

Victorian hotel quarantine system told guests with coronavirus were allowed to leave quarantine, inquiry told - ABC News. Australian Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Infection in Healthcare (2019) Accessing and using the guidelines The guidelines are available on an interactive ‘living guidelines’ platform.

This allows for ‘point of care’ use and for the guidelines to be accessed in both online and offline formats across a range of devices through an application or web browser. Visit MAGICapp From the guidelines list, click on ‘Australian Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Infection in Healthcare (2019)’ to view the guidelines. Look for the NHMRC logo to indicate which guidelines we have authored. Please allow time for the guidelines to load. Help: How to access and use the guidelines - see 'Download' section below If you have any issues accessing the guidelines, please contact icg@nhmrc.gov.au. PAEDS. National Alert System for Critical Antimicrobial Resistances (CARAlert) Four Corners goes inside an Australian coronavirus clinic that tests for cases of COVID-19.
Updated 6 Apr 2020, 7:49amMon 6 Apr 2020, 7:49am From the road, all you can see are some makeshift barricades and a few printed laminated signs to suggest what goes on inside the COVID-19 Screening Clinic.
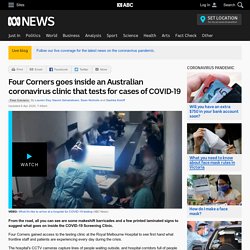
Four Corners gained access to the testing clinic at the Royal Melbourne Hospital to see first hand what frontline staff and patients are experiencing every day during the crisis. The hospital's CCTV cameras capture lines of people waiting outside, and hospital corridors full of people waiting to be seen. Around 100 people per day queue up at the clinic to find out if they've contracted the highly contagious and potentially deadly virus that has stopped the world. The clinic has already processed about 4,000 tests. On arrival at the hospital, the sick are met by a nurse who hands out face masks and then escorts them in for a series of questions about their possible exposure to the virus. Patients are led to another checkpoint, where they have their pulse and blood pressure taken.
Victorian coronavirus infections in healthcare workers nears 1,000 as COVID-19 cases rise - ABC News. How clean are your hands? The answer may change how you wash. Are your hands clean?

Sure, you washed them after you went to the loo, but as the experiment here reveals, you probably didn't clean them anywhere near as well as you thought. And proper hand washing is important - our hands can harbour a nasty colony of illness-inducing bugs including E.coli, salmonella, clostridium difficile, campylobacter, the superbug MRSA (which is resistant to certain antibiotics), as well as cold and flu viruses and norovirus, the winter vomiting bug.
Jennie tested different hand-washing techniques - from the typical 'rinse and shake' to 30 seconds with soap But what constitutes proper hand washing, and are you doing enough to protect yourself? To find out I used a special UV camera to test different hand-washing techniques - from the typical 'rinse and shake' to the 30 seconds recommended by a leading authority on disease control. First, I rub on a gel known as Glo Germ, which simulates how bacteria cling to your skin. Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care. Hundreds of types of face masks withdrawn from sale in Australia amid safety fears. Hundreds of different types of face masks have been withdrawn from Australia’s register of therapeutic goods and the regulator has started a mass audit of the equipment amid concerns that some may not adequately prevent infection.
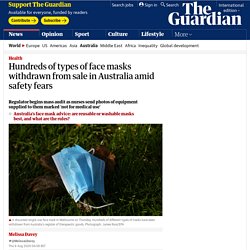
Surgical or examination masks intended to reduce or prevent the transmission of disease are considered medical devices, are regulated by the Therapeutic Goods Administration and must be included in the register of therapeutic goods before they can be supplied. As of Thursday, 286 types of mask had been removed from the register as part of a post-market review triggered by concerns that many masks do not meet regulatory standards and, if used in medical environments, may increase disease spread. Environmental Cleaning in Resource-Limited Settings. Australian Government Department of Health. Intensive Care Units working tirelessly, learning from experience, applying new treatments in the battle against COVID-19 - ABC News.
Coronavirus covid 19 are cloth face masks likely to provide protection against covid 19 0. Experiment Shows Massive Bacteria After Hand Washing, Here's What You Should Do Instead. With everything we know about the coronavirus so far, it has become painstakingly obvious that sterilization is the key to fight it.
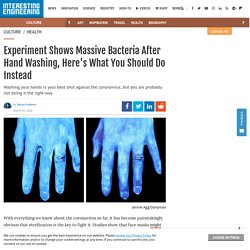
Studies show that face masks might actually increase the risk of infection, and there isn’t a vaccine completed yet. My 5 Moments for Hand Hygiene. WHO: What are the core components for effective infection prevention and control? Infection Prevention and Control Training Video. 9789241597906 eng. Hand hygiene aug 2007. A Complete Guide to Hand Washing. Decontamination and cleaning. The Australian Immunisation Handbook. National Centre for Immunisation Research and Surveillance. The science of immunisation. Measles: everything you need to know In 2014, Australia had eliminated measles—but it's back, and outbreaks are happening across the globe.

To explain why, the Australian Academy of Science has developed a series of videos and articles in partnership with the Australian Government Department of Health to explore why measles is such a serious disease, who is most at risk, and how you can make sure you're protected with vaccination. Australian Government Department of Health. Australian Government Department of Health. Vaccine-preventable conditions and diseases. Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) RACGP - The science of immunisation: Dispelling vaccination myths. News The Australian Academy of Science has joined with the Department of Health to launch a series of videos, articles and images to promote the benefits, safety and science of immunisation.
A recent national science survey revealed that just over one in eight respondents believed parents should be allowed to choose not to vaccinate their children, with risk of autism cited as one of the reasons. The Australian Academy of Science has joined with the Department of Health (DoH) to launch a series of videos, articles and images in a bid to dispel myths about immunisation. Professor Julie Bines, lead rotavirus researcher at the Murdoch Children’s Research Institute, who features in the video Who benefits from vaccines? , said while there is strong evidence that vaccines are working, that message is not getting out to some members of the community. Many topics are explored in the videos, articles and images: CDC Global Health - Vaccines and Immunization. CDC’s Global Immunization Division (GID) is dedicated to ensuring that everyone, everywhere shares in the benefits of immunization.
We do this by providing scientific and public health expertise, and by making evidence for action available for optimal policy and programmatic decision-making at all levels, from community to global. Our vision is a world with healthy people protected from vaccine-preventable diseases, disabilities, and death. Vaccines prevent an estimated 2.5 million deaths among children younger than age 5 every year. Still, 1 child dies every 20 seconds from a disease that could have been prevented by a vaccine.
CDC Global Health - Immunization - New and Underused Vaccines. Vaccine Surveillance & Introduction The Expanded Program on Immunization (EPI) was established by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 1974 to provide protection against six vaccine-preventable diseases through routine infant immunization: tuberculosispoliomyelitisdiphtheriatetanuspertussismeasles Since then, many new vaccines have become available and global public funding for immunization, including the Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunisation (GAVI Alliance), has increased accessibility to these vaccines.

Most of the new or underused vaccines, including hepatitis B (HepB) vaccine, Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccine, pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV), rotavirus (RV) vaccine, and rubella-containing vaccine, are intended to be included in the routine childhood immunization schedule. Immunisation: Why we do it and how 'herd immunity' works. How do eggs protect us from flu? The MMR vaccine and autism: Sensation, refutation, retraction, and fraud. The Biggest Vaccination Myths, Busted. Myth #3: Vaccinations cause the targeted disease Vaccines are designed to stimulate your immune system to produce immunity by mimicking an infection.
With a vaccine, you’re getting an immune response in your body, almost always without the illness and the risks that go with it. Vaccines are formulated to contain either dead versions or weakened live versions of the bacteria or viruses that cause a disease. Vaccines containing dead versions (called “killed vaccines” or “inactivated vaccines”) can’t cause the disease. Vaccines containing weakened live versions (called “live attenuated” vaccines) may rarely cause the disease, but are designed so that they don’t cause serious disease in healthy people. Sometimes, you may experience minor symptoms after a vaccination, such as fever or soreness at the vaccination site. Myth #4: Vaccines carry too high a risk of side effects There’s no denying that vaccines, like other medical treatments, may have side effects.