

First Images of Our Solar System's Tail Revealed. Astronomers have gotten the first-ever peek at our solar system's tail, called the heliotail, finding that it's shaped like a four-leaf clover, NASA scientists announced today (July 10).
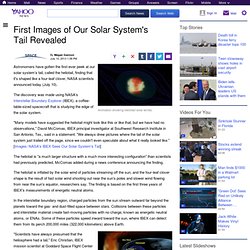
The discovery was made using NASA's Interstellar Boundary Explorer (IBEX), a coffee-table-sized spacecraft that is studying the edge of the solar system. "Many models have suggested the heliotail might look like this or like that, but we have had no observations," David McComas, IBEX principal investigator at Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio, Tex., said in a statement. "We always drew pictures where the tail of the solar system just trailed off the page, since we couldn't even speculate about what it really looked like. " [Images: NASA's IBEX Sees Our Solar System's Tail] The heliotail is "a much larger structure with a much more interesting configuration" than scientists had previously predicted, McComas added during a news conference announcing the finding. View gallery. Black hole powers “cosmic flashlight” illuminating the cosmic web.
Supercomputer simulations predict that matter in the universe is distributed in a network of filaments known as the “cosmic web,” where the vast majority of atoms reside as diffuse hydrogen gas.
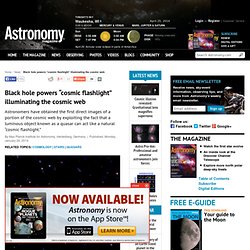
In this picture, galaxies like our Milky Way formed at the nodes of this network, where cool dense gas, the fuel for star formation, funnels in along the intersecting filaments. But direct tests of this model were previously lacking because even at the densest nodes, cosmic web gas is so rarefied that it emits very little light, making it impossible to image even with the world’s largest telescopes. "Mystery of 'Missing Physics' in the Universe" Although the majority of the "normal" matter exists in stars at the center of galaxies, in actuality these stars account for less than 10 percent of the matter in the universe.
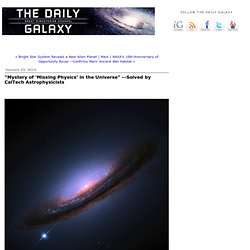
A new set of simulations show that the energy released by individual stars within galaxies can have a substantial effect on where matter is located in the universe. "People have guessed for a long time that the 'missing physics' in these models was what we call feedback from stars," Hopkins says. "When stars form, they should have a dramatic impact on the galaxies in which they arise, through the radiation they emit, the winds they blow off of their surfaces, and their explosions as supernovae. A new wrinkle in the control of waves: Flexible materials could provide new ways to control sound and light. Flexible, layered materials textured with nanoscale wrinkles could provide a new way of controlling the wavelengths and distribution of waves, whether of sound or light.
The new method, developed by researchers at MIT, could eventually find applications from nondestructive testing of materials to sound suppression, and could also provide new insights into soft biological systems and possibly lead to new diagnostic tools. The findings are described in a paper published this week in the journal Physical Review Letters, written by MIT postdoc Stephan Rudykh and Mary Boyce, a former professor of mechanical engineering at MIT who is now dean of the Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science at Columbia University. While materials' properties are known to affect the propagation of light and sound, in most cases these properties are fixed when the material is made or grown, and are difficult to alter later. Computing with silicon neurons: Scientists use artificial nerve cells to classify different types of data.
Scientists from Berlin and Heidelberg are using artificial nerve cells to classify different types of data.
These silicon 'neurons' could recognize handwritten numbers, or distinguish plant species based on their flowers. A bakery assistant who takes the bread from the shelf just to give it to his boss who then hands it over to the customer? Not the most efficient way of doing things. Instead, both work at the same time to sell the baked goods. Similarly, computer programs are more efficient if they process data in parallel rather than to calculate them one after the other. Scientists from Freie Universität Berlin, the Bernstein Center Berlin, and Heidelberg University have now refined a new technology that is based on parallel data processing. "The design of the network architecture has been inspired by the odor-processing nervous system of insects," explains Michael Schmuker, lead author of the study.
When nanotechnology meets quantum physics in one dimension: New experiment supports long-predicted 'Luttinger liquid' model. How would electrons behave if confined to a wire so slender they could pass through it only in single-file?
The question has intrigued scientists for more than half a century. Fur and feathers keep animals warm by scattering light. In work that has major implications for improving the performance of building insulation, scientists at the University of Namur in Belgium and the University of Hassan I in Morocco have calculated that hairs that reflect infrared light may contribute significant insulating power to the exceptionally warm winter coats of polar bears and other animals.

The research was published today in The Optical Society's (OSA) open-access journal, Optics Express. Biophotonics expert Priscilla Simonis, a researcher at the University of Namur and lead author of the Optics Express paper, was intrigued by the ability of polar bears to insulate their bodies to temperatures of 37 degrees Celsius (98.6 F) even during long, cold winters when outside temperatures are a frigid -40 C (-40 F). The feat was especially impressive given that the bears have a layer of fur that is only 5 centimeters thick. The light scattering properties of animals' coats can also have dual purposes, Simonis notes. Solar Flares Fire Off Anti-Matter Particles. Astronomers have detected exotic antimatter particles flying from the sun during solar flares — a discovery that could help scientists understand this mysterious sibling to matter.

Solar flares were predicted to release some antimatter particles among the deluge of charged particles spat out during these eruptions. But this is the first time researchers have observed antimatter coming from the sun. Antimatter particles have the same mass and other characteristics as their regular-matter counterparts, but they have opposite charge. When the universe was born about 13.8 billion years ago in the Big Bang, there was probably about as much matter as antimatter, scientists think. Research could bring new devices that control heat flow. New Discovery: Inner Regions of Milky Way's Disc Formed First. Immediately after the Big Bang, the Universe consisted almost entirely of hydrogen and helium, with levels of "contaminant metals" growing over time.

Consequently, older stars have fewer elements in their make-up - so have lower metallicity. "The different chemical elements of which stars - and we - are made are created at different rates - some in massive stars which live fast and die young, and others in sun-like stars with more sedate multi-billion-year lifetimes," said Professor Gerry Gilmore, lead investigator on the Gaia-ESO Project. Massive stars, which have short lives and die as 'core-collapse supernovae', produce huge amounts of magnesium during their explosive death throes. Flexible, transparent conductor created: Discovery brings bendable cell phone, foldable flat-screen TV closer to reality.
University of Houston researchers have developed a new stretchable and transparent electrical conductor, bringing the potential for a fully foldable cell phone or a flat-screen television that can be folded and carried under your arm closer to reality.
Zhifeng Ren, a physicist at the University of Houston and principal investigator at the Texas Center for Superconductivity, said there long has been research on portable electronics that could be rolled up or otherwise easily transported. But a material that is transparent and has both the necessary flexibility and conductivity has proved elusive -- some materials have two of the components, but until now, finding one with all three has remained difficult.
The material also has potential applications for biomedical devices, said Ren, lead author on the paper. And unlike silver or copper, gold nanomesh does not easily oxidize, which Ren said causes a sharp drop in electrical conductivity in silver and copper nanowires. Health News - 2014 Science and Medicine Articles. As Plant Virus Jumps to Bees, Does it Cause Colony Collapse? Jeff Nesbit was the director of public affairs for two prominent federal science agencies. This article was adapted from one that first appeared in U.S. News & World Report. Nesbit contributed the article to LiveScience's Expert Voices: Op-Ed & Insights. Spy Device? One-Way Sound Machine Created. Scientists have created a one-way sound machine. The device, called an acoustic circulator, breaks the fundamental principle that sound, and other types of waves, are a two-way street.
The findings, published today (Jan. 30) in the journal Science, could lead to the sound equivalent of a one-way mirror. With such a device, people can hear someone talking, but they themselves cannot be heard. [The 9 Biggest Unsolved Mysteries in Physics] Wave nature All waves — whether visible light, sound, radio or otherwise — have a physical property known as time reversal symmetry. "If I am able to talk to you, you should be able to talk to me back," said study co-author Andrea Alù, an electrical engineer at the University of Texas at Austin. Solar Wind Creates Water in Star Dust, Implications for Life. Solar wind can form water on interplanetary dust, potentially adding to the primordial soup that gave rise to life on Earth, scientists say.
On Earth, there is life virtually everywhere water is found. Past research suggests much of this water may have come to Earth from comets raining down on the planet. But scientists have suggested another source of water in the airless void of space — the continuous flow of charged particles from the sun, a stream known as the solar wind. Computing with silicon neurons: Scientists use artificial nerve cells to classify different types of data. Lanl.arxiv.org e-Print archive mirror. Electrical generator uses bacterial spores to harness power of evaporating water.
A new type of electrical generator uses bacterial spores to harness the untapped power of evaporating water, according to research conducted at the Wyss Institute of Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University. Its developers foresee electrical generators driven by changes in humidity from sun-warmed ponds and harbors. The prototype generators work by harnessing the movement of a sheet of rubber coated on one side with spores.
The sheet bends when it dries out, much as a pine cone opens as it dries or a freshly fallen leaf curls, and then straightens when humidity rises. Such bending back and forth means that spore-coated sheets or tiny planks can act as actuators that drive movement, and that movement can be harvested to generate electricity. Water evaporation is the largest power source in nature, Sahin said. But until now no one has tapped that energy to generate electricity. Electrical generator uses bacterial spores to harness power of evaporating water. Torus knot. A (3,−7)-3D torus knot. 300-Year Drought Was Downfall of Ancient Greece. Mini Human 'Brains' Grown in a Dish. The first complete living model of the developing human brain has been created in a lab dish.
Does Its Creation in Stars Suggest a Universe Fine-Tuned for Life? Is the Universe fine-tuned for life? A team of physicists have looked at the conditions necessary to the formation of carbon and oxygen two elements in the universe that are the foundation of life as we currently know it. They’ve found that when it comes to supporting life, the universe leaves very little margin for error. Self-Replicating 'Zombie Whirlpools' Trigger Star Creation. Astronomers accept that in the first steps of a new star’s birth, dense clouds of gas collapse into clumps that, with the aid of angular momentum, spin into one or more Frisbee-like disks where a protostar starts to form.
But for the protostar to grow bigger, the spinning disk needs to lose some of its angular momentum so that the gas can slow down and spiral inward onto the protostar. 200 Billion Free-Floating Starless Planets Roam the Milky Way. ”The Rosette Nebula is home to more than a hundred of these tiny clouds – we call them globulettes”, says Gösta Gahm, astronomer at Stockholm University, who led the project. “They are very small, each with diameter less than 50 times the distance between the Sun and Neptune.
"We can Now Listen to Black Holes Forming Throughout the Universe" The addition of a new technique called ‘quantum squeezing’ at the world’s largest gravitational wave detector allowed researchers to eliminate a lot of the ‘noise’ caused by quantum fluctuations. Astrophysicists Find New Way to Determine How Fast Supermassive Black Holes Spin. Scientist creates lifelike cells out of metal. "A 1.6 Billion-Year-Old Accident Waiting to Happen" Does Its Creation in Stars Suggest a Universe Fine-Tuned for Life?
The Dwarf-Water Planet Unique in the Solar System: NASA Asks "Could It Host Life?" Minerals Essential for Life on Earth Came from Mars. 100 Incredible Lectures from the World's Top Scientists. Mini Human 'Brains' Grown in a Dish. New Mysteries Revealed (Holiday Feature) 3.0 & Beyond... Extraterrestrial Link to Global Climate Shift 12,900 Years Ago. Korea Constructs Road That Wirelessly Charges Moving Electric Buses. Home - Springer.
Universe Grows Like A Brain. Asteroid Impact May have Triggered Evolution of Earth's Multicellular Life. Hubble Telescope Finds Source of Cosmic Stream Near Milky Way (Photos) SPACE. Scientists developing a seawater-desalination chip. Graphene gets even cooler. Wood nanobattery could be green option for large-scale energy storage. Scientists developing a seawater-desalination chip. Waterlife.nfb.ca.flv. Newly Discovered Object Sheds Light on Mysteries of Milky Way's Central Region. Graphene Ink Moves Bendy Gadgets Closer to Reality. Pocket Spacecraft wants to send thousands of personalized satellites to the Moon. "A Neutron Star Collision Was the Source" Incredible Technology: How to See a Black Hole. Soft hydrogels turned into ionic conductors with diverse applications, from artificial muscles to transparent speakers. 13 Technologies You Can't Believe Actually Exist. Enormous Magnetic Fields of Embryonic Black Holes. Scientists. Time Loops May Explain Black Holes.
Magnetic Fields & Magnetic Force. Research could bring new devices that control heat flow. As Plant Virus Jumps to Bees, Does it Cause Colony Collapse? Twelve Things You Should Know About Scalar Weapons. Space-Time Loops May Explain Black Holes. Robots to revolutionize farming, ease labor woes. Solar Wind Creates Water in Star Dust, Implications for Life.
Discovery of quantum vibrations in 'microtubules' inside brain neurons supports controversial theory of consciousness. Hubble and Galaxy Zoo find bars and baby galaxies don't mix. First black hole orbiting a 'spinning' star. Oxygen Brought Earliest Carnivores to Life. When nanotechnology meets quantum physics in one dimension: New experiment supports long-predicted 'Luttinger liquid' model. Discovery of quantum vibrations in 'microtubules' inside brain neurons supports controversial theory of consciousness. First black hole orbiting a 'spinning' star. Watching molecules morph into memories: Breakthrough allows scientists to probe how memories form in nerve cells. Hubble and Galaxy Zoo find bars and baby galaxies don't mix. Artificial "Spiber" silk is tougher than Kevlar. Darwin’s Dark Knight: Scientist Risked Execution for Fox Study (Op-Ed)
Watching molecules morph into memories: Breakthrough allows scientists to probe how memories form in nerve cells. Food processors beware: Salmonella biofilms incredibly resistant to powerful disinfectants. Symphony of life, revealed: New imaging technique captures vibrations of proteins, tiny motions critical to human life. A new wrinkle in the control of waves: Flexible materials could provide new ways to control sound and light. Drone It Yourself turns random objects into RC quadrotors. Fur and feathers keep animals warm by scattering light. Magnetic field. -23.0192833333,-67.7531777778 (Atacama Large Millimeter Array) Enormous Galaxy Formed When Universe was 6% of Its Present Size Puzzles Astronomers. Key Prediction About Origin of the Universe Detected for 1st Time. Key Prediction About Origin of the Universe Detected for 1st Time. Exclusive: Pioneering scientists turn fresh air into petrol in massive boost in fight against energy crisis - Home News - UK. Top Secret America: Who is TSA?
Health & Fitness. Flexible, transparent conductor created: Discovery brings bendable cell phone, foldable flat-screen TV closer to reality. Lectures. 'Magnetic electricity' discovered. Spy Device? One-Way Sound Machine Created. Jabccba - Yahoo Mail.