

Dinosaur directory: Coelophysis (lizard-hipped) Ginkgo Fossils. Plant Fossils. Green River Formation. Localities of the Eocene: One of the most important fossil sites for understanding the Eocene is found at Green River, located in western Colorado, eastern Utah and southwestern Wyoming in the United States.

During the Eocene, this region was located at much the same latitude it is today, though global climate was more equable. Sycamore Plant Fossil Leaf. Platanus2. Fossil Record of the Chromista. Manual of Geology by James Dana, 4th Ed. Table of Contents 006 006 007 Abbreviations 008 008.

PDF/Fossils1.pdf. Fossil 1.0. The Virtual Petrified Wood Museum. Gateway to the Paleobiology Database. Welcome to ZipcodeZoo. Fossils Geological Time and Evolution. Fauna. Simplified schematic of an island's fauna - all its animal species, highlighted in boxes.
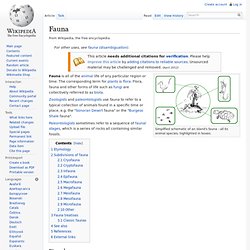
Zoologists and paleontologists use fauna to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the "Sonoran Desert fauna" or the "Burgess Shale fauna". Paleontologists sometimes refer to a sequence of faunal stages, which is a series of rocks all containing similar fossils. Etymology[edit] Subdivisions of fauna[edit] Cryofauna[edit] Cryofauna are animals that live in, or very close to, ice.
Cryptofauna[edit] Cryptofauna are animals that are rarely seen and may be extinct or mythological. Infauna[edit] Introduction to Trilobites. This is NOT the HOME PAGE of this site.
Please click here to go to the true start page. Last revised 15 May 2014 Trilobites are remarkable, hard-shelled, segmented creatures that existed over 520 million years ago in the Earth's ancient seas. Biological classification. The hierarchy of biological classification's eight major taxonomic ranks.
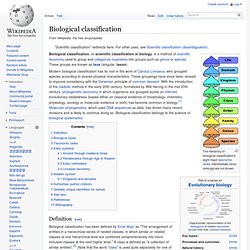
Intermediate minor rankings are not shown. Modern biological classification has its root in the work of Carolus Linnaeus, who grouped species according to shared physical characteristics. These groupings have since been revised to improve consistency with the Darwinian principle of common descent. With the introduction of the cladistic method in the early 20th century, formalized by Willi Hennig in the mid-20th century, phylogenetic taxonomy in which organisms are grouped purely on inferred evolutionary relatedness (based either on classical evidence of morphology, chemistry, physiology, ecology or molecular evidence or both) has become common in biology.[1] Molecular phylogenetics, which uses DNA sequences as data, has driven many recent revisions and is likely to continue doing so.
Cincinnati Dry Dredgers. A Guide to the Orders of Trilobites. Paleontology Home Page. Paleontology. Index fossil. Fossilization, How Do Fossils Form. The term “fossil” is used for any trace of past life.

Fossils are not only the actual remains of organisms, such as teeth, bones, shell, and leaves (body fossils), but also the results of their activity, such as burrows and foot prints (trace fossils), and organic compounds they produce by biochemical processes (chemical fossils). Occasionally, inorganically produced structures may be confused with traces of life, such as dendrites. These are called pseudofossils. The definitions below explain the types of fossils found in the context of fossilization processes. You will find there is some overlaps in the terminology commonly used in paleontology and geology. Paleontology and Geology Glossary. LabExercise08.pdf. Taxonomy.
The micropalaeontologist is concerned with the abandoned, dead shells of foraminifera and classification of fossils species proceeds entirely on the basis of the morphology of the hard shell (test).

In the case of all ‘Larger’ foraminifera, this involves detailed study of the internal chamber arrangement, especially of the initial chambers and is accomplished by splitting, or by making wafer-thin sections of specimens (see fig.3). More commonly, the host rock itself is thin-sectioned to reveal the fossils therein. Morphology Large, flattened disc with complex internal structure. Diagnostic description. Redmond High School Science Club. 2015 Test Exchange - Science Olympiad Student Center Wiki. Science Olympiad Fossils. The Devonian Period: The Age of Fish. Fossils Facts, information, pictures.
Fossil Picture Gallery. BIVALVE Fossils – Fossil Pictures and Information. Bivalves are two-shelled mollusks such as mussels and oysters.
There is no difference between bivalves that lived millions of years ago and those of today? A situation that denies the gradual evolution suggested by Darwinists. Fossil No: SY0336. Facts about Fossils - Fossil information and resources. Fossil Images Pictures of Fossils. The limestones. Fossils Crinoids Crinoids, also known as sea lilies or feather stars can still be found in the oceans today, however were much more abundant in the geological past.

When alive crinoids are essentially characterised by having a mouth at the top of a long stem, which is surround by five feeding arms. FossilGuy.com: The Fossil Hunting Guide - Where to find Fossils, Information About Fossils, Identification, Information, Examples, and Locations! The Virtual Petrified Wood Museum. UCMP Web Lift to Taxa. Fossils - Science is a Blast. Gateway to the Paleobiology Database. Palaeos: Life Through Deep Time. Fossil 1.0. The Virtual Petrified Wood Museum. Gateway to the Paleobiology Database. Welcome to ZipcodeZoo. Fossils Geological Time and Evolution. Fauna. Introduction to Trilobites. Biological classification. Cincinnati Dry Dredgers. A Guide to the Orders of Trilobites. Paleontology Home Page. Index fossil. Fossilization, How Do Fossils Form. Paleontology and Geology Glossary. Fossils - Science Olympiad Student Center Wiki. Fossils is an event identification event which rotates with Rocks and Minerals every three years.
It includes identifying various fossilized animals and plants, providing details about these creatures such as the environment it lived in, its mode of life, how it formed, etc., and answering questions on general paleontology. This article will cover the basic information required for this event as well as give tips on how to succeed at the competition.
There is always a Fossil List you need to be able to identify and know information about. Fossil Formation There are several ways that fossils can form, ranging from the organism being replaced by minerals to the organism getting trapped in amber. Mummification Preserves life form with some tissue or skin intact. External Molds Imprints of the organism embedded in rocks. Casts These are formed when external molds are filled with sediment. Internal molds Petrification/Petrifaction/Silicification Carbonization/Coalification Recrystallization Tar a=age. Fossil List - Science Olympiad Student Center Wiki. The rest of the page contains information about all of the specimens you need to know for the event Fossils. Protists Of all the groups that you are responsible for knowing for this event, protists are the most under-represented.
There are only two groups you need to know- the phylum Foraminifera and the class Bacillariophyta. You also need to know the Fusulinid family and the genus Nummulites. Fossils.gif (675×533) The Paleontology Portal: Home. Www.azmnh.org/pdf/Dinosaur.pdf. Gateway to the Paleobiology Database. Welcome to Fossilworks Fossilworks provides query, download, and analysis tools that utilize the Paleobiology Database's large relational database assembled by hundreds of paleontologists from around the world.
The two websites and their predecessors have been used by professional researchers, students, and the public since 1998. The Paleobiology Database. Palaeos: Life Through Deep Time.