beyond the old brain and the new, the subconscious and the conscious, the right and the left halves - there are yet more subdivisions of the human brain. Where it is known that the brain seems to specialize in activity that requires Beta frequency brain waves during wakefulness, and Alpha frequency waves during sleep or meditation, and Theta waves during rage, and Delta waves in coma - no one is quite sure why. We will tell you. A Glance at the Brain’s Circuit Diagram.
A new method facilitates the mapping of connections between neurons.
The human brain accomplishes its remarkable feats through the interplay of an unimaginable number of neurons that are interconnected in complex networks. A team of scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization, the University of Göttingen and the Bernstein Center for Computational Neuroscience Göttingen has now developed a method for decoding neural circuit diagrams. Using measurements of total neuronal activity, they can determine the probability that two neurons are connected with each other. The human brain consists of around 80 billion neurons, none of which lives or functions in isolation.
The neurons form a tight-knit network that they use to exchange signals with each other. The scientists use data from so-called calcium fluorescence measurements that were recorded in collaboration with the University of Barcelona. BRAIN POWER: From Neurons to Networks. Cooperative Neural Networks Suggest How Intelligence Evolved. Working together can hasten brain evolution, according to a new computer simulation.
When programmed to navigate challenging cooperative tasks, the artificial neural networks set up by scientists to serve as mini-brains "learned" to work together, evolving the virtual equivalent of boosted brainpower over generations. The findings support a long-held theory that social interactions may have triggered brain evolution in human ancestors. "It is the transition to a cooperative group that can lead to maximum selection for intelligence," said study researcher Luke McNally, a doctoral candidate at Trinity College Dublin.
Greater intelligence, in turn, leads to more sophisticated cooperation, McNally told LiveScience. [10 Fun Brain Facts] It also leads to more sophisticated means of cheating, he added. Virtual neurons McNally and his colleagues used artificial neural networks as virtual guinea pigs to test the social theory of brain evolution. Neuroplasticity. Contrary to conventional thought as expressed in this diagram, brain functions are not confined to certain fixed locations.
Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses which are due to changes in behavior, environment and neural processes, as well as changes resulting from bodily injury.[1] Neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how - and in which ways - the brain changes throughout life.[2] Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes due to learning, to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. Brain Structures and Their Functions.
The nervous system is your body's decision and communication center.

The central nervous system (CNS) is made of the brain and the spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) is made of nerves. Together they control every part of your daily life, from breathing and blinking to helping you memorize facts for a test. Science: A New Map of the Human Brain. Who hasn't heard that people are either left-brained or right-brained—either analytical and logical or artistic and intuitive, based on the relative "strengths" of the brain's two hemispheres?

How often do we hear someone remark about thinking with one side or the other? A flourishing industry of books, videos and self-help programs has been built on this dichotomy. You can purportedly "diagnose" your brain, "motivate" one or both sides, indulge in "essence therapy" to "restore balance" and much more. Everyone from babies to elders supposedly can benefit. Cognitive Atlas. The Whole Brain Atlas. Neurotechnology. Neurotechnology is any technology that has a fundamental influence on how people understand the brain and various aspects of consciousness, thought, and higher order activities in the brain.
It also includes technologies that are designed to improve and repair brain function and allow researchers and clinicians to visualize the brain. Background[edit] The field of neurotechnology has been around for nearly half a century but has only reached maturity in the last twenty years. The advent of brain imaging revolutionized the field, allowing researchers to directly monitor the brain’s activities during experiments. Neurotechnology has made significant impact on society, though its presence is so commonplace that many do not realize its ubiquity. As the field’s depth increases it will potentially allow society to control and harness more of what the brain does and how it influences lifestyles and personalities.
Current technologies[edit] Imaging[edit] Cognitive Neuroscience Society. Guillaume Apollinaire site officiel: Page d'Accueil. Cronología de Picasso by Fundación Picasso. Contemporary Art - Public Art - Guillaume Bottazzi.