

Create Pin. Institut d'Estudis Catalans - Diec2. Real Academia Española. Create Pin. Create Pin. Prezi - Ideas matter. Idescat. Institut d'Estadística de Catalunya. Pàgina principal. Create Pin. The Literary Gift Company: Gifts for Book Lovers, Readers and Writers. Free delivery worldwide on all books from The Book Depository. The Literary Gift Company: Gifts for Book Lovers, Readers and Writers.
Post a Tweet. Scrabble Word Lists. Answers - The Most Trusted Place for Answering Life's Questions. Wikipedia. Technological Singularity. The technological singularity is the hypothesis that accelerating progress in technologies will cause a runaway effect wherein artificial intelligence will exceed human intellectual capacity and control, thus radically changing civilization in an event called the singularity.[1] Because the capabilities of such an intelligence may be impossible for a human to comprehend, the technological singularity is an occurrence beyond which events may become unpredictable, unfavorable, or even unfathomable.[2] The first use of the term "singularity" in this context was by mathematician John von Neumann.
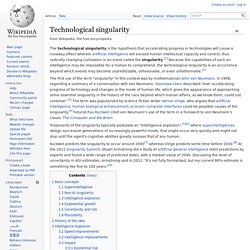
Proponents of the singularity typically postulate an "intelligence explosion",[5][6] where superintelligences design successive generations of increasingly powerful minds, that might occur very quickly and might not stop until the agent's cognitive abilities greatly surpass that of any human. Basic concepts Superintelligence Non-AI singularity. Infographic - The Emergence of Collective Intelligence. Institute for Ethics and Emerging Technologies.
Moore's law. Moore's law is the observation that, over the history of computing hardware, the number of transistors on integrated circuits doubles approximately every two years.
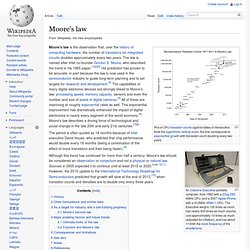
The law is named after Intel co-founder Gordon E. Moore, who described the trend in his 1965 paper.[1][2][3] His prediction has proven to be accurate, in part because the law is now used in the semiconductor industry to guide long-term planning and to set targets for research and development.[4] The capabilities of many digital electronic devices are strongly linked to Moore's law: processing speed, memory capacity, sensors and even the number and size of pixels in digital cameras.[5] All of these are improving at roughly exponential rates as well.
Book scanning. Must read books lists. Free books.