

Apocrypha. Bible: Revised Standard Version. Textual Variants. Bible History Online Images and Resources for Biblical History. A Directory containing out-of-copyright artwork scans. Bible Research by Michael Marlowe. Orach Chayim Torah Study.
The Septuagint. Septuagint. Audio Bible Online (KJV) Greek New Testament - Parallel Greek New Testament by John Hurt. The New Testament - (Greek Original / English) Greek Bible. Greek Lexicon. Parallel Hebrew Old Testament. Hebrew Lexicon. The Old Testament Hebrew lexicon is Brown, Driver, Briggs, Gesenius Lexicon; this is keyed to the "Theological Word Book of the Old Testament.
" Also included are pronunciations of each word with alternate pronunciations if available. Bible Study Tools offers two Bible versions, King James and New American Standard, for studying within the Old Testament lexicons. NOTE: In order to see the actual Greek and Hebrew characters you must download and install the free BST Fonts. Click here to view the BST Fonts page. The Hebrew Lexicon has been designed to help the user understand the original text of the Bible. The Hebrew Lexicon can be searched in three ways: * By Strong's Numbers: If you know the number of the entry you desire to see, you can enter it into the text box and click "Search" to view that entry These files are public domain. Hebrew Glossary. Then name Ashkenaz (Bereishit 10:3) has since the 10th century been identified with Germany.
As the German and French Jews of the medieval period formed a uniform group in culture and religious customs, they were all referred to as Ashkenazim in contradistinction to the Sefardim or Spanish- Portuguese Jews. Ashkenazim are the people who use Nusach Ashkenaz, the prayer arrangement adopted by the medieval Franco-German Jews, including certain variations described as belonging to the Polish custom (Minhag Polin). In the 18th century, the Chasidic movement adopted the Sefardic arrangement of prayers; hence, the Chasidim have been called Sefardim on many occasions. The Ashkenazim in Eastern Europe developed an intense religious life, disseminating Talmudic scholarship among the people to a degree never before surpassed in Jewish history.
A high Jewish literacy existed in an illiterate non-Jewish environment. The vitality of the Ashkenazim still dominates wherever they are transplanted. Hebrew Alphabet. The Hebrew and Yiddish languages use a different alphabet than English.
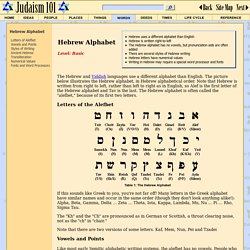
The picture below illustrates the Hebrew alphabet, in Hebrew alphabetical order. Note that Hebrew is written from right to left, rather than left to right as in English, so Alef is the first letter of the Hebrew alphabet and Tav is the last. The Hebrew alphabet is often called the "alefbet," because of its first two letters. Letters of the Alefbet Table 1: The Hebrew Alphabet If this sounds like Greek to you, you're not far off! The "Kh" and the "Ch" are pronounced as in German or Scottish, a throat clearing noise, not as the "ch" in "chair. " Note that there are two versions of some letters. Vowels and Points Like most early Semitic alphabetic writing systems, the alefbet has no vowels.
However, as Hebrew literacy declined, particularly after the Romans expelled the Jews from Israel, the rabbis recognized the need for aids to pronunciation, so they developed a system of dots and dashes called nikkud (points). Hebrew - English Bible. BibleGateway.com: A searchable online Bible in over 35 languages and 50 versions.