

The evolution of human faces in the last 6 million years. Ten Species That Are Evolving Due to the Changing Climate. New Species Of Human Ancestor Discovered In South Africa. Brace yourself: this discovery is huge.
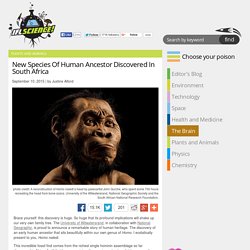
So huge that its profound implications will shake up our very own family tree. The University of Witwatersrand, in collaboration with National Geographic, is proud to announce a remarkable story of human heritage. Here's What Ariel Would Look Like If She Evolved In The Deep Ocean. Princess Ariel – the Disney princess of the water.
Living under the sea in the monarchical society of Atlantica, Ariel is the seventh-born daughter of the reigning family. Not fancying her chances of becoming queen any time soon, Ariel falls in love with the land-based Prince Eric. How Did Life On Earth Start? More than 3.6 billion years ago, a major transition was made on Earth whereby a dilute, swirling cauldron of simple chemical soup made a critical step towards creating the building blocks of life.
The simple chemicals became amino acids, the fundamental building blocks of more complicated protein molecules. These proteins then somehow came together to form a single, primitive cell. Although most scientists are in agreement on the journey that single cells took to becoming multicellular organisms like plants and animals, and recent research has started to reveal how simple chemicals became amino acids, a significant grey area remained. How precisely did the amino acids unite to become all-important proteins? Scientists from the Universiy of North Carolina think they are closer to the answer. Their answer tackles the 'RNA world' theory. The evolutionary voyage from the first single cell (lovingly called LUCA, Last Universal Common Ancestor) to humankind is a baffling and complex process.
What Extinct Animal Are You? - HowStuffWorks. Why did Neanderthals become extinct? You've probably heard the word "Neanderthal" used to insult someone, typically a person acting boorishly or one with a prominent brow ridge.
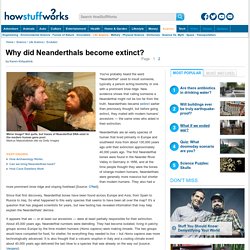
New evidence shows that calling someone a Neanderthal might not be too far from the truth. Neanderthals became extinct earlier than previously thought, but before going extinct, they mated with modern humans' ancestors — the same ones who aided in their extinction. Neanderthals are an early species of human that lived primarily in Europe and southwest Asia from about 130,000 years ago until their extinction approximately 40,000 years ago. The first Neanderthal bones were found in the Neander River Valley in Germany in 1856, and at the time people thought they were the bones of strange modern humans. Neanderthals were generally more massive but shorter than modern humans. Since that first discovery, Neanderthal bones have been found across Europe and Asia, from Spain to Russia to Iraq.
But before Neanderthals left, some mated with modern humans. Evolutionsteorin är ett fuskbygge. Denna artikel publicerades 2009, men sprids nu åter genom sociala medier.
Fem små filmer om evolution: Avsnitt 1 (5) Lots More Information - Why were so many prehistoric animals so big? The six most incredible extinctions ever. Over 99 percent of all the animal species that have ever lived have gone extinct.
When you think about the amazing diversity of life Earth - every bird, bee, spider, sponge, fish, fly, and strange golden horse - and consider that it's all just 1 percent of what's ever lived, breathed, and reproduced on the planet since its very beginnings, it's pretty mind-boggling. So where did everything go? The latest episode of AsapSCIENCE takes us through the biggest extinction events of Earth's history, starting with a cataclysmic event that occurred 440 million years ago and wiped out so many of our very distant sea-dwelling ancestors. "As newly created volcanic rock was worn down by water and wind, it reacted with carbon dioxide and absorbed it," says Mitch in the video.
"As a result, carbon dioxide levels dropped, temperatures fell, and water got locked away as ice. " The result? Watch the latest episode of AsapSCIENCE above to hear about more huge extinction events in Earth's history. How are humans different from our ancestors? If you've ever tried to construct a family tree, you understand how difficult it can be to find information about your ancestors, especially as you dig further and further back through your family history.
Imagine, then, the difficulty of piecing together a family tree that stretches back millions of years, long before Homo sapiens ever walked the planet. And yet scientists and archaeologists have learned a remarkable amount about our ancestors from fossils and geological clues unearthed since Darwin developed his theory of evolution. Half of our HIV strains came from gorillas, study reveals. This article was written by Dustin Welbourne, a Phd Candidate at UNSW Australia, and Will Grant from the Australian National Centre for the Public Awareness of Science (CPAS) at the Australian National University.
It was originally published by The Conversation. Hundreds of hours of video are uploaded to YouTube every minute, and hundreds of millions of hours are viewed daily, including many that cover areas of science. Despite this, if you want to use YouTube for science communication, reaching an audience is not always guaranteed. We’ve analysed nearly 400 science communication videos to understand what the successful YouTube science communicators do – those with numerous subscribers – that less successful communicators do not.