

Simbad. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
SIMBAD (Set of Identifications, Measurements, and Bibliography for Astronomical Data) est une base de données astronomiques des objets en dehors du système solaire. Elle est maintenue par le Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg et permet aux astronomes de facilement connaître les propriétés de base (coordonnées, magnitudes, parallaxe si elle est disponible) de chacun des objets recensés dans un catalogue astronomique. Simbad contient également tous les noms publiés dans la littérature, permettant ainsi d'identifier un objet astronomique quel que soit son nom. Une équipe de documentalistes s'occupe de vérifier et rentrer les nouveaux objets dans la base. En février 2017, SIMBAD contient plus de 9 millions d'objets avec 24 millions de noms différents, et plus de 327 000 références bibliographiques ont été entrées.
Articles connexes[modifier | modifier le code] Lien externe[modifier | modifier le code] ALMA dévoile le fonctionnement d'un système planétaire proche. Eso1216fr — Communiqué de presse scientifique 12 avril 2012 Un nouvel observatoire, encore en construction, a permis aux astronomes de faire une découverte capitale pour comprendre un système planétaire proche et leur a fourni des données essentielles pour comprendre comment de tels systèmes se forment et évoluent.
Les astronomes utilisant le réseau d’antennes millimétrique et submillimétrique de l'Atacama (ALMA pour Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array) ont découvert que les planètes orbitant autour de l'étoile Fomalhaut devaient être de taille beaucoup plus petite que l'on ne pensait. Il s'agit là du tout premier résultat scientifique publié grâce à ALMA, ouvert aux astronomes du monde entier depuis peu pour sa première période d’observation. Leurs calculs ont par ailleurs révélé les probables dimensions des planètes – plus grosses que Mars, mais pas plus grosse quelques fois la taille de la Terre. Notes Plus d'informations L’équipe est composée de : A.
Liens Contacts. Société Astronomique de Montpellier. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg Le Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg (CDS) est un centre de données voué à la collecte et à la distribution dans le monde entier de données astronomiques[1]. Il héberge la base de référence mondiale pour l'identification d'objets astronomiques et ses missions consistent : à rassembler des informations utiles concernant les objets astronomiques, sous forme informatisée ;à distribuer ces informations dans la communauté astronomique internationale ;à conduire des recherches utilisant ces données.
Leaving so soon? Unusual planetary nebula fades mere decades after it arrived. News releases | Research | Science December 3, 2020 Two images of the Stingray Nebula, located in the direction of the southern constellation Ara — or the Altar — captured 20 years apart by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope.
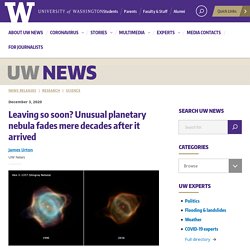
The image on the left was taken in March 1996, while the image on the right was captured in January 2016.NASA/ESA/Bruce Balick/Martín Guerrero/Gerardo Ramos-Larios Stars are rather patient. They can live for billions of years, and they typically make slow transitions — sometimes over many millions of years — between the different stages of their lives.
So when a previously typical star’s behavior rapidly changes in a few decades, astronomers take note and get to work. Le CNRS honore Françoise Combes, une sommité de l'astrophysique. Elle a révélé un pan de l'histoire des galaxies: l'astrophysicienne Françoise Combes a reçu jeudi la médaille d'or du CNRS, l'un des prix scientifiques les plus prestigieux, pour ses travaux qui ont mis en lumière l'évolution de ces structures essentielles de l'Univers.
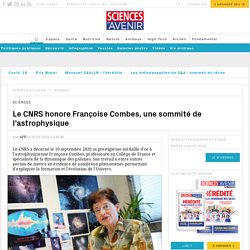
Déjà reconnue par de nombreux prix internationaux, cette chercheuse française de 68 ans est "une sommité scientifique incontestée de la physique extragalactique au niveau mondial", a déclaré le président du CNRS, Antoine Petit, saluant une "carrière scientifique exceptionnelle". Is our galaxy normal? Our home galaxy, the Milky Way, has been a jumping-off point to our understanding of galaxies throughout the universe.
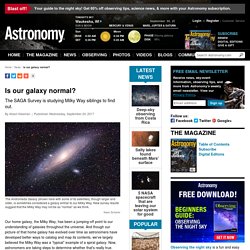
And though our picture of that home galaxy has evolved over time as astronomers have developed better ways to catalog and map its contents, we’ve largely believed the Milky Way was a “typical” example of a spiral galaxy. Now, astronomers are taking steps to determine whether that's really true. Did Sun have an early binary companion? - Cosmos Magazine. In the early days of the Solar System, the Sun may have had a companion star, scientists say, making it part of a binary system like many others in the Milky Way galaxy.
But this doesn’t mean the view from the infant Earth would have looked like that from Tatooine, the fictional planet that was home to Luke Skywalker in Star Wars. This second sun would have been 150 billion kilometres away – so distant it would have merely been a bright pinpoint, casting less light than the full Moon. Clues to its possible existence lie in two peculiarities of the outer Solar System, says Amir Siraj, from Harvard University, US, first author of a paper in Astrophysical Journal Letters. The ABCs of observing. Amateur astronomy is about observing: Each and every time you look through an eyepiece, you make contact with a distant part of the universe.
I’ve assembled this list of observing tips — one for each letter of the alphabet — to help you get the most out of those precious moments behind the eyepiece. I’ve discovered some of them on my own, but others were passed on to me by wise observing buddies. Read them, use them, and add to them. If you do, you’ll become a better observer. AVOID EYE FATIGUE. BATTERIES. CAMERA FOCUSING. Les scientifiques repèrent le `` jumeau '' de la Voie lactée à 12,4 milliards d'années-lumière, ce qui bouleverse notre compréhension de la formation des galaxies (VIDEOS)
Les astronomes ont découvert une copie étonnamment ordonnée et presque de notre galaxie de la Voie lactée à 12,4 milliards d’années-lumière, ce qui pourrait bouleverser nos théories actuelles sur la formation et l’évolution galactiques.

Notre presque jumeau galactique est appelé SPT0418-47 (pas aussi accrocheur que la Voie lactée), et est un disque plat et rotatif avec une masse similaire à notre propre galaxie, bien qu’il n’ait pas été doté de bras en spirale. Searching for supernova neutrinos with DUNE. When a massive star reaches the end of its life, it can explode in a process known as a supernova.
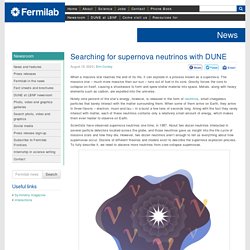
The massive star – much more massive than our sun – runs out of fuel in its core. Gravity forces the core to collapse on itself, causing a shockwave to form and spew stellar material into space. Metals, along with heavy elements such as carbon, are expelled into the universe. Parc du Cosmos. The cold eyes of DUNE. How do you detect a particle that has almost no mass, feels only two of the four fundamental forces, and can travel unhindered through solid lead for an entire light-year without ever interacting with matter? This is the problem posed by neutrinos, ghostly particles that are generated in the trillions by nuclear reactions in stars, including our sun, and on Earth. Scientists can also produce neutrinos to study in controlled experiments using particle accelerators.
One of the ways neutrinos can be detected is with large vats filled with liquid argon and wrapped with a complex web of integrated circuitry that can operate in temperatures colder than the average day on Neptune. Industry does not typically use electronics that operate at cryogenic temperatures, so particle physicists have had to engineer their own. Why doesn't dark matter obscure light? Q: If 85 percent of the mass in the universe is dark matter, why doesn’t it obscure light from distant objects? How could this material not scatter light? Jerome Handley Turlock, California A: Dark matter is called “dark” because it doesn’t give off or interact with light — including through scattering.
Do We Live in a Multiple Universe? The suggestive evidence for this comes from several directions, from the idea of cosmic inflation, from string ttheory and the existence of the famous cosmological constant. Some of the notions that come out of these lines of evidence are pretty counterintuitive. Did dark energy cause the Big Bang? As far as cosmologists can tell, the mysterious force behind the accelerated expansion of the universe, a force that we call dark energy, remains constant. But that's today. It's entirely possible that dark energy changed in the past, according to new research, and those changes may have flooded the universe with the particles of our everyday lives, the scientists behind the new research suggested.
Let's start with the present: Something strange is happening to the cosmos. It's expanding, but it's also full of matter. What happens if string theory is wrong? For more than a decade, the American public has been fascinated with string theory. Science popularizers like Brian Greene produced hit TV documentaries that examined this mathematical construct. Could string theory unite physics into one grand unified theory?
Perhaps, but with strange implications like extra dimensions and, possibly, even a multiverse. La più antica mappa stellare: il Disco di Nebra. La rappresentazione più antica di un cielo notturno è probabilmente una mappa stellare: è il manufatto noto come “Disco di Nebra”, rinvenuto in Germania e risalente al 1600 a.C. Scientist Finds ‘Evidence’ of Another Universe Before This One - Physics-Astronomy2. Before our universe, another universes existed. It's a cosmic cycle that repeats. Before our universe, another universe existed, and another one will emerge after this universe ends. "The next universe will be just like ours — but only in overall appearance, not in detail, of course…” A researcher may just have discovered conclusive evidence that another universe existed before this one.
The other dark matter candidate. In the early 1970s, physics had a symmetry problem. According to the Standard Model, the guiding framework of particle physics, a symmetry between particles and forces in our universe and a mirror version should be broken. It was broken by the weak force, a fundamental force involved in processes like radioactive decay. This breaking should feed into the interactions mediated by another fundamental force, the strong force. But experiments show that, unlike the weak force, the strong force obeys mirror symmetry perfectly. No one could explain it. Astronomers Have Caught a Star Literally Dragging Space-Time Around With It. One of the predictions of Einstein's general theory of relativity is that any spinning body drags the very fabric of space-time in its vicinity around with it.
This is known as "frame-dragging". In everyday life, frame-dragging is both undetectable and inconsequential, as the effect is so ridiculously tiny. Astronomers Detect a Burst of Gravitational Waves From The Direction of Betelgeuse. Gravitational waves are caused by calamitous events in the Universe. Neutron stars that finally merge after circling each other for a long time can create them, and so can two black holes that collide with each other.
But sometimes there's a burst of gravitational waves that doesn't have a clear cause. Bubble-blowing galaxies could help solve a cosmic mystery. HONOLULU – A trio of bubble-blowing galaxies may offer clues about one of the greatest cosmic makeovers in the history of the universe. Sometime during the universe’s first billion or so years, most of the hydrogen atoms in the cosmos became ionized when their electrons were torn away (SN: 11/7/19). Astronomers suspect that this reionization — so called because all hydrogen had been previously ionized for the first few hundred thousand years — was triggered by harsh ultraviolet light from the first generations of stars. Now, researchers say they’ve caught a few galaxies blasting out ionizing light and stripping electrons from surrounding hydrogen just 680 million years after the Big Bang.
Are there even preliminary ideas about what dark energy is? -explosion-supergigante-betelgeuse-inminente-segun-astronomos-202001190057_noticia. Actualizado:19/01/2020 12:42h Guardar. Night sky: Betelgeuse could blow up soon (in astronomical time) Overview - The Dark Energy Survey. The Dark Side of the Moon - The National Space Centre - The National Space Centre. Mysteries behind interstellar buckyballs finally answered. L’étoile de Scholz aurait frôlé le Soleil et bousculé plusieurs comètes il y a 70 000 ans. The NGC / IC Project - Home of the Historically Corrected New General Catalogue (HCNGC) since 1993.
Nouvelle estimation de la constante de Hubble. Aurait-on confondu matière noire et effet de marée ? Planetariu.ro. Researchers find source of cosmic neutrinos ushering in a new era of 'multi-messenger' astronomy. This cosmic Cold Spot challenges our current cosmological model. Animated Galaxies, Black Holes, Supernovas Gifs at Best Animations. Nationalgeographic. Planck : les données définitives de la mission soutiennent fortement le modèle cosmologique standard. Un nouveau modèle cosmologique : symétrie CPT au Big Bang. Nationalgeographic. Nationalgeographic. Nationalgeographic. Guest Blog: Inspiring the Next Generation of Astronomers Through Story. International team publishes roadmap to enhance radioresistance for space colonization.
Confondu avec une aurore boréale, « Steve » est un phénomène lumineux inexpliqué. L'ciel d'min gardin, astronomie a Wancourt. Nationalgeographic. “Nuclear pasta” is certainly not al dente. SPIDER 500A professional radio telescope: Buy online. Top stories: rival giant telescopes, hefty plants, and the mystery behind ‘gluten sensitivity’ Avis dexperts. L'astrométéorologie de la Renaissance. Une observation sans précédent d’un pulsar à 6 500 années-lumières.
Voyage au coeur de la matière : quel est cet univers dans lequel la conscience est apparue ? - 05/04/2018 <span class='container_br_heure' style='display:none;'><br/></span>15:00 à 17:00 - Forum104. Des étoiles et galaxies toutes noires pourraient exister dans l'Univers. L’espace, mode d’emploi (3/4) : L’espace, et au-delà… Planet X: We are closing in on the solar system's new occupant. Detecting Gravitational Waves by Watching Stars.
Orion dans la ligne de mire des lasers du VLT. The Universe's Brightest Lights Have Some Dark... Poeticon astronomicon. We May Have Uncovered the First Ever Evidence of the Multiverse. Music of the spheres: chain of planets rotates at “perfect. Unlocking the secrets of the universe. Ce fascinant ordinateur astronomique a été inventé par les Grecs anciens. Despite Deadly Rays, Pulsars Could Host Habitable Planets. LA STONEHENGE D’ABRUZZO - Il Faro 24! Dark energy must die – these rebel physicists can take it down. Visitez les multivers de Max Tegmark : les univers parallèles d'Everett. Mon rêve ? Devenir ingénieur spatial! - Tremplin Prépabac 2018.
Des archéologues découvrent un ancien modèle de l'univers au Mexique. Dark Energy Survey publicly releases first three years of data - The Dark Energy Survey. La cosmologie quantique. Evidence against a supervoid causing the CMB Cold Spot. Étoile de Tabby : le mystère est résolu! Catalogue - Encyclopédie de la Pléiade - Collectif, Astronomie. "Of a Collapsing Star in a Universe Profoundly Different Than Our Own" (Video/Weekend Feature) - The Daily Galaxy.
Scientists Finally Calculated The Speed of Gravity - Tech Explorist. Des doutes sur l'existence de l'énergie noire ? Galaxies Are Dying. But What's Killing Them? Une planète "monstre" découverte autour d'une étoile naine. Insomniaques, levez les yeux au ciel: cette nuit, la comète de Halley vous offre une pluie d'étoiles filantes.
Le télescope Hubble a observé une planète totalement noire qui « mange » la lumière. La Chanson du mal-aimé, poème de Guillaume Apollinaire - poetica.fr. Astronomers Discover ‘Heavy Metal’ Supernova Rocking Out. The dark side of the universe – a primer. Physics - Viewpoint: Spinning Black Holes May Grow Hair. Brane Cosmology. Ultra-bright star breaks all the rules. IL DESTINO NELLE STELLE : Scienze e Lettere Casa Editrice : Rome Italy. Des montagnes flottantes sur Pluton, ça ne s'invente pas ! Why is there a universe? Scientists show state of NOTHINGNESS impossible. Vacuum decay: the ultimate catastrophe. Cosmologists produce new maps of dark matter dynamics. The Man Who Invented the 26th Dimension – Paul Halpern – Medium. Scientists Propose New Theory About the Noises Meteors Make. Researchers capture first 'image' of a dark matter web that connects galaxies.