

The Arab ruling classes in the 1970s - Mohammad Ja'far. Text of a talk by Mohammed Ja'far on the development of the Arab ruling classes during the 1960s and 1970s, their integration into the world market and the effect this has on the possibility for revolutionary change in the Middle-East.
The Arab ruling classes in the 1970s - Mohammad Ja'far On 28 April, 1979, a day conference organised by Khamsin was held in Birkbeck College, University of London. The general topic of the conference was Nationalism, Religion or Socialism in the Middle East. The following text is a transcript of the opening talk at that conference. Introduction Looking back over the last decade or so of Middle-East politics, I think there is at least one thing no observer would disagree about: that is the accelerated pace at which dramatic events of a political, social and economic character have been taking place in that part of the world.
But equally as important as the fact 'of change itself is the question of who has been in the leadership of these changes. BACKGROUND IN 20TH CENTURY EGYPTIAN HISTORY SINCE 1952 REVOLUTION, Jana Evans Braziel. Egypt Under Sadat - History - Egypt - Africa. You are here :: Anwar al-Sadat, who had been vice president under Nasser, became president upon Nasser’s death.

Sadat was generally assumed to be too weak to hold power for long. He surprised everyone in May 1971 by removing Nasser’s most trusted lieutenants from key leadership positions. Sadat quickly gained popular support by repealing many censorship policies, calling for a new constitution, and changing the country’s name to the Arab Republic of Egypt. Sadat's early initiatives in foreign policy were less successful. Sadat came under increasing domestic pressure to initiate a new war against Israel to recapture the territories lost in 1967. Egypt. More information about Egypt is available on the Egypt Page and from other Department of State publications and other sources listed at the end of this fact sheet.
The United States established diplomatic relations with Egypt in 1922, following its independence from protectorate status under the United Kingdom. The United States and Egypt share a relationship based on mutual interest in Middle East peace and stability, revitalizing the Egyptian economy and strengthening trade relations, and promoting regional security. Egypt has been a key U.S. partner in ensuring regional stability and on a wide range of common security issues, including Middle East peace and countering terrorism. Egypt’s historic transition to democracy, launched in early 2011, will have a profound impact on the political future, not only of Egypt, but also the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region at large. U.S. Bilateral Economic Relations. Egypt Politics, government, and taxation, Information about Politics, government, and taxation in Egypt. Egypt has had 3 presidents since the 1954 revolution that brought popular president Gamal Abdel Nasser to power.
Between 1954 and 1970, Nasser attempted to institute socialist economic principles on the Soviet model, and actively sought to industrialize an agriculture-based economy. Internally, Nasser dismantled the political and economic power of the landed class by nationalizing land previously owned by rich feudal landlords and distributing it to the poor. Biography - president of Egypt. Anwar Sadat, in full Muhammad Anwar el-Sadat, Sadat also spelled Sādāt, el-Sadat also spelled al-Sadat (born December 25, 1918, Mīt Abū al Kawm, Al-Minūfiyyah governorate, Egypt—died October 6, 1981, Cairo), Egyptian army officer and politician who was president of Egypt from 1970 until his assassination in 1981.
He initiated serious peace negotiations with Israel, an achievement for which he shared the 1978 Nobel Prize for Peace with Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin. Under their leadership, Egypt and Israel made peace with each other in 1979. Sadat, Anwar© Kevin Fleming/CorbisSadat graduated from the Cairo Military Academy in 1938. During World War II he plotted to expel the British from Egypt with the help of the Germans.
The British arrested and imprisoned him in 1942, but he escaped two years later. Sadat’s domestic and foreign policies were partly a reaction against those of Nasser and reflected Sadat’s efforts to emerge from his predecessor’s shadow. Sadat's Egypt (1970-1981) Sadat’s Egypt (1970-1981)suarte2015-07-21T18:41:04+00:00 Anwar Sadat (1918-1981) changed course radically.
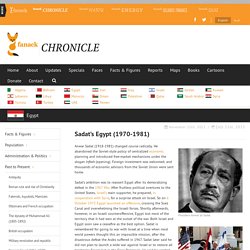
He abandoned the Soviet-style policy of centralized economic planning and introduced free-market mechanisms under the slogan Infitah (opening). Foreign investment was welcomed, and thousands of economic advisors from the Soviet Union were sent home. Sadat’s ambition was to reassert Egypt after its demoralizing defeat in the 1967 War. After fruitless political overtures to the United States, Israel’s main supporter, he prepared, in cooperation with Syria, for a surprise attack on Israel. Camp David Accord In the following years Sadat established friendly relations with the United States and began negotiations with Israel.
Sadat’s economic policies seemed to be paying off.