

This is a method of learning where the consequences of a response determine the probability of it being repeated. Through operant conditioning behavior which is reinforced (rewarded) will likely be repeated, and behavior which is punished will occur less frequently. 8.2 Changing Behaviour through Reinforcement and Punishment: Operant Conditioning – Introduction to Psychology – 1st Canadian Edition. Learning Objectives Outline the principles of operant conditioning.Explain how learning can be shaped through the use of reinforcement schedules and secondary reinforcers. In classical conditioning the organism learns to associate new stimuli with natural biological responses such as salivation or fear. The organism does not learn something new but rather begins to perform an existing behaviour in the presence of a new signal.
Operant conditioning, on the other hand, is learning that occurs based on the consequences of behaviour and can involve the learning of new actions. Operant conditioning occurs when a dog rolls over on command because it has been praised for doing so in the past, when a schoolroom bully threatens his classmates because doing so allows him to get his way, and when a child gets good grades because her parents threaten to punish her if she doesn’t.
What is Operant Conditioning? Sheldon Shaping Penny in Big Bang Theory. Learning: Negative Reinforcement vs. Punishment. Reinforcement Vs Punishment parents. What does Reinforcement and Punishment mean to parents? The Teenage Brain Explained. Youtube. Teenage brain development. Teenage brain development: the basics Children’s brains have a massive growth spurt when they’re very young.
By the time they’re six, their brains are already about 90-95% of adult size. But the brain still needs a lot of remodelling before it can function as an adult brain. This brain remodelling happens intensively during adolescence, continuing into your child’s mid-20s. Some brain changes happen before puberty, and some continue long after. So even though all teenagers’ brains develop in roughly the same way at the same time, there are differences among individual teenagers. Inside the teenage brain Adolescence is a time of significant growth and development inside the teenage brain. The main change is that unused connections in the thinking and processing part of your child’s brain (called the grey matter) are ‘pruned’ away.
Brain Map Frontal Lobes. The frontal lobes are located directly behind the forehead.
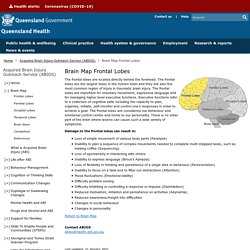
The frontal lobes are the largest lobes in the human brain and they are also the most common region of injury in traumatic brain injury. The frontal lobes are important for voluntary movement, expressive language and for managing higher level executive functions. Executive functions refer to a collection of cognitive skills including the capacity to plan, organise, initiate, self-monitor and control one’s responses in order to achieve a goal. The frontal lobes are considered our behaviour and emotional control centre and home to our personality. There is no other part of the brain where lesions can cause such a wide variety of symptoms. Damage to the frontal lobes can result in: Return to Brain Map1 Contact ABIOSabios@health.qld.gov.au2. Understanding the teenage mind. The Use of Reinforcement and Punishment in Shaping a Child's Behavior. Positive Reinforcement - Tips for teaching and parenting.
Reinforcement vs. Punishment: Changing Behavior. Being a parent has been known as the best thing ever BUT also the most challenging endeavor you will encounter in your lifetime.
Parents strive to raise a healthy and happy child that will one day grow up as a full-fledged mature and independent adult. But to successfully accomplish this goal, a parent must set forth structure or rules throughout their childhood to help them understand and be realigned when their behavior needs to be modified. When a parent recognizes the need to change a behavior, they will likely end up using either reinforcement, punishment, or a mixture of both. When we’re helping to decrease the frequency of a child’s negative behavior, having the reinforcement or punishment methods in our toolkit can help you modify and implement the desired behavior. How does Reinforcement help with changing behavior? There are two basic kinds of reinforcement, positive and negative reinforcement.