

Fisica cuantica. Fractales. Teoria del caos. Termodinamica abierta. Autoorganizacion. Terapia neural. Foro profesional. Dr Lorenz Fischer, Suiza.

Controlled Quantum Dynamics Group. Biologists do not take a quantum physics course during their studies because so far they were able to make sense of biological phenomena without using the counterintuitive laws of physics that govern the atomic scale.
However, in recent years progress in experimental technology has revealed that quantum phenomena are relevant for fundamental biological processes such as photosynthesis, magneto-reception and olfaction. We have helped to initiate the development of this research field and are now working to discover how nature is harnessing quantum dynamics to optimize biological function. S.F. Huelga and M.B. Plenio. Environment assisted quantum bio-dynamics: It is remarkable that quantum phenomena can play a role in warm, wet and noisy biological systems. Environment assisted quantum bio-dynamics: Biological environments are not creating white noise but do actually possess considerable structure. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), also known as poly-aromatic hydrocarbons or polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons, are fused aromatic rings and do not contain heteroatoms or carry substituents.[1] Naphthalene is the simplest example of a PAH.
PAHs occur in oil, coal, and tar deposits, and are produced as byproducts of fuel burning (whether fossil fuel or biomass). Photographer Uses Cheap Home-Made Camera Rig To Take Stunning Close-Ups of Snowflakes. Carbon. Silicon. Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14.
It is a tetravalent metalloid, less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table. Controversy about silicon's character dates to its discovery; it was first prepared and characterized in pure form in 1823. In 1808, it was given the name silicium (from Latin: silex, hard stone or flint), with an -ium word-ending to suggest a metal, a name which the element retains in several non-English languages. Vida en Marte. Marte en un posible pasado lejano o después de una posible Terraformación.
A pesar de los recientes descubrimientos, el espectro de opiniones "educadas" acerca de la posibilidad de vida en Marte, tanto pasada como presente, varía considerablemente, con científicos que sostienen que la vida en Marte es imposible, y científicos que especulan que la vida en Marte es un hecho comprobado.[1] Igualmente debido a la posibilidad de vida marciana, la exploración de Marte (así como la de otros cuerpos celestes) se realiza o planea realizar con la precaución de no provocar una contaminación interplanetaria con microorganismos de la Tierra.
Chronobiology. Chronobiology is a field of biology that examines periodic (cyclic) phenomena in living organisms and their adaptation to solar- and lunar-related rhythms.[1] These cycles are known as biological rhythms.
Chronobiology comes from the ancient Greek χρόνος (chrónos, meaning "time"), and biology, which pertains to the study, or science, of life. The related terms chronomics and chronome have been used in some cases to describe either the molecular mechanisms involved in chronobiological phenomena or the more quantitative aspects of chronobiology, particularly where comparison of cycles between organisms is required. Chronobiological studies include but are not limited to comparative anatomy, physiology, genetics, molecular biology and behavior of organisms within biological rhythms mechanics.[1] Other aspects include development, reproduction, ecology and evolution.
Description[edit] The circadian rhythm can further be broken down into routine cycles during the 24-hour day:[2] History[edit] Phase diagram. Overview[edit] Common components of a phase diagram are lines of equilibrium or phase boundaries, which refer to lines that mark conditions under which multiple phases can coexist at equilibrium.
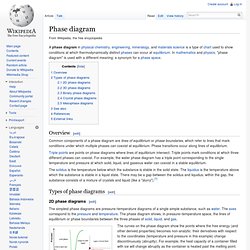
Phase transitions occur along lines of equilibrium. Biological organisation. A population of bees shimmers in response to a predator.
Biological organization, or the hierarchy of life, is the hierarchy of complex biological structures and systems that define life using a reductionistic approach.[1] The traditional hierarchy, as detailed below, extends from atoms (or lower) to biospheres. The higher levels of this scheme are often referred to as ecological organisation. Each level in the hierarchy represents an increase in organisational complexity, with each "object" being primarily composed of the previous level's basic unit.[2] The basic principle behind the organisation is the concept of emergence—the properties and functions found at a hierarchical level are not present and irrelevant at the lower levels.[3] Organisation furthermore refers to the high degree of order of an organism (in comparison to general objects).[4] Ideally, individual organisms of the same species have the same arrangement of the same structures.
Levels[edit] See also[edit] Meaning of life. Questions.
Evolutionary arms race. Montmorillonite. Montmorillonite is a very soft phyllosilicate group of minerals that typically form in microscopic crystals, forming a clay.
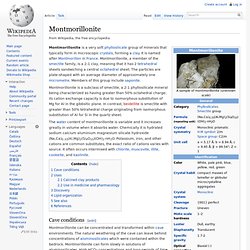
It is named after Montmorillon in France. Montmorillonite, a member of the smectite family, is a 2:1 clay, meaning that it has 2 tetrahedral sheets sandwiching a central octahedral sheet. Foraminifera. Late Heavy Bombardment. Evidence for the LHB event is primarily from dating lunar samples brought back by the Apollo astronauts, which (dates) imply that most impact melt rocks were formed in this rather narrow interval of time. Several hypotheses are now offered to explain the spike in the flux of asteroids or comets in the inner Solar System but no consensus yet exists. The Nice model is popular among planetary scientists; it postulates that the gas giant planets underwent orbital migration and forced objects in the asteroid and/or Kuiper belts into eccentric orbits, and thereby into the path of the terrestrial planets. Artist's impression of the moon during the Late Heavy Bombardment (Lunar Cataclysm) and today Evidence for a cataclysm[edit]
Evolutionary history of life. Life. Life is a characteristic distinguishing objects having signaling and self-sustaining processes from those that do not,[1][2] either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate.[3][4] Biology is science concerned with the study of life. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable.[15][16] Other planets and moons in the Solar System have been examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI have attempted to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.
According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life exists throughout the Universe, and is distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and planetoids.[17] Early theories.