

Long tail. An example of a power law graph showing popularity ranking. To the right (yellow) is the long tail; to the left (green) are the few that dominate. In this example, the areas of both regions are equal. In statistics, a long tail of some distributions of numbers is the portion of the distribution having a large number of occurrences far from the "head" or central part of the distribution. The distribution could involve popularities, random numbers of occurrences of events with various probabilities, etc.[1] A probability distribution is said to have a long tail, if a larger share of population rests within its tail than would under a normal distribution. A long-tail distribution will arise with the inclusion of many values unusually far from the mean, which increase the magnitude of the skewness of the distribution.[2][3] A long-tailed distribution is a particular type of heavy-tailed distribution.
Statistical meaning[edit] Chris Anderson and Clay Shirky[edit] Academic research[edit] Hmth. Sternlab Blog. Instructables - Make, How To, and DIY. Tutorial - Basics - Part 1 - Digital Audio. What is sound?
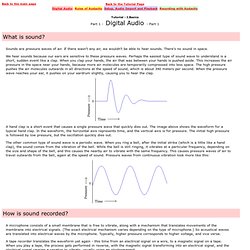
Sounds are pressure waves of air. If there wasn't any air, we wouldn't be able to hear sounds. There's no sound in space. We hear sounds because our ears are sensitive to these pressure waves. Perhaps the easiest type of sound wave to understand is a short, sudden event like a clap. A hand clap is a short event that causes a single pressure wave that quickly dies out. The other common type of sound wave is a periodic wave.
How is sound recorded? A microphone consists of a small membrane that is free to vibrate, along with a mechanism that translates movements of the membrane into electrical signals. A tape recorder translates the waveform yet again - this time from an electrical signal on a wire, to a magnetic signal on a tape. How is sound recorded digitally ? Recording onto a tape is an example of analog recording. The main device used in digital recording is a Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC). Each dot in the figure above represents one audio sample. How Light Bulbs Work" Before the invention of the light bulb, illuminating the world after the sun went down was a messy, arduous, hazardous task.
It took a bunch of candles or torches to fully light up a good-sized room, and oil lamps, while fairly effective, tended to leave a residue of soot on anything in their general vicinity. When the science of electricity really got going in the mid 1800s, inventors everywhere were clamoring to devise a practical, affordable electrical home lighting device. Englishman Sir Joseph Swan and American Thomas Edison both got it right around the same time (in 1878 and 1879, respectively), and within 25 years, millions of people around the world had installed electrical lighting in their homes. The easy-to-use technology was such an improvement over the old ways that the world never looked back. The amazing thing about this historical turn of events is that the light bulb itself could hardly be simpler. Light Basics Light is a form of energy that can be released by an atom. Introduction to LED Light Bulbs" The light bulb that has lit up our homes since the 1800s is officially on its way out.
The inefficient incandescent, which loses most of its energy as heat, has fallen out of favor with the financially and ecologically concerned; starting in 2012, U.S. residents won't be able to buy one even if they want to [source: Linden]. The government is taking the little energy suckers off the market. The prime replacement for the incandescent light bulb is the higher-efficiency compact fluorescent, or CFL. The CFL, though, has its own problems, primarily the inclusion of toxic mercury in the design and a strange, sometimes unpleasant color that even gives some people headaches.
Enter the LED, or light-emitting diode. In the last few years, though, these LED replacement bulbs, the kind you just screw into a lamp like you do an incandescent bulb, have become much more common -- which is to say a fair number of businesses and a handful of households are using them. How LEDs work. How Do LED Lights Work? How Computers Work. How PCs Work" The word computer refers to an object that can accept some input and produce some output. In fact, the human brain itself is a sophisticated computer, and scientists are learning more about how it works with each passing year.
Our most common use of the word computer, though, is to describe an electronic device containing a microprocessor. A microprocessor is a small electronic device that can carry out complex calculations in the blink of an eye. You can find microprocessors in many devices you use each day, such as cars, refrigerators and televisions. The most recognized device with a microprocessor is the personal computer, or PC. When you hear PC, you probably envision an enclosed device with an attached video screen, keyboard and some type of a pointing device, like a mouse or touchpad.
PCs trace their history back to the 1970s when a man named Ed Roberts began to sell computer kits based on a microprocessor chip designed by Intel. What's In a CPU?