

Health Protection - Becky Reynolds. CDC Thailand Global Health Protection. Health Protection » Aboriginal Health & Medical Research Council of NSW. Causes of Death (COD) Visualization. Health Protection: Principles and practice. Corporate plan 2019 20. Australian Health Protection Principal Committee. Office of Health Protection (OHP) The mission of OHP, in partnership with key stakeholders, is to protect the health of the Australian community through effective national leadership and coordination and building of appropriate capacity and capability to detect, prevent and respond to threats to public health and safety.
Health Protection Policy Branch (HPPB) HPPB provides national leadership, policy advice, analysis, coordination and communication of health protection strategies, surveillance and coordination of outbreak responses for communicable diseases and to reduce the impact of blood borne viruses and sexually transmissible infection. Health Emergency Management Branch (HEMB) HEMB is responsible for prevention, preparedness and response activities related to national health emergencies and risks. This encompasses mass casualty incidents, communicable disease outbreaks, acts of terrorism, and the health impacts of natural disasters. Immunisation Branch (IB) Principal Medical Advisers. Departmental organisational structure chart 0. Health Protection Report. Global Public Health: Ecological Foundations - Franklin White, Lorann Stallones, John M. Last. Environmental health.
Policy Position Statements - Public Health Association of Australia Inc. Menu YoutubeTwitterFacebookLinkedin Forgot your password? Home > Advocacy and Policy Policy Position Statements We work collaboratively through our members, branches and special interest groups to produce evidence-based policy positions to improve public health in Australia. PHAA Strategic Plan. Health Protection Program Guidelines. Department of Health. About the Chief Health Officer. Communicable disease information - Public Health - Library Guides at University of Queensland Library. Environmental Epidemiology: The Context - Environmental Epidemiology - NCBI Bookshelf. Control, elimination, eradication and re-emergence of infectious diseases: getting the message right.
Moodle. :: Context checklist Establishing the context means building a profile of the activity and the environment in which that activity will occur.
It involves establishing the parameters and boundaries of the organisation or activity being undertaken and determining such issues as time frames, resources required, roles and responsibilities, etc. This will help define the scope of the risk assessment, determine the evaluation criteria and establish the stakeholder objectives. :: Steps in determining the context Text version of diagram (html pop up) Municipal Public Health and Wellbeing Plan - City of Melbourne. The City of Melbourne is required under the Public Health and Wellbeing Act 2008 to prepare a Municipal Public Health and Wellbeing Plan every four years or include public health and wellbeing matters into the Council Plan.
The City of Melbourne views health and wellbeing as vital to a liveable city. For this reason we have chosen to elevate our commitment to our community’s wellbeing by integrating our Municipal Public Health and Wellbeing Plan priorities into the Council Plan. Australian Institute of Health & Safety. Our Vision is safe and healthy people in productive workplaces and communities.
Everything we do is about shaping workplace health and safety now and in the generations to come, because we believe that every Australian deserves to be safe and healthy at work. We focus our resources on: Public Health Assessment Guidance Manual (2005 Update) MSc Public Healthcare: Health protection and improvement - the assessment. CDC LC Quick Learn: Using an Epi Curve to Determine Mode of Spread. This Quick Learn lesson will take approximately 10 minutes to complete.
When you are finished, you will be able to determine the outbreak's likely mode of spread by analyzing an epidemic curve, or “epi curve.” You can move through this lesson by using the NEXT and BACK icons below. Next Page » X and Y Axes An epidemic curve, or “epi curve,” is a visual display of the onset of illness among cases associated with an outbreak. The horizontal x-axis is the date or time of illness onset among cases. The vertical y-axis is the number of cases. Each axis is divided into equally spaced intervals, although the intervals for the two axes may differ. Next Page »« Prev Page What an Epi Curve Can Tell You. Upstream or downstream? An Educational Blog on Healthcare Associated Conditions. Zero draft Shanghai Declaration on Health Promotion. Six steps planning hp programs. Haddon Matrix and Hazardous Events. Looking at hazards in different ways, through different conceptual frameworks is always useful as it tends to make you think about things, however slightly, in a different way.
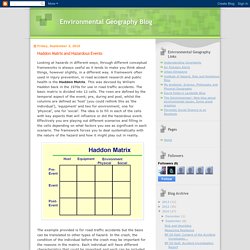
A framework often used in injury prevention, in road accident research and public health is the Haddon Matrix. This was devised by William Haddon back in the 1970s for use in road traffic accidents. The basic matrix is divided into 12 cells. The rows are defined by the temporal aspect of the event; pre, during and post, whilst the columns are defined as ‘host’ (you could rethink this as ‘the individual’), ‘equipment’ and two for environment; one for ‘physical’, one for ‘social’. The idea is to fill in each of the cells with key aspects that will influence or did the hazardous event.
The example provided is for road traffic accidents but the basis can be translated to other types of hazard. This framework does have its limitations. Human Health Risk Assessment. Identify, assess and control hazards. Risk assessment on COVID-19, 10 August 2020. As countries regained control of transmission and alleviated the burden on healthcare, many measures were relaxed or removed to allow for a more viable way of life with the virus in circulation.

Subsequently, a recent increase in COVID-19 cases has been reported in many EU/EEA countries. What is the risk of further escalation of COVID-19 in the countries that have reported a recent increase in COVID-19 cases, as of 10 August 2020? In EU/EEA countries and the UK where a recent increase in cases has been reported: The risk of further escalation of COVID-19 is high in countries that have also had an increase in hospitalisations, providing a strong indication that there is a genuine increase in transmission occurring.