

Aeneas. In Greco-Roman mythology, Aeneas (/ɪˈniːəs/; Greek: Αἰνείας, Aineías, possibly derived from Greek αἰνή meaning "praise") was a Trojan hero, the son of the prince Anchises and the goddess Aphrodite (Venus).
His father was the second cousin of King Priam of Troy, making Aeneas Priam's second cousin, once removed. He is a character in Greek mythology and is mentioned in Homer's Iliad, and receives full treatment in Roman mythology as the legendary founder of what would become Ancient Rome, most extensively in Virgil's Aeneid. He became the first true hero of Rome. Henry Livingston, Jr. Henry Livingston, Jr.
(October 13, 1748 - February 29, 1828) has been proposed as being the uncredited author of the poem "A Visit from St. Nicholas", more popularly known (after its first line) as "The Night Before Christmas. " The poem has always been attributed to Clement Clarke Moore, and the Livingston claim is hotly disputed. Biography[edit] He was born on October 13, 1748 in Poughkeepsie, New York, to Henry Livingston, Sr. and Susannah Conklin.[1] Clement Clarke Moore. Clement Clarke Moore (July 15, 1779 – July 10, 1863) was an American Professor of Oriental and Greek Literature, as well as Divinity and Biblical Learning, at the General Theological Seminary of the Protestant Episcopal Church, in New York City.
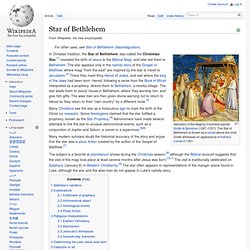
Located on land donated by the "Bard of Chelsea" himself, the seminary still stands today on Ninth Avenue between 20th and 21st Streets, in an area known as Chelsea Square. Moore's connection with that institution continued for over twenty-five years. He is the author of the yuletide poem "A Visit from St. Nicholas", which later became famous as "'Twas the Night Before Christmas". Star of Bethlehem. Adoration of the Magi by Florentine painter Giotto di Bondone (1267–1337).
Santa Claus's reindeer. Santa Claus and seven of his reindeer in a parade in Toronto 2007.
Santa Claus's reindeer form an imaginary team of flying reindeer traditionally held to pull the sleigh of Santa Claus and help him deliver Christmas gifts. Rudolph the Red-Nosed Reindeer. Rudolph the Red-Nosed Reindeer is a fictional male reindeer with a glowing red nose, popularly known as "Santa's 9th Reindeer.
" When depicted, he is the lead reindeer pulling Santa's sleigh on Christmas Eve. The luminosity of his nose is so great that it illuminates the team's path through inclement winter weather. Rudolph first appeared in a 1939 booklet written by Robert L. May and published by Montgomery Ward.[1][2][3] Publication history[edit] Robert L. Paganism (contemporary) Modern paganism, also known as contemporary paganism, and neopaganism, is a group of contemporary religious movements influenced by or claiming to be derived from the various historical pagan beliefs of pre-modern Europe.
Although they do share commonalities, contemporary Pagan religious movements are diverse and no single set of beliefs, practices, or texts are shared by them all. Contemporary Paganism has been characterised by Dennis Carpenter as "a synthesis of historical inspiration and present-day creativity",[5] in this manner drawing influences from pre-Christian, folkloric and ethnographic sources in order to fashion new religious movements. Terminology and definition[edit] A Slavic Rodnover ritual in modern Russia. Slavic Rodnovery is an ethnic religion that attempts to recreate forms of Slavic polytheism. Horned God. The term Horned God itself predates Wicca, and is an early 20th-century syncretic term for a horned or antlered anthropomorphic god with pseudohistorical origins[4] who, according to Margaret Murray's 1921 The Witch-Cult in Western Europe, was the deity worshipped by a pan-European witchcraft-based cult, and was demonized into the form of the Devil by the Mediaeval Church.
The Horned God has been explored within several psychological theories, and has become a recurrent theme in fantasy literature.[5]:872. Triple Goddess. The Triple Goddess is the subject of much of the writing of Robert Graves, and has been adopted by many neopagans as one of their primary deities.
The term triple goddess is infrequently used outside of Neopaganism to instead refer to historical goddess triads and single goddesses of three forms or aspects. Mistletoe. Mistletoe in the genus Viscum[edit] The name mistletoe was originally applied to Viscum album (European mistletoe, of the family Santalaceae in the order Santalales), the only species native in Great Britain and much of Europe.
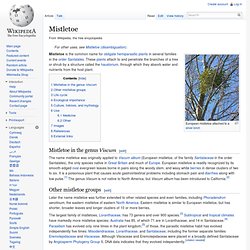
European mistletoe is readily recognized by its smooth-edged oval evergreen leaves borne in pairs along the woody stem, and waxy white berries in dense clusters of two to six. It is a poisonous plant that causes acute gastrointestinal problems including stomach pain and diarrhea along with low pulse.[1] The genus Viscum is not native to North America, but Viscum album has been introduced to California.[2] Other mistletoe groups[edit] Later the name mistletoe was further extended to other related species and even families, including Phoradendron serotinum, the eastern mistletoe of eastern North America.
Life cycle[edit] Mistletoe in winter Most mistletoe seeds are spread by birds that eat the fruits (drupes). Ecological importance[edit] Mistletoe. Prose Edda. Yule.