

Kraft Foods Supplier Quality and Food Safety Web Site. Search. Food Safety. The International Food Safety Authorities Network (INFOSAN) CRISPR. Diagram of the possible mechanism for CRISPR.[1] CRISPRs are found in approximately 40% of sequenced eubacteria genomes and 90% of sequenced archaea.[3][4] CRISPRs are often associated with cas genes that code for proteins related to CRISPRs.
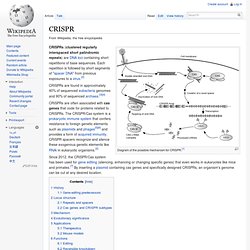
The CRISPR/Cas system is a prokaryotic immune system that confers resistance to foreign genetic elements such as plasmids and phages[5][6] and provides a form of acquired immunity. CRISPR spacers recognize and silence these exogenous genetic elements like RNAi in eukaryotic organisms.[2] Since 2012, the CRISPR/Cas system has been used for gene editing (silencing, enhancing or changing specific genes) that even works in eukaryotes like mice and primates.[7] By inserting a plasmid containing cas genes and specifically designed CRISPRs, an organism's genome can be cut at any desired location.
History[edit] Bacteria may incorporate foreign DNA in other circumstances and even to scavenge damaged DNA from their environment.[8] Gene-editing predecessors[edit] New food labelling regulation published. ISO 22000 Food Safety Standard in Plain English. ISO 22000 Food Safety. Sustainability measurement. Sustainability measurement is a term that denotes the measurements used as the quantitative basis for the informed management of sustainability.[1] The metrics used for the measurement of sustainability (involving the sustainability of environmental, social and economic domains, both individually and in various combinations) are still evolving: they include indicators, benchmarks, audits, indexes and accounting, as well as assessment, appraisal[2] and other reporting systems.
They are applied over a wide range of spatial and temporal scales.[3][4] Some of the best known and most widely used sustainability measures include corporate sustainability reporting, Triple Bottom Line accounting, and estimates of the quality of sustainability governance for individual countries using the Environmental Sustainability Index and Environmental Performance Index. Sustainability indicators and their function[edit] Metrics at the global scale[edit] United Nations Indicators[edit] Metrics Auditing. SAFE FOODS. Thematic research areas[edit] A broad range of research disciplines are used in the SAFE FOODS project, including molecular biology, microbiology, toxicology, probabilistic modeling, and disciplines of the social sciences and the political sciences.
SAFE FOODS is divided in 5 sub-projects, namely. BSI British Standards publishes food safety specification for the food manufacturing industry. FSSC 22000: Requirements, tutorials, flow chart & tools. Introduction to FSSC 22000 Food Safety System Certification, (FSSC 22000) is a Food Safety Management System Certification Scheme that is recognized by the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI).
The scheme is managed by the Foundation for Food Safety Certification. Other similar schemes recognized by GFSI include SQF, BRC and IFS. If you are just starting to investigate options for registration you may want to investigate these schemes as well. The requirements are similar between the standards, but not exactly the same. FSSC 22000 is a well recognized scheme that now has over 5000 certified companies around the globe. If you are not a food processor you would need to obtain the appropriate Publicly Available Specification (PAS) for your industry. Gather resources and educate management on the system and requirements during your preparations for your project. How long does it take to achieve certification? The time it takes will depend on several factors. ISO 22000:2005 Food Safety, haccp Documents, ISO 22000 Consultant - Global Manager Group. International Food Safety & Quality Network (IFSQN.com) Comparison_of_iso_9001_and_iso_22000. Requirements for any organization in the food chain.
Risk assessment. Risk assessment is the determination of quantitative or qualitative value of risk related to a concrete situation and a recognized threat (also called hazard).

Quantitative risk assessment requires calculations of two components of risk (R):, the magnitude of the potential loss (L), and the probability (p) that the loss will occur. Acceptable risk is a risk that is understood and tolerated usually because the cost or difficulty of implementing an effective countermeasure for the associated vulnerability exceeds the expectation of loss.[1] In all types of engineering of complex systems sophisticated risk assessments are often made within Safety engineering and Reliability engineering when it concerns threats to life, environment or machine functioning.
The nuclear, aerospace, oil, rail and military industries have a long history of dealing with risk assessment. Also, medical, hospital, social service[2] and food industries control risks and perform risk assessments on a continual basis. Food safety. Food safety is a scientific discipline describing handling, preparation, and storage of food in ways that prevent foodborne illness.
This includes a number of routines that should be followed to avoid potentially severe health hazards. The tracks within this line of thought are safety between industry and the market and then between the market and the consumer. ISO 22000. ISO 22000 is a standard developed by the International Organization for Standardization dealing with food safety.
It is a general derivative of ISO 9000. Institute of Food Research.