

How Massage Uses Your Own Body to Reduce Pain and Heal Injuries. As WLP’s massage therapist, I help people feel better and recover faster, and all they have to do is lie down and let me get to work.
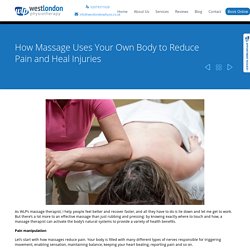
But there’s a lot more to an effective massage than just rubbing and pressing: by knowing exactly where to touch and how, a massage therapist can activate the body’s natural systems to provide a variety of health benefits. Pain manipulation Let’s start with how massages reduce pain. Your body is filled with many different types of nerves responsible for triggering movement, enabling sensation, maintaining balance, keeping your heart beating, reporting pain and so on. One of the many ways that massage can help your body is by interrupting or overwhelming the nerves that report pain in injured tissue, called nociceptors. On top of the neurological effects, massage – like exercise – also releases endorphins which act as a natural analgesic. Restoring movement Improving circulation Maggie Perez Claiden.
Effect of Mechanical Stretch on the DNCB-induced Proinflammatory Cytokine Secretion in Human Keratinocytes. Secretion of proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 by HaCaTs in response to DNCB This study investigated the effects of each or both chemical stimulants and mechanical stretch on the production of proinflammatory cytokines in HaCaTs.

The stretchable chip for cell culture was designed to control the chemical and mechanical environments of cells in vitro (Figs 1a and S1a). As shown in Fig. 1b, HaCaTs were seeded in the stretchable chip and the cells were incubated with a chemical stimulant and/or stretched cyclically. Clinical anxiety, cortisol and interleukin-6: Evidence for specificity in emotion–biology relationships. A Compound in Chamomile May Benefit Brain Cells - MPR. Apigenin, a flavonoid found in some spices and herbs, may improve neuron formation and strengthen connections between brain cells, researchers from D’Or Institute for Research and Education reported.
Findings from the study were published in Advances in Regenerative Biology. Apigenin is found in parsley, thyme, chamomile, and red pepper. This is the first research to show the positive effects of apigenin directly on human cells and the first to explain its mechanism.
Body Fluids and Fluid Compartments. Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to:

Breathing to younger skin: ‘reversing the molecular mechanism of skin aging with yoga’ Extracellular Matrix. Cells. Biochemistry. Muscles and Bones. Endocrine system. Lympathic system. Immune system. Brain. Biomagnetic fields. DNA. How Our Sense of Touch is a Lot Like the Way We Hear – Science Life. When you walk into a darkened room, your first instinct is to feel around for a light switch.

You slide your hand along the wall, feeling the transition from the doorframe to the painted drywall, and then up and down until you find the metal or plastic plate of the switch. During the process you use your sense of touch to develop an image in your mind of the wall’s surface and make a better guess for where the switch is. Sliman Bensmaia, PhD, assistant professor of organismal biology and anatomy at the University of Chicago, studies the neural basis of tactile perception, or how our hands convey this information to the brain.
In a new study published in the Journal of Neuroscience, he and his colleagues found that the timing and frequency of vibrations produced in the skin when you run your hands along a surface, like searching a wall for a light switch, play an important role in how we use our sense of touch to gather information about the objects and surfaces around us. Like this: 7 Weird Ways Your Body Can Heal Itself. The 4 Most Euphoric Nootropics (No Prescription Drugs) - Brain Health. The point of nootropics is to take your brain into a spot to perform at its best. Some of them have an extra benefit of eliciting feelings of euphoria. If you are looking for euphoria that is on par with taking MDMA at a rave, then this isn’t the article for you. What this article covers is nootropics that elicit euphoria but also increase brain function. Also, you can either get them in the store or online legally.
With that said, this post will talk about the science behind euphoria and also spotlight four nootropics with euphoric effects. The Science Behind Euphoria Euphoria is a state of pleasure in which you experience feelings of well-being, happiness, and excitement. The euphoria is caused by chemical reactions in the brain. For instance, continuous aerobic exercise such as running releases dopamine within the nucleus accumbens. Essentiallly, any nootropic we want to take to elicit euphoria needs to interact with dopamine in some way, shape, or form. PEA (Phenethylamine) Sulbutiamine.