

Use Cases. This page lists use cases for the DBpedia knowledge base together with references to ongoing work into these directions. 1.

Revolutionize Wikipedia Search Wikipedia currently only supports keyword-based search and does not allow more expressive queries like “Give me all cities in New Jersey with more than 10,000 inhabitants” or “Give me all Italian musicians from the 18th century.” This lowers the overall utility of Wikipedia. One major application domain for the DBpedia data set is to enable sophisticated queries against Wikipedia, which could revolutionize the access to this valuable knowledge source. Here are three prototypical search interfaces using different approaches to improve Wikipedia search: DBpedia Faceted Search – allows you to explore Wikipedia via a faceted browsing interface.
Examples of different queries that can be asked against DBpedia are found on the OnlineAccess and Datasets pages. 2. The Driving Force Behind Big Data: Data Connectivity. In most organizations, stakeholders maintain the perspective that Big Data offers tremendous benefits to the enterprise, especially when it comes to more agile business intelligence and analytics.
Unfortunately, the days of complete visibility into Big Data are numbered – there is simply too much of it. While we may see companies promoting fancy strategies for managing ‘fire hose data’, only the ones focused on analytics will get close to creating meaning from the massive deluge. As a result, companies are looking to plug into new advancements in relational and non-relational programming frameworks that support the processing of large data sets. Data connectivity components, such as drivers, help enterprise organizations effectively satisfy the bulk data access requirements for a broad array of use cases. Large-scale graph computing at Google. Speech and Language Processing (2nd Ed.): Updates.
AdaBoost. While every learning algorithm will tend to suit some problem types better than others, and will typically have many different parameters and configurations to be adjusted before achieving optimal performance on a dataset, AdaBoost (with decision trees as the weak learners) is often referred to as the best out-of-the-box classifier.
When used with decision tree learning, information gathered at each stage of the AdaBoost algorithm about the relative 'hardness' of each training sample is fed into the tree growing algorithm such that later trees tend to focus on harder to classify examples. Overview[edit] Training[edit] AdaBoost refers to a particular method of training a boosted classifier. Quiver (mathematics) A quiver Γ consists of:
Aurelius. Windy City DB - Recommendation Engine with Neo4j. How to beat the CAP theorem. The CAP theorem states a database cannot guarantee consistency, availability, and partition-tolerance at the same time.

But you can't sacrifice partition-tolerance (see here and here), so you must make a tradeoff between availability and consistency. Managing this tradeoff is a central focus of the NoSQL movement. Consistency means that after you do a successful write, future reads will always take that write into account. TinkerPop. Marko A. Rodriguez. EC2 Instance Types. Use Cases Small and mid-size databases, data processing tasks that require additional memory, caching fleets, and for running backend servers for SAP, Microsoft SharePoint, cluster computing, and other enterprise applications.
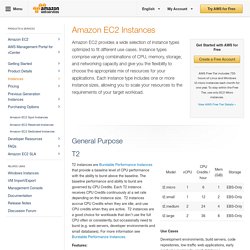
*M3 instances may also launch as an Intel Xeon E5-2670 (Sandy Bridge) Processor running at 2.6 GHz. High performance front-end fleets, web-servers, batch processing, distributed analytics, high performance science and engineering applications, ad serving, MMO gaming, video-encoding, and distributed analytics. Graph database. Graph databases are part of the NoSQL databases created to address the limitations of the existing relational databases.
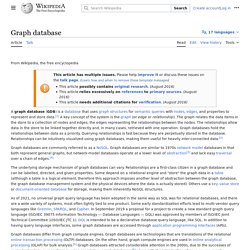
While the graph model explicitly lays out the dependencies between nodes of data, the relational model and other NoSQL database models link the data by implicit connections. Graph databases, by design, allow simple and fast retrieval[citation needed] of complex hierarchical structures that are difficult to model[according to whom?] In relational systems. Graph databases are similar to 1970s network model databases in that both represent general graphs, but network-model databases operate at a lower level of abstraction[3] and lack easy traversal over a chain of edges.[4] Graph databases differ from graph compute engines.
Background. Algorithms for Large Data Sets: Slides. Node.js to Heroku with Neo4j. Dictionary of Algorithms and Data Structures. This web site is hosted by the Software and Systems Division, Information Technology Laboratory, NIST. Development of this dictionary started in 1998 under the editorship of Paul E. Black. After 20 years, DADS needs to move. If you are interested in taking over DADS, please contact Paul Black. Twitris: Social Media Analysis with Semantic Web Technology. Seeking a Semantic Web Sweet Spot. Seeking a Semantic Web Sweet Spot » AI3:::Adaptive Information . Reference Structures Provide a Third Way. Redland RDF Libraries. Easing The Job Of Working With Linked Data. Working with Linked Data could be a little bit easier than it is, and a collaborative project between MediaEvent Services and the Freie Universität of Berlin aims to make it so.
Home - Taxonomy Strategies. World's Leading Graph Database » What is Neo4j? Semantic Web: Is Schema.org good or bad for the Semantic Web. Is 'big data' indifferent to the semantic web, i.e. linked data.