

When your teen breaks your trust. We’ve all heard the phrase that “being a parent is tough”.
It’s probably more cogent to say being a parent to a teenager is tough. Learning how to manage your own needs versus the needs of a growing child can be hard to envision. To be a good parent, you need to show tough love. As parents we are generally wracked with guilt and anxiety when managing our children.
We often feel inadequate and try very hard to be “good parents”. We may, for example, do our utmost to avoid punishing them. Teenage Behavior Problems. Understanding Teenage Behavior Problems Dealing with a teenager is not easy.
No matter how good a parent you are, and how great your relationship with your children is, you are likely to face parenting roadblocks when it comes to your teenager. Behavior problems are common in teenagers. Why Teenagers Reject Parents’ Solutions to Their Problems. As hard as it is for parents to stop ourselves, rushing in with suggestions carries the risk that you’ll be communicating the idea, “You can’t fix this, but I can.”
This might strike our teenagers as a vote of no confidence when they are mainly seeking our reassurance that they can handle whatever life throws at them. Instead of proposing solutions, we might bolster adolescents as they sort things out. Saying, “I’ve seen you get through things like this before” or “This is tough, but you are too” can effectively loan teenagers a bit of perspective and confidence when their own feels shaken. Even teenagers who have already addressed a problem may still seek our reassurance. Dealing with Difficult Teenage Daughters.
Reading Time: 7 minutes For parents, dealing with difficult teenage daughters can be challenging.
Teen girls are smart, spirited, and strong. They have their own opinions, and they feel things deeply. Skinner’s Operant Conditioning: Rewards & Punishments. Operant Conditioning. How Reinforcement and Punishment Modify Behavior Operant conditioning, also known as instrumental conditioning, is a method of learning normally attributed to B.F. Skinner, where the consequences of a response determine the probability of it being repeated. Through operant conditioning behavior which is reinforced (rewarded) will likely be repeated, and behavior which is punished will occur less frequently.
By the 1920s, John B. Operant conditioning. Images Website for this image What Is 'positive Punishment'?
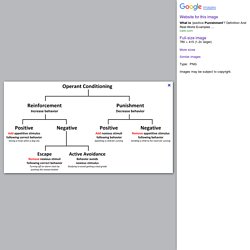
Definition And Real-World Examples ... care.com Similar images. Reinforcement & Punishment. Punishment. Reinforcement. Reinforcement Theory of Motivation. Positive Reinforcement Example. Negative Reinforcement vs Positive Punishment. Positive and Negative Reinforcement example. Negative punishment example. Negative punishment example. (Positive Reinforcement examples) Positive Reinforcement in Psychology (Definition + 5 Examples) If you read our earlier piece on positive punishment, you know that there are different methods of teaching and instilling good habits and behaviors.
One of the most powerful and effective methods is one that you’re probably at least somewhat familiar with: positive reinforcement. Before you read on, we thought you might like to download our 3 Positive Psychology Exercises for free. These science-based exercises will explore fundamental aspects of positive psychology including strengths, values and self-compassion and will give you the tools to enhance the wellbeing of your clients, students or employees. Schedules of Reinforcement. Operant conditioning is a learning process in which new behaviors are acquired and modified through their association with consequences.

Reinforcing a behavior increases the likelihood it will occur again in the future while punishing a behavior decreases the likelihood that it will be repeated. In operant conditioning, schedules of reinforcement are an important component of the learning process. When and how often we reinforce a behavior can have a dramatic impact on the strength and rate of the response. Schedule of Reinforcement A schedule of reinforcement is basically a rule stating which instances of behavior will be reinforced. Schedules of Reinforcement. Schedules of Reinforcement. Pigeon - schedule of reinforcement. Schedule of reinforcement. Tips on the Misuses of Negative Reinforcement for Parents. So often, parents become frustrated with their little ones as the twists and turns of toddler logic throw adults for a loop.

The "because I said so" that seemed so unfair to us just years ago is now the only response that doesn't start a bartering session. Some parents reach for negative reinforcement, when positive reinforcement doesn't seem to be enough. Negative reinforcement is when a parent rewards a child for good behavior by taking away an aversion in his daily life. For instance, if a preschooler picks up all the cereal he spilled on the floor, she doesn't have to help mom clean the bathroom. Accidental Use. How to Use Positive Reinforcement to Improve Your Child's Behavior.
When your child misbehaves, rewards might be the last thing on your mind.
But, positive reinforcement can be one of the most effective behavior modification techniques.1 You can use positive reinforcement to encourage prosocial behaviors, like sharing or following directions. And, you can use it to prevent misbehavior, like hitting and rule violations. Positive reinforcement can also be an effective way to encourage and motivate your child to be responsible, do their chores, get along with their siblings, or complete their homework assignments without arguing. How Positive Reinforcement Works Most adults go to work so they can receive a paycheck.