

3 Reasons the "Little Brain" Might Become the Next Big Thing. This early 20th-century anatomical illustration of the human brain (from below) shows the left and right hemispheres of both the cerebellum and cerebrum.
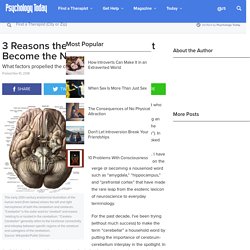
"Cerebellar" is the sister word to "cerebral" and means 'relating to or located in the cerebellum.' "Cerebro-Cerebellar" generally refers to the functional connectivity and interplay between specific regions of the cerebrum and subregions of the cerebellum. Source: Wikipedia/Public Domain As an evidence-based journalist who follows newsworthy trends in neuroscience, I’ve been keeping an eye on the rising popularity of the cerebellum (Latin for “little brain”). In recent weeks, this often-overlooked subcortical brain region has skyrocketed to buzzword status. Article continues after advertisement For the past decade, I’ve been trying (without much success) to make the term “cerebellar” a household word by putting the importance of cerebrum-cerebellum interplay in the spotlight. Cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") in red. 1. 2. 3. My stroke of insight [ TED Talk : Jill Bolte Taylor ]
How the Brain Can Boost Your Emotional Intelligence. Boost Your Emotional Intelligence Many people think “you can’t teach an old dog new tricks,” but not Daniel Goleman and Daniel Siegel.
They understand the brain science, which shows we can all grow new pathways in our brain that support our emotional intelligence and Mindsight. That science explains the mechanism of neuroplasticity – lasting change to the brain. During the Brainpower webcast series, Dr. Goleman and Dr. How to Develop a Connected Brain A key to emotional intelligence and Mindsight is having a connected brain, where different parts of the brain communicate well with each other. Dr. “Here are the steps to making a more connected brain. So, how do you build myelin? Neuroscience and the Three Brains of Leadership. By Grant Soosalu and Marvin Oka Abstract Recent Neuroscience findings have uncovered that we have complex and functional neural networks - or ‘brains’- in our heart and gut, giving scientific credence to the growing body of leadership literature showing how the world’s best companies are guided by leaders who can tap into the intelligence of their head, heart and guts.

Combining these Neuroscience findings with behavioral modeling research conducted by the authors, a number of key insights have been found about the roles of the heart and gut brains for adaptive and generative leadership. In the increasingly complex and volatile social and business environments that organizations operate in, leaders who are unable to tap into and harness the full intuitive and innate intelligence of their multiple brains (head, heart and gut brains aligned together) are at a distinct disadvantage.
[Note: scroll to the bottom of this page to download a copy of this article as a printable PDF] Creativity. How Synapses Work. Neurogenesis: How To Grow New Brain Cells. Adults can still grow new brain cells — neurogenesis — but what are they for?
For a long time scientists believed that neurogenesis was impossible: adults had all the brain cells they were ever going to have. Now we know that’s not true. In fact, we continue to grow new brain cells into adulthood. The race is on to find out what these brain cells are for and how we can grow more of them. A new review of the scientific literature, published in the journal Trends in Cognitive Sciences, argues that the growth of new cells aids adaptation to the environment (Opendak & Gould, 2015).
The authors focus on new cells growing in the hippocampus, an area of the brain linked to memory and learning. Maya Opendak, who co-authored the study, said: “New neurons may serve as a means to fine-tune the hippocampus to the predicted environment.In particular, seeking out rewarding experiences or avoiding stressful experiences may help each individual optimize his or her own brain.” Ms Opendak said: ‘Male’ vs. ‘Female’ Brains: How Different Are They? How are male and female brains different?
This is a question that we are asked routinely by both men and women alike. It is unsurprising that this is such a common question, given that as neuroscience theories go, this topic always seems to be enthusiastically picked up by news-media outlets. Unlike the peer-review process for publishing scientific research, mainstream media outlets will often share the most attention-grabbing snippets of studies, even before the research has been concluded. Consequently, the idea that there is a typical ‘male brain’ and ‘female brain’, is one of the most common myths in the neuroscience space. This idea has many iterations, a common version being that men have bigger brains than women, and that this can be extrapolated to imply something about intelligence. So, what are the differences between male and female brains?
Altered State of Consciousness. Gut–Brain Axis. Brain Benefits Of Physical Activity. Books. Genetics. "Mind Reading" Technology. Animal-Assisted Therapy.