

Celtic mythology. Overview[edit] Though the Celtic world at its apex covered much of western and central Europe, it was not politically unified nor was there any substantial central source of cultural influence or homogeneity; as a result, there was a great deal of variation in local practices of Celtic religion (although certain motifs, for example the god Lugh, appear to have diffused throughout the Celtic world).
Inscriptions of more than three hundred deities, often equated with their Roman counterparts, have survived, but of these most appear to have been genii locorum, local or tribal gods, and few were widely worshipped. However, from what has survived of Celtic mythology, it is possible to discern commonalities which hint at a more unified pantheon than is often given credit. Celtic mythology is found in a number of distinct, if related, subgroups, largely corresponding to the branches of the Celtic languages: Historical sources[edit] Irish mythology[edit] Cuchulainn carries Ferdiad across the river. Classical mythology. Classical mythology or Greco-Roman mythology is the body of myths from the ancient Greeks and Romans as they are used or transformed by cultural reception.
Etruscan mythology. The Etruscans were a people with a distinct language and culture during the period of earliest European writing, in the Mediterranean Iron Age in the second half of the first millennium B.C.
They ranged over the Po Valley and some of its alpine slopes, southward along the west coast of Italy, most intensely in Etruria with enclaves as far south as Campania, and inland into the Appennine mountains. Their prehistory can be traced with certainty to about 1000 BC. At their height about 500 BC, they were a significant maritime power with a presence in Sardinia and the Aegean Sea. Germanic mythology. Thor or Donar, god of thunder, one of the major figures in Germanic mythology.
Germanic mythology is a comprehensive term for myths associated with historical Germanic paganism, including Norse mythology, Anglo-Saxon mythology, Continental Germanic mythology, and other versions of the mythologies of the Germanic peoples. Germanic mythology ultimately derives from Indo-European mythology, also known as Indo-Germanic mythology.
Greek mythology. Greek mythology is explicitly embodied in a large collection of narratives, and implicitly in Greek representational arts, such as vase-paintings and votive gifts.
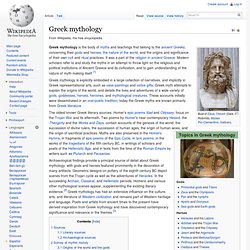
Greek myth attempts to explain the origins of the world, and details the lives and adventures of a wide variety of gods, goddesses, heroes, heroines, and mythological creatures. These accounts initially were disseminated in an oral-poetic tradition; today the Greek myths are known primarily from Greek literature. Archaeological findings provide a principal source of detail about Greek mythology, with gods and heroes featured prominently in the decoration of many artifacts. Geometric designs on pottery of the eighth century BC depict scenes from the Trojan cycle as well as the adventures of Heracles. Sources Literary sources The poetry of the Hellenistic and Roman ages was primarily composed as a literary rather than cultic exercise. Archaeological sources Survey of mythic history. Norse mythology. An undead völva, a Scandinavian seeress, tells the spear-wielding god Odin of what has been and what will be in Odin and the Völva by Lorenz Frølich (1895) For the practices and social institutions of the Norse pagans, see Norse paganism Norse mythology, or Scandinavian mythology, is the body of mythology of the North Germanic people stemming from Norse paganism and continuing after the Christianization of Scandinavia and into the Scandinavian folklore of the modern period.
Roman mythology. Roman mythology is the body of traditional stories pertaining to ancient Rome's legendary origins and religious system, as represented in the literature and visual arts of the Romans.
"Roman mythology" may also refer to the modern study of these representations, and to the subject matter as represented in the literature and art of other cultures in any period. The Romans usually treated their traditional narratives as historical, even when these have miraculous or supernatural elements. The stories are often concerned with politics and morality, and how an individual's personal integrity relates to his or her responsibility to the community or Roman state.
Heroism is an important theme. When the stories illuminate Roman religious practices, they are more concerned with ritual, augury, and institutions than with theology or cosmogony.[1]