

Home. Simple mathematical pattern describes shape of neuron ‘jungle’ Neuron shape model: target points (red) distributed in a spherical volume and connected to optimize wiring in a tree (black) (credit: H.
Cuntz et al. /PNAS) University College London (UCL) neuroscientists have found that there is a simple pattern that describes the tree-like shape of all neurons. Neurons look remarkably like trees, and connect to other cells with many branches that effectively act like wires in an electrical circuit, carrying impulses that represent sensation, emotion, thought and action. Over 100 years ago, Santiago Ramon y Cajal, the father of modern neuroscience, sought to systematically describe the shapes of neurons, and was convinced that there must be a unifying principle underlying their diversity.
Cajal proposed that neurons spread out their branches so as to use as little wiring as possible to reach other cells in the network. New work by UCL neuroscientists has revisited this century-old hypothesis using modern computational methods. The First Micro-Structure Atlas Of The Human Brain Created. Brain Initiative. BRAIN Initiative. Understanding how the brain works is arguably one of the greatest scientific challenges of our time.
The BRAIN Initiative (Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies, also referred to as the Brain Activity Map Project) is a proposed collaborative research initiative announced by the Obama administration on April 2, 2013, with the goal of mapping the activity of every neuron in the human brain.[2][3][4][5][6] Based upon the Human Genome Project, the initiative has been projected to cost more than $300 million per year for ten years.[2] Announcement[edit] Experimental approaches[edit] Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies (BRAIN) NIH Home > Research & Training What is the BRAIN Initiative?
The Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies (BRAIN) Initiative is part of a new Presidential focus aimed at revolutionizing our understanding of the human brain. By accelerating the development and application of innovative technologies, researchers will be able to produce a revolutionary new dynamic picture of the brain that, for the first time, shows how individual cells and complex neural circuits interact in both time and space.
Human Brain Project - Home. The Brain Is Ready for Its Close-Up. Bluebrain. First map of the human brain reveals a simple, grid-like structure between neurons. In an astonishing new study, scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH), have imaged human and monkey brains and found… well, the image above says it all.
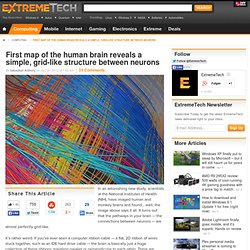
It turns out that the pathways in your brain — the connections between neurons — are almost perfectly grid-like. It’s rather weird: If you’ve ever seen a computer ribbon cable — a flat, 2D ribbon of wires stuck together, such as an IDE hard drive cable — the brain is basically just a huge collection of these ribbons, traveling parallel or perpendicular to each other. There are almost zero diagonals, nor single neurons that stray from the neuronal highways. IBM scientists create most comprehensive map of the brain’s network. "The Mandala of the Mind": The long-distance network of the Macaque monkey brain, spanning the cortex, thalamus, and basal ganglia, showing 6,602 long-distance connections between 383 brain regions.
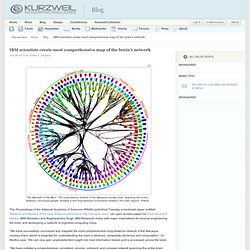
(PNAS) The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) published Tuesday a landmark paper entitled “Network architecture of the long-distance pathways in the macaque brain” (an open-access paper) by Dharmendra S. Modha (IBM Almaden) and Raghavendra Singh (IBM Research-India) with major implications for reverse-engineering the brain and developing a network of cognitive-computing chips. The Human Connectome Project. Sequencing the Connectome. Converting connectivity into a sequencing problem can be broken down conceptually into three components.
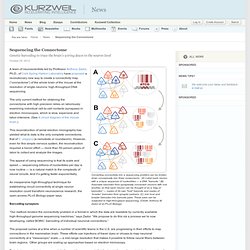
(A) Label each neuron with a unique sequence of nucleotides — a DNA “barcode.” (B) Associate barcodes from synaptically connected neurons with one another, so that each neuron can be thought of as a “bag of barcodes” — copies of its own “host” barcode and copies of “invader” barcodes from synaptic partners. (C) Join host and invader barcodes into barcode pairs. These pairs can be subjected to high-throughput sequencing. (Credit: Anthony M. Human Connectome Project. The Human Connectome Project (HCP) is a five-year project sponsored by sixteen components of the National Institutes of Health, split between two consortia of research institutions.
The project was launched in July 2009[1] as the first of three Grand Challenges of the NIH's Blueprint for Neuroscience Research.[2] On September 15, 2010, the NIH announced that it would award two grants: $30 million over five years to a consortium led by Washington University in Saint Louis and the University of Minnesota, and $8.5 million over three years to a consortium led by Harvard University, Massachusetts General Hospital and the University of California Los Angeles.[3] Sebastian Seung: I am my connectome.
A Game to Map the Brain. 70,000+ Have Played ‘Eyewire’ Game That Trains Computers To Map the Brain. Your connectome, the map of all 86 billion connected neurons in your brain, is hopelessly complex.
In fact, one human connectome has a staggering 10,000 times that number of neural pathways. Every thought you have and every memory you hold exists in your connectome, and major efforts are under way to map it. The good news is that you don’t need a fancy neuroscience degree to help out. In fact, the fancy degreed neuroscientists are hoping that you might pitch in. Created by scientists at MIT, Eyewire is a browser game that lets players take on the challenge of mapping neural pathways in brains — no scientific background required.
In an amplifying way, the team at MIT hopes that these human assisted computers will one day learn to map neurons by themselves. To date, over 70,000 gamers from over 100 countries have signed up to play Eyewire, and it’s a good thing they did. Connectomics. Connectomics is the production and study of connectomes: comprehensive maps of connections within an organism's nervous system, typically its brain or eye.
Because these structures are extremely complex, methods within this field use a high-throughput application of neural imaging and histological techniques in order to increase the speed, efficiency, and resolution of maps of the multitude of neural connections in a nervous system. While the principal focus of such a project is the brain, any neural connections could theoretically be mapped by connectomics, including, for example, neuromuscular junctions.
Tools[edit] Model Systems[edit] The Connectome — Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences. Lead investigators Hanspeter Pfister (SEAS ), Jeff Lichtman (FAS/Molecular & Cellular Biology, Center for Brain Science) and Clay Reid (HMS/Neurobiology, Center for Brain Science) Description.
Collectively reverse-engineering the brain one synapse at a time. Home - Organization for Human Brain Mapping. The Brain CONNECT Project. List of topics related to brain mapping. The following is a list of topics related to brain mapping, and major brain mapping research projects (listed below). Coverage is intended to be broad and comprehensive, and adequately cover the entire brain mapping field. Topics included are in rough proportion to their generally accepted overall importance to the human brain structure and function.
It is not intended to be recursively exhaustive in every possible direction but to give an overview of what areas of knowledge may be impacted by the large new brain mapping research initiatives. While the emphasis here is on physical brain structure, functional aspects are also included. Mind concepts (as in mind vs. body), and cognitive and behavioral aspects, are introduced where they have at least a fairly direct connection to physical aspects of the brain, neurons, spinal cord, nerve networks, neurotransmitters, etc. Topics are roughly clustered as shown in the table of contents. Broad Scope[edit] Genetic Atlas Of The Brain Created. Brain Mapping Foundation - Home Page. Allen Brain Atlas - Welcome.
Brainmapping.ORG. List of animals by number of neurons.