

Joseph Mede. Joseph Mede[1] (1586 in Berden – 1639) was an English scholar with a wide range of interests.
He was educated at Christ's College, Cambridge, where he became a Fellow from 1613.[2] He is now remembered as a biblical scholar.[3] He was also a naturalist and Egyptologist. He was a Hebraist, and became Lecturer of Greek.[4] Joseph Mede. Welcome. Welcome. Rosicrucian Texts. Sacred-texts Esoteric Sub RosaBuy CD-ROM These texts are historical documents relating to the 'Brotherhood of the Rosy Cross', a renaissance German secret society.
This group had a huge impact on more recent organizations such as the Golden Dawn, and is often cited by conspiracy theorists for completely different reasons. Pythagoras. 6th century BC Ionian Greek philosopher and mystic Pythagoras of Samos[a] (c. 570 – c. 495 BC)[b] was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism.
His political and religious teachings were well known in Magna Graecia and influenced the philosophies of Plato, Aristotle, and, through them, Western philosophy. Knowledge of his life is clouded by legend, but he appears to have been the son of Mnesarchus, a gem-engraver on the island of Samos. Pythagoras. Aristarchus of Samos. Ancient Greek astronomer Aristarchus of Samos (; Greek: Ἀρίσταρχος ὁ Σάμιος, Aristarkhos ho Samios; c. 310 – c. 230 BC) was an ancient Greek astronomer and mathematician who presented the first known heliocentric model that placed the Sun at the center of the known universe, with the Earth revolving around the Sun once a year and rotating about its axis once a day.
He was influenced by Philolaus of Croton, but Aristarchus identified the "central fire" with the Sun, and he put the other planets in their correct order of distance around the Sun.[2] Like Anaxagoras before him, he suspected that the stars were just other bodies like the Sun, albeit farther away from Earth. Book of Ezekiel. The Book of Ezekiel is the third of the Latter Prophets in the Tanakh and one of the major prophetic books in the Old Testament, following Isaiah and Jeremiah.
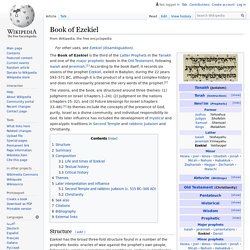
According to the book itself, it records six visions of the prophet Ezekiel, exiled in Babylon, during the 22 years 593–571 BC, although it is the product of a long and complex history and does not necessarily preserve the very words of the prophet. The visions, and the book, are structured around three themes: (1) Judgment on Israel (chapters 1–24); (2) Judgment on the nations (chapters 25–32); and (3) Future blessings for Israel (chapters 33–48).
Its themes include the concepts of the presence of God, purity, Israel as a divine community, and individual responsibility to God. Solomon's Temple. Legendary temple described in the Hebrew Bible Because of the religious sensitivities involved, and the politically volatile situation in Jerusalem, only limited archaeological surveys of the Temple Mount have been conducted.
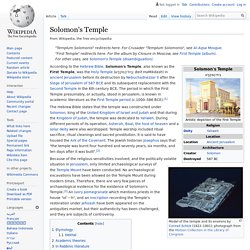
No archaeological excavations have been allowed on the Temple Mount during modern times. Therefore, there are very few pieces of archaeological evidence for the existence of Solomon's Temple.[3] An ivory pomegranate which mentions priests in the house "of ---h", and an inscription recording the Temple's restoration under Jehoash have both appeared on the antiquities market, but their authenticity has been challenged, and they are subjects of controversy. Juan Bautista Villalpando, S.J. This site has been archived for historical purposes.

These pages are no longer being updated. East elevation of Solomon's templeJuan Bautista Villalpando, S.J. was born in Cordova and died in Rome. He studied geometry and architecture under Juan de Herrera, the royal architect of the Spanish king Philip II. Juan Bautista Villalpando, S.J.