

DESCRIPTION LOGICS course. Warning: the course material has been recently completely revised.

The bibliography and the reference material have been updated; most slides were rewritten. Slides of modules 5 and 6 are still to be revised. (March 2002) Find Similar or Opposite words at WordHippo. Christian Calculus. Linguistic description. All scholarly research in linguistics is descriptive; like all other sciences, its aim is to observe the linguistic world as it is, without the bias of preconceived ideas about how it ought to be.[1] Modern descriptive linguistics is based on a structural approach to language, as exemplified in the work of Leonard Bloomfield and others.
[not verified in body] Linguistic description is often contrasted with linguistic prescription, which is found especially in education and in publishing. Prescription seeks to define standard language forms and give advice on effective language use, and can be thought of as a presentation of the fruits of descriptive research in a learnable form, though it also draws on more subjective aspects of language aesthetics. Classification scheme. In metadata a classification scheme is an arrangement of kinds of things (classes) or groups of kinds of things.
It is often represented as a hierarchical structure and accompanied by descriptive information of the classes or groups. A classification scheme is intended to be used for an arrangement or division of individual objects into the classes or groups. The classes or groups are based on characteristics which the objects (members) have in common. In linguistics, the subordinate concept is called a hyponym of its superordinate. Typically a hyponym is 'a kind of' its superordinate (Keith Allan, Natural language Semantics[1]). The ISO/IEC 11179 metadata registry standard uses classification schemes as a way to classify administered items, such as data elements, in a metadata registry. Some quality criteria for classification schemes are: Whether different kinds are grouped together.
Quadrivio. Da Wikipedia, l'enciclopedia libera.
Il quadrivio o quadrivium (letterelmente "quattro vie"), in epoca medievale, indicava, assieme al trivio la formazione scolastica delle Arti liberali, propedeutica all'insegnamento della teologia e della filosofia. Esso comprendeva quattro discipline attribuite alla sfera matematica: Trivium. In medieval universities, the trivium comprised the three subjects that were taught first: grammar, logic and rhetoric.
The word is a Latin term meaning "the three ways" or "the three roads" forming the foundation of a medieval liberal arts education. This study was preparatory for the quadrivium, which consists of geometry, arithmetic, astronomy, and music. Combining the trivium and quadrivium results in the seven liberal arts of classical study. The trivium is implicit in the De nuptiis of Martianus Capella, although the term was not used until the Carolingian era when it was coined in imitation of the earlier quadrivium.[1] It was later systematized in part by Petrus Ramus as an essential part of Ramism. Untitled Prezi by Felipe Silveira on Prezi.
Arti liberali. Da Wikipedia, l'enciclopedia libera.
Arti liberali era l'espressione con la quale, durante il Medioevo, s'intendeva il curriculum di studi seguito dai chierici prima di accedere agli studi universitari. Più in generale le arti liberali erano quelle attività dov'era necessario un lavoro prettamente intellettuale, a fronte delle "arti meccaniche" che richiedevano lo sforzo fisico. The Academic Family Tree. Four Arts. Origin of the concept[edit] Although the individual elements of the concept have very long histories as activities befitting a learned person, the earliest written source putting the four together is Zhang Yanyuan's Fashu Yaolu from the Tang Dynasty.
Qín[edit] The Guqin Qín 琴 is the musical instrument of the literati, the gǔqín. Although it exclusively meant this instrument in ancient times, it has now come to mean all musical instruments, but essentially it refers to gǔqín only considering the context. Set theory. The modern study of set theory was initiated by Georg Cantor and Richard Dedekind in the 1870s.
Quadrivium. The quadrivium consisted of arithmetic, geometry, music, and astronomy. These followed the preparatory work of the trivium made up of grammar, logic, and rhetoric. In turn, the quadrivium was considered preparatory work for the serious study of philosophy (sometimes called the "liberal art par excellence")[citation needed] and theology. The word "trivia" has been rarely used to refer to the trivium.[1] Origins[edit] List of mnemonics. This article contains lists of some common mnemonics.
Art[edit] To remember the Elements of Art: Space, Form, Texture, Shape, Line, Value, Color. Spaceships Fly Through Space Looking Very CoolThe Fat Cat Sings Songs Very Loudly Astronomy[edit] My Very Easy Memory Jingle Seems Useful Naming Planets My Very Educated Mother Just Served Us Nachos Many Very Educated Men Justify Stealing Unique Ninth. Concepts are Containers. You are here:Index Conceptual Science Imagine you had four identical carrier bags.
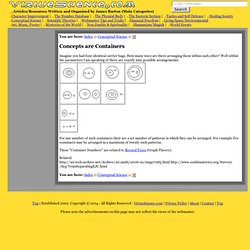
How many ways are there arranging them within each other? Well within the parameters I am speaking of there are exactly nine possible arrangements: Glossary of category theory. This is a glossary of properties and concepts in category theory in mathematics. Categories[edit] Morphisms[edit] Natural transformation. Definition[edit] If F and G are functors between the categories C and D, then a natural transformation η from F to G is a family of morphisms that satisfy two requirements. The natural transformation must associate to every object X in C a morphism ηX : F(X) → G(X) between objects of D.
The morphism ηX is called the component of η at X.Components must be such that for every morphism f : X → Y in C we have: The last equation can conveniently be expressed by the commutative diagram. Category theory. A category with objects X, Y, Z and morphisms f, g, g ∘ f, and three identity morphisms (not shown) 1X, 1Y and 1Z. Several terms used in category theory, including the term "morphism", differ from their uses within mathematics itself. In category theory, a "morphism" obeys a set of conditions specific to category theory itself. Thus, care must be taken to understand the context in which statements are made.
Category. Journal of Logic and Analysis. Categorization - definition of categorization by The Free Dictionary. Compartmentalisation - definition of compartmentalisation by The Free Dictionary. Zeno's paradoxes. Zeno's arguments are perhaps the first examples of a method of proof called reductio ad absurdum also known as proof by contradiction.
They are also credited as a source of the dialectic method used by Socrates.[3] Some mathematicians and historians, such as Carl Boyer, hold that Zeno's paradoxes are simply mathematical problems, for which modern calculus provides a mathematical solution.[4] Some philosophers, however, say that Zeno's paradoxes and their variations (see Thomson's lamp) remain relevant metaphysical problems.[5][6][7]
Paradossi di Zenone. Da Wikipedia, l'enciclopedia libera. Le argomentazioni di Zenone costituiscono forse i primi esempi del metodo di dimostrazione noto come reductio ad absurdum o dimostrazione per assurdo. Sono anche considerate un primo esempio del metodo dialettico, usato in seguito dai sofisti e da Socrate ed inoltre furono il primo strumento che mise in difficoltà l'ambizione dei pitagorici di ridurre tutta la realtà in numeri. Oggi non si attribuisce valore fisico alle argomentazioni di Zenone, ma la loro influenza è stata molto importante nella storia del pensiero filosofico e matematico.
I paradossi di Zenone restano anche un utile esercizio di logica, per riflettere sulla modalità di costruzione dei ragionamenti umani.