

Foraging: 52 Wild Plants You Can Eat. Here are a few common North American goodies that are safe to eat if you find yourself stuck in the wild: Blackberries: Many wild berries are not safe to eat, it’s best to stay away from them.

But wild blackberries are 100% safe to eat and easy to recognize. They have red branches that have long thorns similar to a rose, the green leaves are wide and jagged. They are best to find in the spring when their white flowers bloom, they are clustered all around the bush and their flowers have 5 points. Dandelions: The easiest to recognize is the dandelion, in the spring they show their bright yellow buds. Asparagus: The vegetable that makes your pee smell funny grows in the wild in most of Europe and parts of North Africa, West Asia, and North America. Elderberries: An elderberry shrub can grow easily grow about 10 feet and yield tons of food, their leaf structure is usually 7 main leaves on a long stretched out stem, the leaves are long and round and the leaves themselves have jagged edges.
52 Wild Plants You Can Eat - Updated. 52 Plants In The Wild You Can Eat. What is the universal edibility test?" Getting lost or stranded in the wilderness is serious business, and you need to make sound decisions to give yourself the best chance at survival.
It also helps to know some basic wilderness survival skills. Why Eat Wild Herbs and Edible Plants? The Benefits of Wild Edible Plants For hundreds of years people took advantage of the medicine cabinet at their doorstep.

Before the advent of processed foods and modern convenience stores, wild plants were a common dietary supplement. They were the ultimate natural multivitamin! Often the plants we call weeds have therapeutic value. Our pharmaceutical industry bases many new medicines on the healing factors in herbs. AZ of Bushcraft (E for Edible wild food) Edible and Medicinal Plants. The information on this page is presented in an older format.

We have vastly expanded our edible plants information with far more information, and far more plants. You can find this information at our new site Wildcrafting.net Abal Calligonum comosum Description: The abal is one of the few shrubby plants that exists in the shady deserts. This plant grows to about 1.2 meters, and its branches look like wisps from a broom. The Fantastic Four – 4 Essential Wild Edible Plants that May Just Save Your Life. Did you realize that knowing just 4 wild edible plants could one day save your life?
If there were any four categories of plants that I would recommend all people to know how to use and identify it would be these: Grass, Oak, Pine, and Cattail. For the knowledgeable survivor, knowing just these four plants can make the difference between life and death if stranded in the wilds – for each one is an excellent food source which can sustain you until help arrives. Throughout this week and part of the next, I’ll be going into details on how you can prepare and eat these plants. For now though, here’s a quick overview into what they have to offer: Grass. How to eat wild stuff and not get poisoned (how-to) Let's play pretend for a moment.
Are you with me? Let's pretend you can't go down to the supermarket for food to eat. In fact, let's pretend that there is not a supermarket for one hundred miles in any direction, and you don't have any food with you. In this pretend land, you are stranded in the wilderness. Perhaps your GPS navigation unit directed you to detour onto a closed mining road in the middle of nowhere, and you didn't have the sense to second-guess it until your rental car got stuck in seasonal mud, and you decide to head out into the woods instead of following the road back.
Does this seem unlikely? Foraging With the "Wildman" Wild Food School - Urban Foraging Guide and Foraging eBooks. Wanted to know more about foraging for wild foods in an urban or metropolitan environment, well the will help you get on the right tracks. This Foraging Guide in PDF format covers about 50 plants, trees and shrubs which have something to offer the urban forager, with images of about 20 main edible species. The format is designed to allow you to print out the pictures on standard 10 x 15 cm. photo paper and then bind them together (with or without laminating the pages). Just print out all the ODD pages numbers and then repeat the process with the EVEN pages. Correctly printed out you will find plant picture and text side by side like the example below. Click wfsURBANGUIDE.pdf to download [approx. 2.4Mb] ForageSF.com. Wild Plants Used for Medicine and Food. Learning wild plants used for medicine, food, and tools is also known as the study of ethnobotany (how people utilize plants).
Edible and medicinal plants can provide healthy alternatives to highly processed foods and pharmaceuticals, bringing greater health into our lives. To effectively use wild plants, one must learn basic plant identification skills, especially for poisonous plants, as well as proper collection and preparation methods. This section of the online library provides articles on wild plants used for medicine, food, and utilitarian purposes. Articles often include references to excellent books, resources, and classes. Food Foraging: Wild Edible Plants & Mushrooms. Adventures in Field Botany / Illustrated-Glossary. Leaf Morphology: Phyllode/ Cladode: modifyed stems that act as leaves.
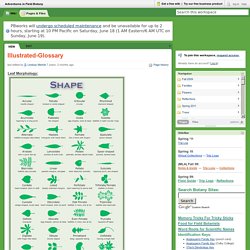
Ensiform: leaves sharp edges, taper into a slender point (fern) Stellate: hairs come up like fingers. Looks like cluster of hair. Peltate: "petiole joins to the center" in leaves. Glossary of Terms: WHORLED - more than two (2) opposite leaves. OPPOSITE - leaf nodes are on opposite sides of twig. ALTERNATE - leaf nodes alternate in pattern along branch. DECUSSATE - Arranged on a stem in opposite pairs at right angles to those above or below, resulting in vertical rows of leaves. PALMATE - consisting of leaflets or lobes radiating from the base of the leaf. CAPSULE - a hollow dry fruit with 3+ locules (chambers) Dehiscent = splits open to release the seed. Indehiscent: remaining closed, do not split open at maturity. Capsule Types-