

18 Ways to Improve Your Body Language. There is no specific advice on how to use your body language.
What you do might be interpreted in several ways, depending on the setting and who you are talking to. The 4 Ways You Can Use Body Language To Influence Success. If you see someone frowning, head bowed, shoulders slumped, it’s a fair bet they’re feeling low in confidence.

But which came first: the slumped shoulders or the bad mood? Your body language doesn’t merely reflect your emotions, it’s often the cause. By learning some of the principal ways that your own posture, gestures, facial expression and even tone of voice affect your mind, you will be more aware of the factors influencing your mood, and give yourself an edge in presentations and negotiations. 1. Know the “Power Posture” Body Language. How to Read Body Language More Effectively. BODY LANGUAGE.
How to Understand Different Types of Meditation: 2 Steps. Meditation. The 52 Lists Project. Wisdom Quotes. Wisdom Quotes. Curio`psy` Online Etymology Dictionary. Old English purpul, dissimilation (first recorded in Northumbrian, in Lindisfarne gospel) of purpure "purple dye, a purple garment," purpuren (adj.)

"purple," a borrowing by 9c. from Latin purpura "purple color, purple-dyed cloak, purple dye," also "shellfish from which purple was made," and "splendid attire generally," from Greek porphyra "purple dye, purple" (see porphyry), of uncertain origin, perhaps Semitic, originally the name for the shellfish (murex) from which it was obtained.
Purpur continued as a parallel form until 15c., and through 19c. in heraldry. As a color name, attested from early 15c. Tyrian purple, produced around Tyre, was prized as dye for royal garments. Stress: Portrait of a Killer » Q&A: Why does psychological stres. Free online mind mapping software. Rosenberg self esteem scale.
The Rosenberg self-esteem scale (RSES), developed by sociologist Dr.
Self-esteem. Self-esteem is a disposition that a person has which represents their judgments of their own worthiness.[5] In the mid-1960s, sociologist Morris Rosenberg defined self-esteem as a feeling of self-worth and developed the Rosenberg self-esteem scale (RSES), which became the most-widely used scale to measure self-esteem in the social sciences.[6] Nathaniel Branden in 1969 defined self-esteem as "the experience of being competent to cope with the basic challenges of life and being worthy of happiness.

" According to Branden, self-esteem is the sum of self-confidence (a feeling of personal capacity) and self-respect (a feeling of personal worth). It exists as a consequence of the implicit judgment that every person has of their ability to face life's challenges, to understand and solve problems, and their right to achieve happiness, and be given respect.[7] Theories[edit] Many early theories suggested that self-esteem is a basic human need or motivation. Development[edit] Psychological manipulation. Psychological manipulation is a type of social influence that aims to change the perception or behavior of others through underhanded, deceptive, or even abusive tactics.[1] By advancing the interests of the manipulator, often at another's expense, such methods could be considered exploitative, abusive, devious, and deceptive.
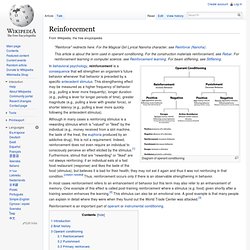
Social influence is not necessarily negative. For example, doctors can try to persuade patients to change unhealthy habits. Social influence is generally perceived to be harmless when it respects the right of the influenced to accept or reject and is not unduly coercive. Depending on the context and motivations, social influence may constitute underhanded manipulation. Reinforcement. Diagram of operant conditioning Although in many cases a reinforcing stimulus is a rewarding stimulus which is "valued" or "liked" by the individual (e.g., money received from a slot machine, the taste of the treat, the euphoria produced by an addictive drug), this is not a requirement.
Indeed, reinforcement does not even require an individual to consciously perceive an effect elicited by the stimulus.[1] Furthermore, stimuli that are "rewarding" or "liked" are not always reinforcing: if an individual eats at a fast food restaurant (response) and likes the taste of the food (stimulus), but believes it is bad for their health, they may not eat it again and thus it was not reinforcing in that condition. [citation needed] Thus, reinforcement occurs only if there is an observable strengthening in behavior. In most cases reinforcement refers to an enhancement of behavior but this term may also refer to an enhancement of memory. Introduction[edit] B.F. Brief history[edit] Test Yourself. Want to Know If Someone Likes You? Ever wondered if someone you're attracted to likes you or not, whether someone is your friend or foe, or whether your employees respect you?
There's an easy way to find out... try to make them laugh . If the laughter comes easy, the answer is likely yes. If it doesn't, the answer is likely no. In my bachelor days, I spent many years slowly learning about the ins and outs of the mating market. Somewhere along the way, I noticed one fairly consistent dynamic: whenever a woman I recently met and was talking to would say to me, "You're really funny! " In my first corporate job, I was working on a project team for a few months where I didn't really like my two supervisors all that much. Many years later in grad school (my advisor was Prof. Human Intelligence: Robert J. Sternberg. This page is now located at an updated address.
Please update your bookmarks! The new address is posted below. You will be redirected to the new page in 15 seconds or you can click the link below. Robert J. Personality Disorder Information. Brain Training, Brain Exercise, Brain Fitness by Brain Training 101. Addictive Tips - Tips to make you smarter! Psychology: Theories, Experiments, and Quizzes. Print › Psychology Core Concepts Chapter 13: Therapies for Psychological Disorders. Therapy A general term for any treatment process; in psychology and psychiatry, it refers to a variety of psychological and biomedical techniques aimed at dealing with mental disorders or coping with problems of living Psychological therapies Therapies based on psychological principles (rather than on the biomedical approach); often called "psychotheraphy"
PersonalityQuiz.net Site - the seaside. Analysis The room represents childhood. The room's comfort level represents your childhood experiences. Inviting surroundings suggest a pleasant childhood, whilst uninviting surroundings suggest an unexciting or sad childhood. The number of furnishings and the degree of detail in your description show how many childhood memories you have. Playing the Blame Game as a Manipulation Tactic. Psychological Manipulation Resources. What is Psychological Manipulation? Psychological Manipulation is a type of influence that attempts to change the behavior or perception of others through underhanded, deceptive and abusive techniques. This advances the interests of the manipulator, generally at the victim's expense, in methods that may be considered abusive, devious, deceptive, and exploitative.
In order to be successful, the art of manipulation involves two things - concealing aggressive or subversive intentions and behaviors while knowing the psychological vulnerabilities of the victim well enough to know what will be the most effective psychological weapons or tactics to be used against them. Body Language Websites. Using Body Language. Techniques > Using Body Language Message clusters | Core patterns | Parts-of-body language | Other notes | See also Body language is an important part of communication which can constitute 50% or more of what we are communicating.
If you wish to communicate well, then it makes sense to understand how you can (and cannot) use your body to say what you mean. Message clusters Body language comes in clusters of signals and postures, depending on the internal emotions and mental states. Aggressive Body Language: Showing physical threat. Core patterns. Usability Body of Knowledge.