

Germ form theory: Peer production in a historical perspective. Introduction How can development be conceived?

The answer, in our opinion, is anything but obvious. This text is intended to seek an answer to this question and to present a number of historical and contemporary examples underlining our views. In general, development apparently is conceived as the expansion of possibilities by a process of accumulating increasingly greater means to advance development. In other words, this is a perspective of mere quantitative growth. Origins The Five Step Model has been influenced by a number of precursors. One prominent aspect Hegel emphasises is that the principles of development can and should never be separated from the subject of the original analysis. It was Klaus Holzkamp, the founder of German Critical Psychology, who--in the Hegelian sense--pursues an in our view viable approach: In a first step, he analyses his subject and discovers its principles of development.
Overview. Dynamics of Complex Systems. Www.necsi.edu New England Complex Systems Institute 238 Main Street Suite 319, Cambridge, MA 02142 Phone: 617-547-4100 Fax: 617-661-7711 Textbook for seminar/course on complex systems.View full text in PDF format The study of complex systems in a unified framework has become recognized in recent years as a new scientific discipline, the ultimate of interdisciplinary fields.

Breaking down the barriers between physics, chemistry and biology and the so-called soft sciences of psychology, sociology, economics, and anthropology, this text explores the universal physical and mathematical principles that govern the emergence of complex systems from simple components. Dynamics of Complex Systems is the first text describing the modern unified study of complex systems. It is designed for upper-undergraduate/beginning graduate-level students, and covers a wide range of applications in a wide array of disciplines. Professor Yaneer Bar-Yam received his S.B. and Ph.D. (1984) from MIT. Complexity Rising: From Human Beings to Human Civilization, a Complexity Profile. Since time immemorial humans have complained that life is becoming more complex, but it is only now that we have a hope to analyze formally and verify this lament.

This article analyzes the human social environment using the "complexity profile," a mathematical tool for characterizing the collective behavior of a system. The analysis is used to justify the qualitative observation that complexity of existence has increased and is increasing. The increase in complexity is directly related to sweeping changes in the structure and dynamics of human civilization—the increasing interdependence of the global economic and social system and the instabilities of dictatorships, communism and corporate hierarchies.
Our complex social environment is consistent with identifying global human civilization as an organism capable of complex behavior that protects its components (us) and which should be capable of responding effectively to complex environmental demands. The Entropy of Nations. The 18th century writer Adam Smith provided a workable metaphor for the way society utilizes resources.
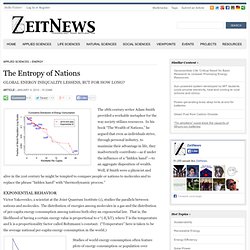
In his book “The Wealth of Nations,” he argued that even as individuals strive, through personal industry, to maximize their advantage in life, they inadvertently contribute---as if under the influence of a “hidden hand”---to an aggregate disposition of wealth. Well, if Smith were a physicist and alive in the 21st century he might be tempted to compare people or nations to molecules and to replace the phrase “hidden hand” with “thermodynamic process.” Victor Yakovenko, a scientist at the Joint Quantum Institute (1), studies the parallels between nations and molecules. The distribution of energies among molecules in a gas and the distribution of per-capita energy consumption among nations both obey an exponential law. Figure 1. Studies of world energy consumption often feature plots of energy consumption or population over time. A Neuroscientist's Radical Theory of How Networks Become Conscious - Wired Science.
It’s a question that’s perplexed philosophers for centuries and scientists for decades: Where does consciousness come from?
We know it exists, at least in ourselves. But how it arises from chemistry and electricity in our brains is an unsolved mystery. Neuroscientist Christof Koch, chief scientific officer at the Allen Institute for Brain Science, thinks he might know the answer. According to Koch, consciousness arises within any sufficiently complex, information-processing system. All animals, from humans on down to earthworms, are conscious; even the internet could be. “The electric charge of an electron doesn’t arise out of more elemental properties. What Koch proposes is a scientifically refined version of an ancient philosophical doctrine called panpsychism — and, coming from someone else, it might sound more like spirituality than science. WIRED: How did you come to believe in panpsychism? Christof Koch: I grew up Roman Catholic, and also grew up with a dog. Koch: That’s true. Systems Theories.
Self-organization.