

Organic certification. The National Organic Program (run by the USDA) is in charge of the legal definition of organic in the United States and also performs organic certification.
Organic vegetables at a farmers' market in Argentina. Insurance. According to study texts of The Chartered Insurance Institute, there are the following categories of risk:[1] Financial risks which means that the risk must have financial measurement.Pure risks which means that the risk must be real and not related to gamblingParticular risks which means that these risks are not widespread in their effect, for example such as earthquake risk for the region prone to it.
It is commonly accepted that only financial, pure and particular risks are insurable. An insurer, or insurance carrier, is a company selling the insurance; the insured, or policyholder, is the person or entity buying the insurance policy. The amount of money to be charged for a certain amount of insurance coverage is called the premium. Risk management, the practice of appraising and controlling risk, has evolved as a discrete field of study and practice.
History[edit] Early methods[edit] Merchants have sought methods to minimize risks since early times. Bank. A bank is a financial institution and a financial intermediary that accepts deposits and channels those deposits into lending activities, either directly by loaning or indirectly through capital markets.
A bank links together customers that have capital deficits and customers with capital surpluses. Medicine. Medicine (also called conventional, orthodox, scientific, or mainstream medicine, especially in connection with alternative medicine, UK English i/ˈmɛdsɨn/, US English The word medicine is derived from the Latin ars medicina, meaning the art of healing.[3][4] Clinical practice[edit]
Luxury. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Luxury may refer to:
World Wide Web. The World Wide Web (abbreviated as WWW or W3,[3] commonly known as the web) is a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet.
With a web browser, one can view web pages that may contain text, images, videos, and other multimedia and navigate between them via hyperlinks. History[edit] In the May 1970 issue of Popular Science magazine, Arthur C. Clarke predicted that satellites would someday "bring the accumulated knowledge of the world to your fingertips" using a console that would combine the functionality of the photocopier, telephone, television and a small computer, allowing data transfer and video conferencing around the globe.[10] On March 12, 1989, Tim Berners-Lee wrote a proposal that referenced ENQUIRE, a database and software project he had built in 1980, and described a more elaborate information management system.[11] The CERN datacenter in 2010 housing some WWW servers Berners-Lee's breakthrough was to marry hypertext to the Internet.
Function[edit] Media. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Media may refer to: Energy. All of the many forms of energy are convertible to other kinds of energy, and obey the conservation of energy.
Common energy forms include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the radiant energy carried by light, the potential energy stored by an object's position in a force field,(gravitational, electric or magnetic) elastic energy stored by stretching solid objects, chemical energy released when a fuel burns, and the thermal energy due to an object's temperature.
According to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass when stationary,(called rest mass) also has an equivalent amount of energy whose form is called rest energy. Solar energy. Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the sun harnessed using a range of ever-evolving technologies such as solar heating, solar photovoltaics, solar thermal energy, solar architecture and artificial photosynthesis.[1][2] In 2011, the International Energy Agency said that "the development of affordable, inexhaustible and clean solar energy technologies will have huge longer-term benefits.
It will increase countries’ energy security through reliance on an indigenous, inexhaustible and mostly import-independent resource, enhance sustainability, reduce pollution, lower the costs of mitigating global warming, and keep fossil fuel prices lower than otherwise. These advantages are global. Hence the additional costs of the incentives for early deployment should be considered learning investments; they must be wisely spent and need to be widely shared".[1] Energy from the Sun About half the incoming solar energy reaches the Earth's surface. Early commercial adaption Solar thermal Water heating.
SPWR quote - Yahoo Finance Search Results. Wind power. Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into a useful form of energy, such as using wind turbines to make electrical power, windmills for mechanical power, windpumps for water pumping or drainage, or sails to propel ships.
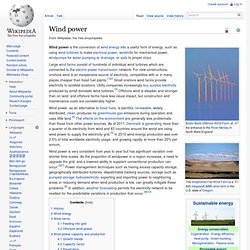
Large wind farms consist of hundreds of individual wind turbines which are connected to the electric power transmission network. For new constructions, onshore wind is an inexpensive source of electricity, competitive with or in many places cheaper than fossil fuel plants.[1][2] Small onshore wind farms provide electricity to isolated locations. Utility companies increasingly buy surplus electricity produced by small domestic wind turbines.[3] Offshore wind is steadier and stronger than on land, and offshore farms have less visual impact, but construction and maintenance costs are considerably higher. Wind power is very consistent from year to year but has significant variation over shorter time scales.
History. GE: Summary for General Electric Company Common. General Electric Company (GE) Quotes delayed, except where indicated otherwise.
Currency in USD. Featured on Yahoo Finance The broker you select will become the default broker for Trade Now Key Statistics Analysts Business Summary General Electric Company operates as an infrastructure and financial services company worldwide. Hydroelectricity. Hydroelectricity is the term referring to electricity generated by hydropower; the production of electrical power through the use of the gravitational force of falling or flowing water. It is the most widely used form of renewable energy, accounting for 16 percent of global electricity generation – 3,427 terawatt-hours of electricity production in 2010,[1] and is expected to increase about 3.1% each year for the next 25 years. Hydropower is produced in 150 countries, with the Asia-Pacific region generating 32 percent of global hydropower in 2010.
Food. Historically, people secured food through two methods: hunting and gathering, and agriculture. Today, most of the food energy required by the ever increasing population of the world is supplied by the food industry. ANIMAL. Animal source foods (ASF) include many food item that comes from an animal source such as meat, milk, fish, eggs, cheese and yogurt. Many individuals do not consume ASF or consume little ASF by either personal choice or necessity as ASF may not be accessible or available to these people.[1] Nutrition of animal source foods[edit] Aside from performed vitamin A, vitamin B12 and vitamin D, all vitamins found in animal source foods may also be found in plant-derived foods. Examples are tofu to replace meat (both contain protein in sufficient amounts), and certain seaweeds and vegetables as respectively kombu and kale to replace dairy foods as milk (both contain calcium in sufficient amounts).
There are some nutrients which are rare to find in sufficient density in plant based foods. Most humans eat an omnivorous diet (comprising animal source foods and plant source foods) though some civilisations have eaten only animal foods. PLANTS. Various foods Foods from plant sources.