

How to Search on Google: 31 Google Advanced Search Tips. If you’re like me, you probably use Google many times a day.
But chances are, unless you're a technology geek, you probably still use Google in its simplest form. If your current use of Google is limited to typing in a few words and changing your query until you find what you’re looking for, I’m here to tell you that there’s a better way -- and it’s not hard to learn. On the other hand, even if you are a technology geek and can use Google like the best of them already, I still suggest you bookmark this article of Google advanced search tips. Then, you’ll then have the tips on hand when you're ready to pull your hair out in frustration watching a neophyte repeatedly type in basic queries in a desperate attempt to find something. → Download Now: SEO Starter Pack [Free Kit] The following Google advanced search tips are based on my own experience and things that I actually find useful.
Here's an overview of some of the most useful Google search tricks. 1. Example Search: "inbound marketing" Biology Index. Atlas of Living Australia « sharing biodiversity knowledge. Difen Biology. Replication vs Transcription. Cell division is essential for an organism to grow, but when a cell divides it must replicate the DNA in its genome so that the two daughter cells have the same genetic information as their parent.
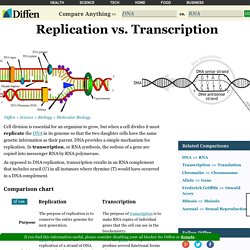
DNA provides a simple mechanism for replication. In transcription, or RNA synthesis, the codons of a gene are copied into messenger RNA by RNA polymerase. As opposed to DNA replication, transcription results in an RNA complement that includes uracil (U) in all instances where thymine (T) would have occurred in a DNA complement. Share this comparison: DNA vs RNA. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is like a blueprint of biological guidelines that a living organism must follow to exist and remain functional.
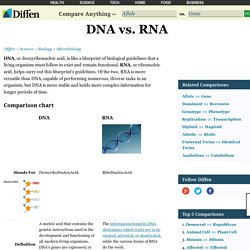
RNA, or ribonucleic acid, helps carry out this blueprint's guidelines. Of the two, RNA is more versatile than DNA, capable of performing numerous, diverse tasks in an organism, but DNA is more stable and holds more complex information for longer periods of time. Structure DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are long biological macromolecules that consist of smaller molecules called nucleotides. Eukaryotic Cell vs Prokaryotic Cell. The distinction between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is considered to be the most important distinction among groups of organisms.
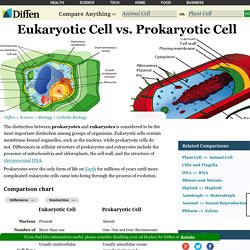
Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles, such as the nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not. Plant Cell vs Animal Cell. Plant and animal cells have several differences and similarities.
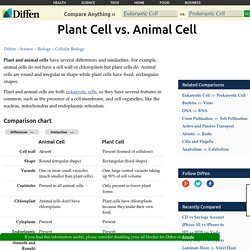
For example, animal cells do not have a cell wall or chloroplasts but plant cells do. Active and Passive Transport. Active and passive transport are biological processes that move oxygen, water and nutrients into cells and remove waste products.
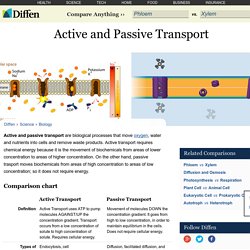
Active transport requires chemical energy because it is the movement of biochemicals from areas of lower concentration to areas of higher concentration. On the other hand, passive trasport moves biochemicals from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration; so it does not require energy. Process There are two types of active transport: primary and secondary. In primary active transport, specialized trans-membrane proteins recognize the presence of a substance that needs to be transported and serve as pumps, powered by the chemical energy ATP, to carry the desired biochemicals across.
Mitosis and Meiosis - Comparison Chart, Video and Pictures. Cells divide and reproduce in two ways: mitosis and meiosis.
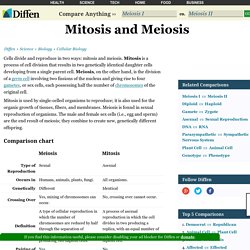
Mitosis is a process of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells developing from a single parent cell. Meiosis, on the other hand, is the division of a germ cell involving two fissions of the nucleus and giving rise to four gametes, or sex cells, each possessing half the number of chromosomes of the original cell. Mitosis is used by single-celled organisms to reproduce; it is also used for the organic growth of tissues, fibers, and membranes.
Meiosis is found in sexual reproduction of organisms. The male and female sex cells (i.e., egg and sperm) are the end result of meiosis; they combine to create new, genetically different offspring. Differences in Purpose. ARKive - Discover the world's most endangered species. Wildscreen's Arkive project was launched in 2003 and grew to become the world's biggest encyclopaedia of life on Earth.
With the help of over 7,000 of the world’s best wildlife filmmakers and photographers, conservationists and scientists, Arkive.org featured multi-media fact-files for more than 16,000 endangered species. Freely accessible to everyone, over half a million people every month, from over 200 countries, used Arkive to learn and discover the wonders of the natural world. Since 2013 Wildscreen was unable to raise sufficient funds from trusts, foundations, corporates and individual donors to support the year-round costs of keeping Arkive online. Therefore, the charity had been using its reserves to keep the project online and was unable to fund any dedicated staff to maintain Arkive, let alone future-proof it, for over half a decade.
Biology. Bioman Biology: The Fun Place to Learn Biology! Learn.Genetics.utah.edu.