

Trainers made from fruits and vegetables. Spotted: Many people today are concerned about the impact of the fashion industry on the environment.
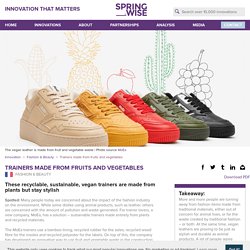
While some dislike using animal products, such as leather, others are concerned with the amount of pollution and waste generated. For trainer lovers, a new company, MoEa, has a solution – sustainable trainers made entirely from plants and recycled materials. The MoEa trainers use a bamboo lining, recycled rubber for the soles, recycled wood fibre for the insoles and recycled polyester for the labels.
Nanosensor reduces food waste by monitoring ripeness. Spotted: Semi-conducting carbon nanotubes detect the presence of ethylene, a plant growth hormone.
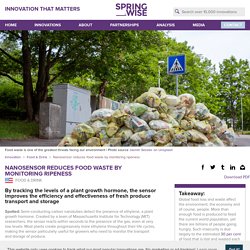
Created by a team of Massachusetts Institute for Technology (MIT) researchers, the sensor reacts within seconds to the presence of the gas, even at very low levels. Most plants create progressively more ethylene throughout their life cycles, making the sensor particularly useful for growers who need to monitor the transport and storage of produce. The nanotubes use palladium to create oxidation in the presence of ethylene, which makes the tubes conductive, and thus produces a current. The rise and fall of the current indicate levels of ethylene, providing a much more specific indication of the freshness of stored produce. The sensor is capable of detecting very low levels of ethylene, around 15 parts per billion, and when there is no gas present, the sensor remains in its resting, non-conductive state.
HOLYCRAB! – Invasive Delicatessen. Österreichs erstes Eis aus gerettetem Speiseeis. 40 food innovations you should know about. What is food innovation, and why is it important?
Food innovation is the development and commoditization of new food products, processes, and services. Right now, it’s happening rapidly.
Foresight paper. Sustainable Restaurants. Food of the Future. Supermarkets of the Future. Future Market Leaders. Algae and the circular economy. Political Instruments. Blue Planet Blue Jobs Project - by Women Fishers Society. FLIS STEEP+V and POI Horizon Scan April 2021 (Created by Intern of Sylvie at GEA) Transformative technology potentials. Impact of home office on eating habits? Wastewaterintegration (Recycle/Reuse) Small Scale Farming - Microfinance Solutions.
Agritech. Design. Organic carbon recycling. Value and supply chain tracking. Rural transformation and the future of cereal-based agri-food systems. Localized Urban Food Systems. Introduction Localized urban food systems are gaining attention from policy makers, planners, and advocates for benefits that go beyond food production and consumption to include community building, diversified economies, civic engagement, and climate resilience (Pothukuchi and Kaufman, 1999; Horst et al., 2017; Ballamingie et al., 2020).
In addition, urban consumers are a significant source of sales for much US local food system activity (Low et al., 2015). Also referred to as alternative agrifood initiatives and civic agriculture, local food systems aim to create an alternative to the existing food system by rooting food production and marketing in a particular place in a way that is economically viable, ecologically sound, and socially just (Allen et al., 2003). To account for the social, cultural, educational, and environmental impacts of localized urban food systems, a framework is needed that incorporates the multiple, integrated services that agriculture can provide.
Microbial CO2 sequestration. Bradford MA, Keiser AD, Davies CA, Mersmann CA, Strickland MS (2013) Empirical evidence that soil carbon formation from plant inputs is positively related to microbial growth.

Biogeochemistry 113:271–281CAS Article Google Scholar Chen J, Luo Y, van Groenigen KJ, Hungate BA, Cao J, Zhou X, Wang R (2018) A keystone microbial enzyme for nitrogen control of soil carbon storage. Sci Adv 4:eaaq1689CAS Article Google Scholar Chen J, Xiao W, Zheng C, Zhu B (2020) Nitrogen addition has contrasting effects on particulate and mineral-associated soil organic carbon in a subtropical forest. Soil Biol Biochem 142:107708CAS Article Google Scholar Cheng Y, Wang J, Wang J, Wang S, Chang SX, Cai Z, Zhang J, Niu S, Hu S (2020) Nitrogen deposition differentially affects soil gross nitrogen transformations in organic and mineral horizons.
First cell-cultured meat approval in singapore. Cultured meat made from animal cells without animal slaughter has been approved for sale for the first time.
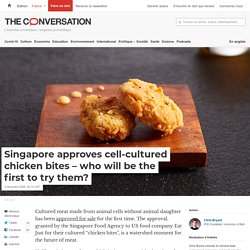
The approval, granted by the Singapore Food Agency to US food company Eat Just for their cultured “chicken bites”, is a watershed moment for the future of meat. Unlike existing products, which imitate meat with plant-based ingredients, cultured meat will provide us with a new way to make the real thing. As well as avoiding animal slaughter, cultured meat could be key to addressing public health concerns linked to meat from animals and has just a fraction of the environmental impact of conventional meat. Although not quite as green as eating plants only, cultured meat may be a way to satiate our global appetite for animal meat without all the problems animal farming entails. The technology has been in development for many years, with Nasa first experimenting with cultured meat in 2001. Full article: The future of food production – a text-mining approach. Declaration Aiming at Policy intervention for COP 26. Bundles agrifood transformation.