

Edutopia. How Do You Stir Curiosity in Your Classroom? - OnCUE. You know those moments in class when we have our students on the edge of their seats?
What is Innovation? Inquiries into Spoofs - Scientific Literacy and the Media. A colleague shared a video with me recently that really made me think.
It got me thinking about Scientific Literacy and the Media. I watch this video and I see spoof. No questions. Visual Thinking Strategies Visual Thinking Strategies is a research-based education nonprofit that believes thoughtful, facilitated discussion of art activates transformational learning accessible to all. Educational Leadership:Creativity Now!:Assessing Creativity.
WebbsDOK. Scaffolding for Deep Understanding. How CAN we help our students be the kind of thinkers we want?
My friend and colleague, @brendasherry, recently wrote a thoughtful post called What is Deep Understanding? She asked several excellent questions: what is deep understanding? Can schools really provide the learning environment to nurture and develop it? In thinking about these questions, I would like to ask: “How can we help novice learners become more expert learners?” Novice Learners versus Expert Learners Having said that, let’s look at the difference between novice and expert learner. Novices typically don’t plan, monitor, and reflect on their learningThese metacognitive skills include setting goals and subgoals; identifying approaches; monitoring one’s progress to the task; revising goals where necessary; and, reflection after task completion.Expert learners use ‘multiple representations’to build a fuller, more complete understanding.
Scaffolded Journal Writing. Punctuation in novels. Punctuation in novels When we think of novels, of newspapers and blogs, we think of words.
We easily forget the little suggestions pushed in between: the punctuation. Untitled. 25 Ways to Develop 21st Century Thinkers. The need to develop critical thinkers has never been as urgent as it is now.

In a world that is digitally focused and where there is an outpouring of information surfeit, students need to be equipped with the right tools to live up to the new learning exigencies. Critical thinking as a skill is the mother of all other skills and one that underpins and solidify students overall learning. Given the importance of cultivating a culture of critical thinking inside our classrooms and to help teachers have access to a wide range of resources on how to teach and enhance students critical thinking skills, Educational Technology and mobile Learning has devoted an entire section to everything teachers need in order to teach and integrate this skills in their teaching. You can access it HERE. Today, we are adding another great resource. Alphabet of the obsolete. A Wonder Room – every school should have one. The large white 1950s telephone could have been a prop from the set of Mad Men.
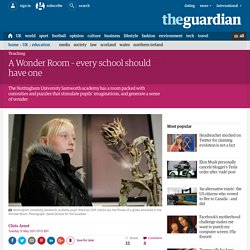
It shares a shelf with a vinyl-clad Vector Radio that looks as though it should be permanently tuned to Radio Luxembourg. Nearby is a black typewriter so old it might have been used in Billy Wilder's adaptation of The Front Page. All three items seem to fascinate the young visitors to the Wonder Room at the Nottingham University Samworth academy (Nusa), a shiny new school sponsored by the university in Bilborough, a former council estate. The room is crammed with curiosities – the pre-war typewriter is particularly popular with pupils more used to the sleek and silent computer technology of the 21st century. Questioning Toolkit.
Essential Questions.
Defining Critical Thinking. It entails the examination of those structures or elements of thought implicit in all reasoning: purpose, problem, or question-at-issue; assumptions; concepts; empirical grounding; reasoning leading to conclusions; implications and consequences; objections from alternative viewpoints; and frame of reference.
Critical thinking — in being responsive to variable subject matter, issues, and purposes — is incorporated in a family of interwoven modes of thinking, among them: scientific thinking, mathematical thinking, historical thinking, anthropological thinking, economic thinking, moral thinking, and philosophical thinking. Critical thinking can be seen as having two components: 1) a set of information and belief generating and processing skills, and 2) the habit, based on intellectual commitment, of using those skills to guide behavior. Critical thinking varies according to the motivation underlying it. Another Brief Conceptualization of Critical Thinking. 50 Resources For Teaching With Bloom's Taxonomy - Bloom’s for Kindergarten: Simple suggestions for applying the taxonomy to kindergarten-level children.

Lesson Planet: This source gives the goods on creating complete lesson plans using Bloom’s Taxonomy. Prezi: Enjoy this stylish Prezi presentation on Bloom’s Taxonomy. Questioning - Top Ten Strategies. “Learn from yesterday, live for today, hope for tomorrow.

The important thing is to not stop questioning.” – Albert Einstein. CYMATICS: Science Vs. Music - Nigel Stanford. White Oak teacher creates a Lego wall for her classroom. A Coweta teacher is using her passion for Legos to bring more creativity to her students, by creating a Lego wall in her classroom. “I am always looking for innovative ways to engage students,” said Paula Corley, REACH teacher at White Oak Elementary School. “A few years ago, my passion for Legos was reignited with my own child and his interest. Then, I began teaching Lego robotics for the first time last year. “At Coweta's STEM Conference last year, I went to a class about Makerspaces, which is a movement related to STEM that reinforces innovation, design, logic, and problem solving in students.
Blooms Taxonomy Flip Chart for Student Use. Virtual Tours and Fieldtrips. Virtual Fieldtrips, Virtual Tours Virtual Tours of Museums and Exhibits Tour The American Museum of Natural History You can find 360 degree tours of dioramas, pictures, and video. CrashCourse. Technology and the Curious Mind. Visible Thinking. 12 Best YouTube Channels for Kids and Teens. YouTube's statistics never cease to amaze: more than 1 billion unique users per month, over 6 billion hours of video watched per month, 100 hours of video uploaded to YouTube every minute. Fine, but what if you want to find something for your kids to watch besides expletive-laced game commentary and twerking videos? You're in luck. Among the millions and billions, there's a tiny slice of really good stuff -- stuff that's creative, innovative, eye-opening, mind-expanding, and even practical. But the truly excellent content is not always easy to find.
Just when you think you've found a kid-friendly channel, your kid clicks off into something totally age-inappropriate. We set out to find the 10 best channels for kids on YouTube; we wound up with 12. Mother Goose Club. Simple Kids Crafts. The Brain Scoop. Teaching for Rigor Marzano (1) Kids Speak Out on Student Engagement. A while back, I was asked, "What engages students?
" Sure, I could respond, sharing anecdotes about what I believed to be engaging, but I thought it would be so much better to lob that question to my own eighth graders. The responses I received from all 220 of them seemed to fall under 10 categories, representing reoccuring themes that appeared again and again. So, from the mouths of babes, here are my students' answers to the question: "What engages students? " 1. Working with their peers. 7 Myths About Rigor In The Classroom. 7 Myths About Rigor In The Classroom. 4 Phases of Inquiry-Based Learning: A Guide For Teachers. According to Indiana University Bloomington, Inquiry-based learning is an “instructional model that centers learning on a solving a particular problem or answering a central question.
There are several different inquiry-based learning models, but most have several general elements in common: Why Ask Why in the Classroom. Striving for Higher-Order Thinking and Depth of Knowledge. A little over a year ago, I read Higher-order thinking is the exception rather than the norm for most classrooms on Scott McLeod's blog, Dangerously Irrelevant, and have been mulling it over, wondering if our school district is any different.
Over the past year, our teachers periodically collect data with their teams on the types of questions/tasks they ask students. One teacher records teacher questions and the other records student responses on a shared Google Doc; then teams sort through their own data, plotting teacher questions by Bloom's Revised Taxonomy, and student responses to those questions/tasks with Webb's Depth of Knowledge (DOK). The 2012-2013 data showed we were not very different from other districts; therefore, our teams set their own goals for higher-order thinking and depth of knowledge. How Creativity Works. Wring Out a Washcloth in Space. Two 10th-grade students wanted to know what happens when you wring out a water-soaked washcloth in zero gravity. Canadian astronaut Chris Hadfield, who currently lives on the International Space Station, was happy to oblige.
What Does Earth Look Like? Big Thinkers: Judy Willis on the Science of Learning. How to Mind Map. Questioning Toolkit. Unleashing Creativity. Beyond Cut-and-Paste. 101questions. Everyday Mysteries: Fun Science Facts from the Library of Congress. When are Students Engaged? (Updated 11/2013) Educational author and former teacher, Dr. Video Library on Questioning. Poptropica. 4 Strategies to Spark Curiosity. British archaeologist Mary Leakey described her own learning as being "compelled by curiosity.
" ThinkQuest. Wonders. The 4th Grade Arcade of Imagination and Creativity.