

Webvolution.jpg (Image JPEG, 590x435 pixels) Web-evolution-2.png (Image PNG, 450x315 pixels) The Difference Between the Internet and the World Wide Web. Main » Did You Know » Internet » Updated December 22, 2016 / Posted June 24, 2010 By Vangie Beal Many people use the terms Internet and World Wide Web (aka. the Web) interchangeably, but in fact the two terms are not synonymous.
The Internet and the Web are two separate but related things. What is The Internet? History of the Web. Sir Tim Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web in 1989.
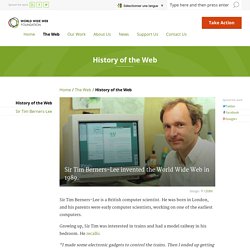
Sir Tim Berners-Lee is a British computer scientist. He was born in London, and his parents were early computer scientists, working on one of the earliest computers. Growing up, Sir Tim was interested in trains and had a model railway in his bedroom. Web-1-à-4.png (Image PNG, 1500x1130 pixels) - Redimensionnée (76%) Web-3.0.png (Image PNG, 535x303 pixels) Web1to31.jpg (Image JPEG, 640x426 pixels) Evolution-Web.png (Image PNG, 1529x1040 pixels) - Redimensionnée (82%) Webvolution.jpg (Image JPEG, 590x435 pixels) Web-evolution-2.png (Image PNG, 450x315 pixels) 1998 - In the Garage Where Google Was Born. It all started in a garage that you can still find with minimal effort — especially if you're using Google Maps.
Less than one mile off U.S. Route 101, the highway that links San Francisco to the rest of Silicon Valley, you'll come to a quiet neighborhood a stone's throw from Stanford's beautifully manicured campus. How 20 popular websites looked when they launched. 2. facebook.com - launched in 2004 3. myspace.com - launched in 2003 4. yahoo.com - launched in 1994 5. youtube.com - launched in 2005 6. wikipedia.org - launched in 2001.
The World Wide Web project. The WorldWideWeb (W3) is a wide-area hypermedia information retrieval initiative aiming to give universal access to a large universe of documents. Everything there is online about W3 is linked directly or indirectly to this document, including an executive summary of the project, Mailing lists , Policy , November's W3 news , Frequently Asked Questions .
What's out there? Pointers to the world's online information, subjects , W3 servers, etc. Help. World Wide Web born at CERN 25 years ago. In March 1989 Tim Berners-Lee, a scientist working at CERN, submitted a proposal to develop a radical new way of linking and sharing information over the internet.
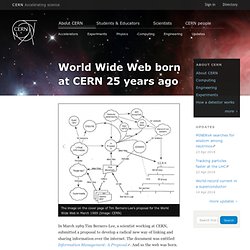
The document was entitled Information Management: A Proposal. And so the web was born. The first website at CERN – and in the world – was dedicated to the World Wide Web project itself. The birth of the World Wide Web. By Christmas 1990, Berners-Lee had defined the Web’s basic concepts, the URL, http and html, and he had written the first browser and server software.
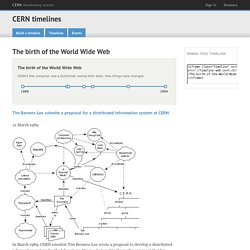
Info.cern.ch was the address of the world's first website and web server, running on a NeXT computer at CERN. The world's first web page address was which centred on information regarding the WWW project. Minitel Research Lab, USA. RFC 675 - Specification of Internet Transmission Control Program. [Docs] [txt|pdf] Network Working Group Vinton Cerf Request for Comments: 675 Yogen Dalal NIC: 2 Carl Sunshine INWG: 72 December 1974 December 1974 Version This document describes the functions to be performed by the internetwork Transmission Control Program [TCP] and its interface to programs or users that require its services.

1971 The @-symbol, part 1 of 2. In 1971, Ray Tomlinson was a 29-year-old computer engineer working for the consulting firm Bolt, Beranek and Newman.[1] Founded just over two decades previously,[2]BBN had recently been awarded a contract by the US government’s Advanced Research Projects Agency to undertake an ambitious project to connect computers all over America.[3] The so-called ‘ARPANET’ would go on to provide the foundations for the modern Internet, and quite apart from his technical contributions to it, Tomlinson would also inadvertently grant it its first global emblem in the form of the ‘@’ symbol.

The origins of the ARPANET project lay in the rapidly advancing state of the art in computing and the problems faced in making best use of this novel resource. In the early days, leaving a ruinously expensive mainframe idle even for a short time was a cardinal sin, and a so-called ‘batch processing’ mode of operation was adopted to minimise down time. Some of the heavyweights of the time did not even bid. 1971 Meet the Man Who Put the '@' in Your E-Mail. Who invented e-mail?
That’s a bit like asking, “Who invented the internet?” Even those with intimate knowledge of its creation can’t agree on the moment it actually came to life. But amid all the bluster over the origins of e-mail, one man holds a claim that resonates well beyond the rest. UCLA Alumni. Professor Leonard Kleinrock guided the UCLA team that sent the first “host-to-host” message.
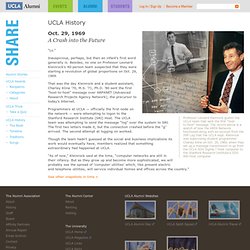
The record above is a sketch of how the ARPA Network functioned along with an excerpt from the IMP Log that the UCLA kept. Kleinrock was supervising student programmer Charley Kline on Oct. 29, 1969, when they set up a message transmission to go from the UCLA SDS Sigma 7 Host computer to the Stanford Research Institute's SDS 940 Host computer. “Lo.” Inauspicious, perhaps, but then an infant's first word generally is. The Internet in 1969 - pre-conceived version. Oct 1969. This Is The Room Where The Internet Was Born.