

The Holocaust Library of Congress Resources. Introduction: Nuremberg Race Laws | Kristallnacht | GhettosConcentration Camps: Dachau | Bergen-Belsen | AuschwitzRighteous Among the Nations: Gies | Schindler | Winton | Grueninger Primary Source and Analysis Tools | Library of Congress Resources Primary Source Sets | PDF Version Library of Congress Resources Exhibits Herblock!

: Psychopathic Ward. Herblock's History: Political Cartoons from the Crash to the Millennium. American Memory The Hannah Arendt Papers at the Library of Congress. American Life Histories: Manuscripts from the Federal Writers' Project, 1936-1940. Voices of the Holocaust. During the 1930s and 40s, the Nazis and their collaborators murdered six million Jews.
Hitler's intention was to destroy all Jewish communities, and to build a 'master race' of Aryans. Many other 'non-aryans' were persecuted including Romanies, homosexuals, and the disabled, as well as those who were politically opposed to the Nazis. This terrible moment in history is now known as the Holocaust. It remains one of the most horrific examples in recent European history of indifference, inhumanity, prejudice and genocide. Voices of the Holocaust consists of oral history testimonies gathered from Jewish men and women who came to live in Britain during or after WWII.
Further interviews with Jewish survivors of the Holocaust can be found on the Sounds website. Survivor testimonies Listen to personal stories from Jewish Holocaust survivors, and learn what life was like for Jews during Hitler's reign. Information cards. Anne Frank - Biography - Anne Frank was a teen writer who went into hiding during the Holocaust, journaling her experiences in the renowned work The Diary of Anne Frank.
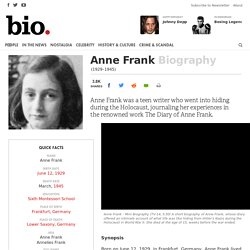
Synopsis Born on June 12, 1929, in Frankfurt, Germany, Anne Frank lived in Amsterdam with her family during World War II. Auschwitz: Inside the Nazi State . Auschwitz 1940-1945 . The Killing Evolution. Funeral of inmates who died or were killed just prior to liberation The Nazis did not start World War II with a plan to eliminate the Jews.
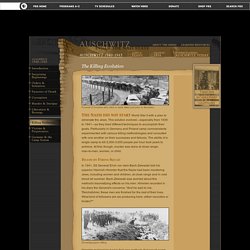
This solution evolved—especially from 1939 to 1941—as they tried different techniques to accomplish their goals. Particularly in Germany and Poland camp commandants experimented with various killing methodologies and consulted with one another on their successes and failures. The ability of a single camp to kill 2,000-3,000 people per hour took years to achieve. At first, though, murder was done at close range-man-to-man, woman, or child. Death by Firing Squad In 1941, SS General Erich von dem Bach-Zelewski told his superior Heinrich Himmler that the Nazis had been murdering Jews, including women and children, at close range and in cold blood all summer. Einsatzgruppen killing Himmler realized he had to find new methods that would spare his troops the psychological strain of killing human beings at close range. Carbon Monoxide Hell Vans Zyklon B. The Danish Center for Holocaust and Genocide Studies. Concentration camps and extermination camps belonged to two widely different camp systems: Extermination camps were only constructed with one purpose: to mass murder Jews and other “unwanted”.
Concentration camps, on the other hand, had a number of purposes, among these to work as reformatory facilities, “punishment camps”, POW camps, transit camps, etc. But the concentration camps did not work directly as extermination sites! Auschwitz Concentration Camp. What Was Auschwitz?
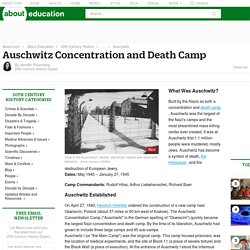
Concentration camps - Key Stage 3 - The Holocaust Explained. A concentration camp is a place where people are detained or confined without trial.

Prisoners were kept in extremely harsh conditions and without any rights. Information for Students. Holocaust Facts - 33 Things You Should Know. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Corporate Site. The combined resources and expertise of three world leaders in education―the Anti-Defamation League, USC Shoah Foundation, and Yad Vashem―have resulted in a robust educational program to help educators deliver accurate and authentic Holocaust education to today’s students.

Echoes and Reflections provides comprehensive professional development for middle and high school educators and multimedia resources suitable for history/social studies, English/language arts, fine arts, social sciences, religion, and other content areas. The Echoes and Reflections program has provided professional development to over 20,000 educators and community leaders across the United States. These facilitator-led programs model active and collaborative learning as participants explore the Echoes and Reflections Teacher’s Resource Guide, including the visual history testimony from USC Shoah Foundation’s Visual History Archive incorporated into each lesson. Links to Britannica’s resources can be found here. United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. What is Antisemitism - Key Stage 3 - The Holocaust Explained.
What is prejudice?

The word prejudice means to pre-judge, to make up your mind about someone before you know anything about them. When you first meet someone, what is the first thing you notice? Their hair, the colour of their skin, their clothes and the way they speak? We often make instant judgments about each other, which later prove to be untrue. Most people feel more comfortable in their own group, gang or tribe. Sometimes the anger of the majority group is taken out on another group. What is antisemitism? Antisemitism is the term used when people are prejudiced against Jews just because they are Jewish.
An Introductory History of the Holocaust. The Holocaust (also called Ha-Shoah in Hebrew) refers to the period from January 30, 1933 - when Adolf Hitler became chancellor of Germany - to May 8, 1945, when the war in Europe officially ended.
During this time, Jews in Europe were subjected to progressively harsher persecution that ultimately led to the murder of 6,000,000 Jews (1.5 million of these being children) and the destruction of 5,000 Jewish communities. These deaths represented two-thirds of European Jewry and one-third of all world Jewry. The Jews who died were not casualties of the fighting that ravaged Europe during World War II.