

The Light of Egypt or the Science of the Soul and the Stars.
Pyramids. Ancient Egypt. Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt.
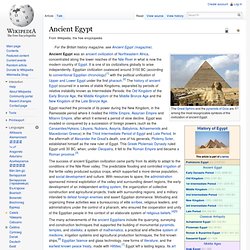
It is one of six civilizations globally to arise independently. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology)[1] with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh.[2] The history of ancient Egypt occurred in a series of stable Kingdoms, separated by periods of relative instability known as Intermediate Periods: the Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age, the Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age and the New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. History Map of ancient Egypt, showing major cities and sites of the Dynastic period (c. 3150 BC to 30 BC) Predynastic period A typical Naqada II jar decorated with gazelles. In Predynastic and Early Dynastic times, the Egyptian climate was much less arid than it is today. Early Dynastic Period (c. 3050 –2686 BC) Ancient Egyptian creation myths. The sun rises over the circular mound of creation as goddesses pour out the primeval waters around it Ancient Egyptian creation myths are the ancient Egyptian accounts of the creation of the world.
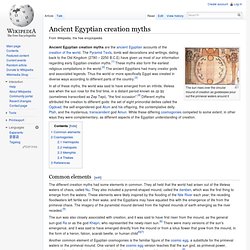
The Pyramid Texts, tomb wall decorations and writings, dating back to the Old Kingdom (2780 – 2250 B.C.E) have given us most of our information regarding early Egyptian creation myths.[1] These myths also form the earliest religious compilations in the world.[2] The ancient Egyptians had many creator gods and associated legends. Thus the world or more specifically Egypt was created in diverse ways according to different parts of the country.[3] Common elements[edit] History of ancient Egypt. The history of Ancient Egypt spans the period from the early predynastic settlements of the northern Nile Valley to the Roman conquest in 30 BC.
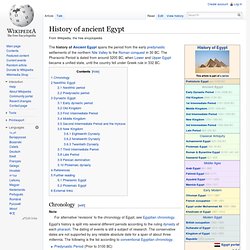
The Pharaonic Period is dated from around 3200 BC, when Lower and Upper Egypt became a unified state, until the country fell under Greek rule in 332 BC. Chronology[edit] Note For alternative 'revisions' to the chronology of Egypt, see Egyptian chronology. Egypt's history is split into several different periods according to the ruling dynasty of each pharaoh. Predynastic Period (Prior to 3100 BC)Protodynastic Period (Approximately 3100–3000 BC)Early Dynastic Period (1st–2nd Dynasties)Old Kingdom (3rd–6th Dynasties)First Intermediate Period (7th–11th Dynasties)Middle Kingdom (12th–13th Dynasties)Second Intermediate Period (14th–17th Dynasties)New Kingdom (18th–20th Dynasties)Third Intermediate Period (21st–25th Dynasties) (also known as the Libyan Period)Late Period (26th–31st Dynasties) Neolithic Egypt[edit] Neolithic period[edit] Dynastic Egypt[edit]
Ancient history. Ancient history is the aggregate of past events[1] from the beginning of recorded human history to the Early Middle Ages or the Postclassical Era. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, with Sumerian Cuneiform script, the oldest discovered form of coherent writing, from the protoliterate period around the 30th century BC.[2] The term classical antiquity is often used to refer to history in the Old World from the beginning of recorded Greek history in 776 BC (First Olympiad). This roughly coincides with the traditional date of the founding of Rome in 753 BC, the beginning of the history of ancient Rome, and the beginning of the Archaic period in Ancient Greece.
The Relationship Between The Great Pyramid and the Book of the D. The Relationship Between The Great Pyramid and The Book of the Dead It has been proposed that the Great Pyramid of Giza is the Egyptian “Book of the Dead” symbolized in stone.

Marsham Adams first proposed this in 1895. “The intimate connection between the secret doctrine of Egypt’s most venerated books, and the secret significance of her most venerable monument, seems impossible to separate, and each form illustrates and interpenetrates the other. Marsham Adams proposed that the unique system of passages and chambers (particularly the Grand Gallery, obviously unnecessary in a tomb) has an allegorical significance only explained by reference to the Egyptian “Book of the Dead”. Egyptian.