

Human science. Psychology. Psychology is an academic and applied discipline that involves the scientific study of mental functions and behaviors.[1][2] Psychology has the immediate goal of understanding individuals and groups by both establishing general principles and researching specific cases,[3][4] and by many accounts it ultimately aims to benefit society.[5][6] In this field, a professional practitioner or researcher is called a psychologist and can be classified as a social, behavioral, or cognitive scientist.
Psychologists attempt to understand the role of mental functions in individual and social behavior, while also exploring the physiological and biological processes that underlie cognitive functions and behaviors. While psychological knowledge is often applied to the assessment and treatment of mental health problems, it is also directed towards understanding and solving problems in many different spheres of human activity.
Etymology History Structuralism Functionalism Psychoanalysis Behaviorism Humanistic. Economics. For a topical guide to this subject, see Outline of economics.
Economics is the social science that studies the behavior of individuals, households, and organizations (called economic actors, players, or agents), when they manage or use scarce resources, which have alternative uses, to achieve desired ends. Agents are assumed to act rationally, have multiple desirable ends in sight, limited resources to obtain these ends, a set of stable preferences, a definite overall guiding objective, and the capability of making a choice.
There exists an economic problem, subject to study by economic science, when a decision (choice) has to be made by one or more resource-controlling players to attain the best possible outcome under bounded rational conditions. In other words, resource-controlling agents must maximize value subject to the constraints imposed by the information the agents have, their cognitive limitations, and the finite amount of time they have to make and execute a decision. J. Geography. Geography (from Greek γεωγραφία, geographia, lit.
"earth description"[1]) is a field of science dedicated to the study of the lands, the features, the inhabitants, and the phenomena of the Earth.[2] A literal translation would be "to describe or write about the Earth". The first person to use the word "geography" was Eratosthenes (276–194 BC).[3] Four historical traditions in geographical research are spatial analysis of the natural and the human phenomena (geography as the study of distribution), area studies (places and regions), study of the man-land relationship, and research in the Earth sciences.[4] Nonetheless, modern geography is an all-encompassing discipline that foremost seeks to understand the Earth and all of its human and natural complexities - not merely where objects are, but how they have changed and come to be.
Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and the physical science". Introduction Branches Physical geography Geomatics. Linguistics. In the early 20th century Ferdinand de Saussure distinguished between the notions of langue and parole in his formulation of structural linguistics.
According to him, parole is the specific utterance of speech, whereas langue refers to an abstract phenomenon that theoretically defines the principles and system of rules that govern a language.[9] This distinction resembles the one made by Noam Chomsky between competence and performance, where competence is individual's ideal knowledge of a language, while performance is the specific way in which it is used.[10] In classical Indian philosophy of language, the Sanskrit philosophers like Patanjali and Katyayana had distinguished between sphota (light) and dhvani (sound). In the late 20th century, French philosopher Jacques Derrida distinguished between the notions of speech and writing.[11] Nomenclature[edit] Variation and Universality[edit] Lexicon[edit] The lexicon is a catalogue of words and terms that are stored in a speaker's mind. Anthropology. Anthropology /ænθrɵˈpɒlədʒi/ is the study of humankind, past and present,[1][2] that draws and builds upon knowledge from social and biological sciences, as well as the humanities and the natural sciences.[3][4] Since the work of Franz Boas and Bronisław Malinowski in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, anthropology in Great Britain and the US has been distinguished from ethnology[5] and from other social sciences by its emphasis on cross-cultural comparisons, long-term in-depth examination of context, and the importance it places on participant-observation or experiential immersion in the area of research.
In those European countries that did not have overseas colonies, where ethnology (a term coined and defined by Adam F. Origin of the term[edit] The term anthropology originates from the Greek anthrōpos (ἄνθρωπος), "human being" (understood to mean humankind or humanity), and -λογία -logia, "study. " Fields[edit] According to Clifford Geertz, Sociocultural[edit] Biological[edit] List of academic disciplines. An academic discipline or field of study is a branch of knowledge that is taught and researched as part of higher education.
A discipline usually has several sub-disciplines or branches, but the distinguishing lines between these are often both arbitrary and ambiguous.[1] Overlap leading to a complex networks rather than a simple heirarchies. (e.g. medicine - not currently listed here - takes from selections of health science and life sciences) Overview[edit] In the early 20th century, new disciplines such as education and psychology were added. Science. Science (from Latin scientia, meaning "knowledge"[1]) is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.[2][3] In an older and closely related meaning, "science" also refers to a body of knowledge itself, of the type that can be rationally explained and reliably applied.
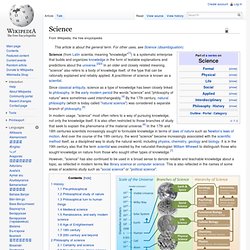
A practitioner of science is known as a scientist. Since classical antiquity, science as a type of knowledge has been closely linked to philosophy. Philosophy. Philosophy is the study of general and fundamental problems, such as those connected with reality, existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language.[1][2] Philosophy is distinguished from other ways of addressing such problems by its critical, generally systematic approach and its reliance on rational argument.[3] In more casual speech, by extension, "philosophy" can refer to "the most basic beliefs, concepts, and attitudes of an individual or group".[4] The word "philosophy" comes from the Ancient Greek φιλοσοφία (philosophia), which literally means "love of wisdom".[5][6][7] The introduction of the terms "philosopher" and "philosophy" has been ascribed to the Greek thinker Pythagoras.[8] Areas of inquiry Philosophy is divided into many sub-fields.

Political science. Sociology.