

Field Guide to X-ray Astronomy. Dark MatterA term used to describe matter that can be inferred to exist from its gravitational effects, but does not emit or absorb detectable amounts of light.

Dark-Matter Galaxy Detected: Hidden Dwarf Lurks Nearby? Richard A. Lovett in Seattle, Washington An entire galaxy may be lurking, unseen, just outside our own, scientists announced Thursday. Dark Energy - Did Einstein Predict Dark Energy? Albert Einstein, 1947.

Einstein used his "cosmological constant" to help describe a static universe. When he learned the universe was expanding, he discarded it. Dark Energy - Fate of the Universe. Gravity always pulls matter together.
The baseball moves too slowly and gets pulled back to Earth. The spaceship moves fast enough to escape Earth, but it never escapes gravity entirely. Dark Energy - What Is Dark Energy? So what is dark energy?

Well, the simple answer is that we don't know. It seems to contradict many of our understandings about the way the universe works. We all know that light waves, also called radiation, carry energy. You feel that energy the moment you step outside on a hot summer day. Einstein's famous equation, E = mc2, teaches us that matter and energy are interchangeable, merely different forms of the same thing. Something from Nothing. Hubble Discoveries - Dark Energy. Dark Matter 2. Dark Universe / Transient Universe | Outer Solar System | Near Earth Objects | Milky Way | LSST Tour Dark Matter | Dark Energy | 3D mass Illustration of strong gravitaional lensing.
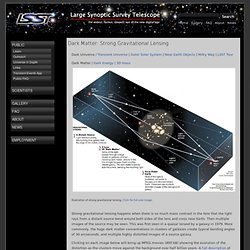
Click for full-size image. Strong gravitational lensing happens when there is so much mass contrast in the lens that the light rays from a distant source bend around both sides of the lens and cross near Earth. Then multiple images of the source may be seen. Clicking on each image below will bring up MPEG movies (800 kB) showing the evolution of the distortion as the clusters move against the background over half billion years. Two simulations of strong lensing by a massive cluster of galaxies. Biology's 'dark matter' hints at fourth domain of life - life - 18 March 2011. Read more: Click here to read the updated version of this story Step far enough back from the tree of life and it begins to look quite simple.
At its heart are just three stout branches, representing the three domains of life: bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes. But that's too simple, according to a band of biologists who believe we may be on the verge of discovering the fourth domain of life. The bold statement is the result of an analysis of water samples collected from the world's seas. Jonathan Eisen at the University of California, Davis, Genome Center has identified gene sequences hidden within these samples that are so unusual they seem to have come from organisms that are only distantly related to cellular life as we know it. Most species on the planet look like tiny single cells, and to work out where they fit on the tree of life biologists need to be able to grow them in the lab. Martin White: Dark Matter. We believe that most of the matter in the universe is dark, i.e. cannot be detected from the light which it emits (or fails to emit).

This is "stuff" which cannot be seen directly -- so what makes us think that it exists at all? Its presence is inferred indirectly from the motions of astronomical objects, specifically stellar, galactic, and galaxy cluster/supercluster observations. How Dark Matter Works" In the 1978 follow-up album to "Born to Run," Bruce Springsteen uses darkness on the edge of town as a metaphor for the desolate unknown we all face as we grow up and try to understand the world.
Cosmologists working to decipher the origin and fate of the universe must identify completely with The Boss' sense of tragic yearning. These stargazing scientists have been facing their own darkness on the edge of town (or on the edge of galaxies) for a long time as they try to explain one of astronomy's greatest mysteries. It's known as dark matter, which is itself a placeholder – like the x or y used in algebra class – for something unknown and heretofore unseen. One day, it will enjoy a new name, but today we're stuck with the temporary label and its connotations of shadowy uncertainty. Just because scientists don't know what to call dark matter doesn't mean they don't know anything about it.
Dark Matter. There are many reasons to believe that the universe is full of "dark matter", matter that influences the evolution of the universe gravitationally, but is not seen directly in our present observations.

FIGURE: Superposed on an optical picture of a group of galaxies is an X-ray image taken by ROSAT. The image shows hot gas (which produces X-rays) highlighted in false red color (Ref). Dark Matter. Dark Matter - Introduction. Dark matter. Dark Matter. Dark Matter. Dark Energy, Dark Matter. Dark Energy, Dark Matter In the early 1990s, one thing was fairly certain about the expansion of the Universe.

It might have enough energy density to stop its expansion and recollapse, it might have so little energy density that it would never stop expanding, but gravity was certain to slow the expansion as time went on. Granted, the slowing had not been observed, but, theoretically, the Universe had to slow. The Universe is full of matter and the attractive force of gravity pulls all matter together. Then came 1998 and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) observations of very distant supernovae that showed that, a long time ago, the Universe was actually expanding more slowly than it is today. Eventually theorists came up with three sorts of explanations.