

Paulo Ribeiro de Lemos
"I have no special gift. I am only passionately curious." Albert Einstein 1879-1955
Technology. By the mid 20th century, humans had achieved a mastery of technology sufficient to leave the atmosphere of the Earth for the first time and explore space.
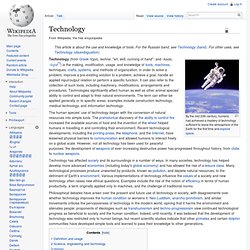
Technology (from Greek τέχνη, techne, "art, skill, cunning of hand"; and -λογία, -logia[1]) is the making, modification, usage, and knowledge of tools, machines, techniques, crafts, systems, and methods of organization, in order to solve a problem, improve a pre-existing solution to a problem, achieve a goal, handle an applied input/output relation or perform a specific function. It can also refer to the collection of such tools, including machinery, modifications, arrangements and procedures. Technologies significantly affect human as well as other animal species' ability to control and adapt to their natural environments. The term can either be applied generally or to specific areas: examples include construction technology, medical technology, and information technology. Definition and usage Science, engineering and technology History. The Bahá’í Faith.
Bahai Faith Index. Bahá'u'lláh. Bahá’í Prayers. The Bahá’í Faith - United States. Bahai Distribution Service. Bahá’í International Community - United Nations Office. Bahá’í Reference Library. One Country. Administrative Site for the Baha'is of the United States. Global Governance. Global governance or world governance is a social movement toward political integration of transnational actors aimed at solving problems that affect more than one state or region when there is no power of enforcing compliance.
The modern question of world governance exists in the context of globalization. In response to the acceleration of interdependence on a worldwide scale, both between human societies and between humankind and the biosphere, the term "world governance" may also be used to designate laws, rules, or regulations intended for a global scale. Definition[edit] In a simple and broad-based definition of world governance, the term is used to designate all regulations intended for organization and centralization of human societies on a global scale.[1] Traditionally, government has been associated with "governing," or with political authority, institutions, and, ultimately, control. Usage[edit] Context[edit]
International Monetary Fund. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. United Nations. UNICEF. World Bank Group. The World Economic Forum. Print and Broadcast Media. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Media may refer to: Communications[edit] Computing[edit] Fine art[edit] Life sciences[edit] Growth medium, objects in which microorganisms or cells can experience growthMedia filter, a filter consisting of several different filter materialsTunica media, the middle layer of the wall of a blood vesselA group of insect wing veins in the Comstock-Needham system Locations[edit] Music[edit] Phonology[edit] Traditional name of Voiced stop. The New York Times.
Chaos Theory and Complexity Theory. A double rod pendulum animation showing chaotic behavior.
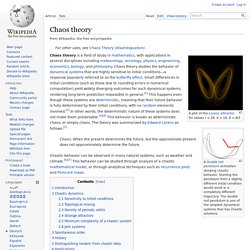
Starting the pendulum from a slightly different initial condition would result in a completely different trajectory. The double rod pendulum is one of the simplest dynamical systems that has chaotic solutions. Chaos: When the present determines the future, but the approximate present does not approximately determine the future. Chaotic behavior can be observed in many natural systems, such as weather and climate.[6][7] This behavior can be studied through analysis of a chaotic mathematical model, or through analytical techniques such as recurrence plots and Poincaré maps. Introduction[edit] Chaos theory concerns deterministic systems whose behavior can in principle be predicted. Chaotic dynamics[edit] The map defined by x → 4 x (1 – x) and y → x + y mod 1 displays sensitivity to initial conditions. In common usage, "chaos" means "a state of disorder".[9] However, in chaos theory, the term is defined more precisely.
Where. New England Complex Systems Institute. Santa Fe Institute. Los Alamos National Laboratory.