

Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies. Fragmented landscape illustrating forest patches ofdifferent sizes embedded within a non-forested matrix.Small patches appear to pose higher risk of exposureto Lyme disease.

The conversion of forest into suburban developments and agricultural fields has resulted in the fragmentation of forested landscapes in eastern and central North America. The result is a series of landscapes in which a gradient of forest patches exists, from small woodlots (<1 hectare) to expanses of continuous forest. Recent field studies in Indiana and Illinois indicate that population densities of white-footed mice are considerably higher in forest patches than in continuous forest, and that mouse density tends to be inversely correlated with patch size. The ecological mechanisms behind this pattern are not entirely clear, but a possible mechanism is that natural enemies of mice, such as carnivores, raptors, and competing small mammals decline or disappear when forest habitat is highly fragmented. Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies. WILL'S SKULL PAGE.
Ecology Lesson Plans: Environment, Energy Flow, Cycles. How Wolves Change Rivers. Watch: Bird Mimics Caterpillar (and Other Animal Imposters) In nature, it doesn't always pay to be yourself.
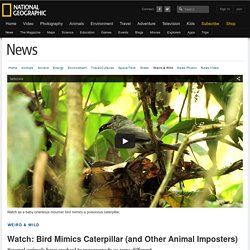
In fact, pretending to be something you're not can keep you alive. Take the cinereous mourner (Laniocera hypopyrra), a bird that lives in the Amazon rain forest. Chicks of this species sport brilliant orange feathers with black polka dots—plumage that pretty much advertises them to passersby. (See "Masters of Deception: 5 Two-Faced Species. ") For a defenseless bird that can't even fly yet, you'd think this is a bad evolutionary strategy. "The chicks of this species look like a hairy caterpillar," said Gustavo Londoño, a researcher at ICESI University in Colombia, "and that caterpillar is known to be toxic. " Londoño discovered the ruse a few years ago in the Madre de Dios region (map) of Peru. In a study, published in the January issue of the American Naturalist, Londoño's team reveal another discovery: The nestlings perform the same dance when their parents return to the nest.
Photograph by Bill Coster, Alamy Praying Mantis "Orchid" Biofilms: The Hypertextbook. Biofilms: The Hypertextbook is a hypertextbook about biofilms.
Biofilms and Biodiversity. The Chesapeake Bay is the largest, most productive estuary in the United States, providing habitat for some 2,700 species of plants and animals.

The health of the Bay depends on maintaining this high level of biodiversity (the number and variety of species located within an ecosystem). One way to measure biodiversity is to examine biofilm communities. Biofilms are bacterial colonies that form in layers. They can be found in many areas of the human body and in the environment. The interactive lessons that are part of Biofilms and Biodiversity are an excellent way to engage students in project-based learning.
In Maryland Sea Grant’s interactive lesson Biofilms and Biodiversity, you will evaluate biofilm communities grown on plexiglass discs suspended vertically in the Baltimore Inner Harbor water. In this project, you will be asked to answer these questions: What tiny creatures lurk in Inner Harbor water? See and use the the interactive lessons on the Biofilms and Biodiversity website. Current population of Australia. Australia Population clock Population of Australia 2014 The population of Australia will increase by 260 849 persons or 1.13% in 2014.
It is expected that 280 162 children will be born and about 156 327 persons will die. Amount of people who moves into Australia (to which they are not native) in order to settle there as permanent residents (immigrants) will prevail over the amount of people who leaves the country to settle permanently in another country (emigrants).The difference (Net migration) will be approximately 137 014 persons. There are 768 children are born in Australia average per day. A person dies every 202 sec. So taking into account natural increase of population (live births and deaths) and net migration (the difference between immigrants and emigrants) the population growth for Australia is about 260 849 annually or 715 persons daily. Australia Population 1960 - 2014. Climate Connections Video.
Cool Craniums. Bones are a critical part of vertebrate anatomy because they provide structure and serve as an anchor for musculature.
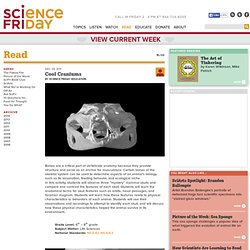
Certain bones of the skeletal system can be used to determine aspects of an animal’s biology, such as its locomotion, feeding behavior, and ecological niche. In this activity, students will observe three “mystery” mammal skulls and compare and contrast the features of each skull. Students will learn the anatomical terms for skull features such as orbits, nasal passages, and foramen magnum. Students will learn how these features relate to physical characteristics or behaviors of each animal. Students will use their observations and recordings to attempt to identify each skull, and will discuss how these physical characteristics helped the animal survive in its environment. Grade Level: 6th – 8th gradeSubject Matter: Life SciencesNational Standards:NS.5-8.1, NS.5-8.3 Bones Come To Life With 3-D Scans *Purchasing skulls can be expensive. Search online for discounted skulls. Animal Diversity Web. Java: Population Dynamics.