

Our brains are wired so we can better hear ourselves speak, new study shows. Like the mute button on the TV remote control, our brains filter out unwanted noise so we can focus on what we’re listening to.
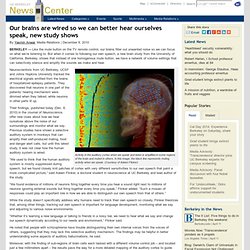
But when it comes to following our own speech, a new brain study from the University of California, Berkeley, shows that instead of one homogenous mute button, we have a network of volume settings that can selectively silence and amplify the sounds we make and hear. Activity in the auditory cortex when we speak and listen is amplified in some regions of the brain and muted in others.
In this image, the black line represents muting activity when we speak. (Courtesy of Adeen Flinker) Neuroscientists from UC Berkeley, UCSF and Johns Hopkins University tracked the electrical signals emitted from the brains of hospitalized epilepsy patients. The fine dopamine line between creativity and schizophrenia.
New research shows a possible explanation for the link between mental health and creativity.

By studying receptors in the brain, researchers at the Swedish medical university Karolinska Institutet have managed to show that the dopamine system in healthy, highly creative people is similar in some respects to that seen in people with schizophrenia. High creative skills have been shown to be somewhat more common in people who have mental illness in the family. Creativity is also linked to a slightly higher risk of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Certain psychological traits, such as the ability to make unusual pr bizarre associations are also shared by schizophrenics and healthy, highly creative people.
Rosenhan experiment. Rosenhan's study was done in two parts.
The first part involved the use of healthy associates or "pseudopatients" (three women and five men, including Rosenhan himself) who briefly feigned auditory hallucinations in an attempt to gain admission to 12 different psychiatric hospitals in five different states in various locations in the United States. All were admitted and diagnosed with psychiatric disorders. After admission, the pseudopatients acted normally and told staff that they felt fine and had no longer experienced any additional hallucinations. All were forced to admit to having a mental illness and agree to take antipsychotic drugs as a condition of their release. Type A and Type B personality theory. Type A and Type B personality theory describes two contrasting personality types that could either raise or lower, respectively, one's chances of developing coronary heart disease.
There is considerable controversy about the role of these personality types in coronary heart disease and the role of tobacco industry funding of early research in this area. History[edit] Type A personality behavior was first described as a potential risk factor for heart disease in the 1950s by cardiologists Meyer Friedman and Ray Rosenman. After an eight-and-a-half-year-long study of healthy men between the ages of 35 and 59, Friedman and Rosenman estimated that Type A behavior doubles the risk of coronary heart disease in otherwise healthy individuals.[1] The individuals enrolled in this study were followed well beyond the original time frame of the study.
The types[edit] Type A[edit] Type B[edit] The theory describes "Type B" individuals as a contrast to those with Type A personalities. Criticism[edit] Psychology studies relevant to everyday life - PsyBlog. The Ten Most Revealing Psych Experiments. Psychology is the study of the human mind and mental processes in relation to human behaviors - human nature.

Due to its subject matter, psychology is not considered a 'hard' science, even though psychologists do experiment and publish their findings in respected journals. Some of the experiments psychologists have conducted over the years reveal things about the way we humans think and behave that we might not want to embrace, but which can at least help keep us humble. That's something. 1. 'Lord of the Flies': Social Identity Theory The Robbers Cave Experiment is a classic social psychology experiment conducted with two groups of 11-year old boys at a state park in Oklahoma, and demonstrates just how easily an exclusive group identity is adopted and how quickly the group can degenerate into prejudice and antagonism toward outsiders.
Researcher Muzafer Sherif actually conducted a series of 3 experiments. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 10 Brilliant Social Psychology Studies. Ten of the most influential social psychology experiments.
“I have been primarily interested in how and why ordinary people do unusual things, things that seem alien to their natures.Why do good people sometimes act evil? Why do smart people sometimes do dumb or irrational things?” –Philip Zimbardo Like eminent social psychologist Professor Philip Zimbardo (author of The Lucifer Effect: Understanding How Good People Turn Evil), I’m also obsessed with why we do dumb or irrational things. The answer quite often is because of other people – something social psychologists have comprehensively shown. Over the past few months I’ve been describing 10 of the most influential social psychology experiments. Each one tells a unique, insightful story relevant to all our lives, every day. 10 More Brilliant Social Psychology Studies: Why Smart People Do.
10 Practical Uses For Psychological Research in Everyday Life. People love to give each other advice.
The web is full to bursting with all types of pseudo-psychological advice about life. The problem is, how much of this is based on real scientific evidence? Well, here on PsyBlog we’ve got the scientific evidence. So here’s my top 10 list of what you can learn practically from the psychological research discussed here recently. 1.