

Text Analysis Info. Data Mining, Predictive Modeling, Techniques. Data Mining Data Mining is an analytic process designed to explore data (usually large amounts of data - typically business or market related - also known as "big data") in search of consistent patterns and/or systematic relationships between variables, and then to validate the findings by applying the detected patterns to new subsets of data.
The ultimate goal of data mining is prediction - and predictive data mining is the most common type of data mining and one that has the most direct business applications. The process of data mining consists of three stages: (1) the initial exploration, (2) model building or pattern identification with validation/verification, and (3) deployment (i.e., the application of the model to new data in order to generate predictions). Stage 1: Exploration.
Stage 2: Model building and validation. Stage 3: Deployment. For information on Data Mining techniques, review the summary topics included below. Berry, M., J., A., & Linoff, G., S., (2000). Fayyad, U. The Open Source Analysis of Competing Hypotheses Project. Force Field Analysis (Forcefield Analysis) - Decision-Making Skills Training from MindTools. Analyzing the Pressures For and Against Change How to use Force Field Analysis, with James Manktelow & Amy Carlson.
Force Field Analysis is a useful decision-making technique. It helps you make a decision by analyzing the forces for and against a change, and it helps you communicate the reasoning behind your decision. You can use it for two purposes: to decide whether to go ahead with the change; and to increase your chances of success, by strengthening the forces supporting change and weakening those against it. About the Tool Force Field Analysis was created by Kurt Lewin in the 1940s. Balanced scorecard. The balanced scorecard (BSC) is a strategy performance management tool - a semi-standard structured report, supported by design methods and automation tools, that can be used by managers to keep track of the execution of activities by the staff within their control and to monitor the consequences arising from these actions.[1][2] Characteristics[edit] The characteristic of the balanced scorecard and its derivatives is the presentation of a mixture of financial and non-financial measures each compared to a 'target' value within a single concise report.
The report is not meant to be a replacement for traditional financial or operational reports but a succinct summary that captures the information most relevant to those reading it. It is the method by which this 'most relevant' information is determined (i.e., the design processes used to select the content) that most differentiates the various versions of the tool in circulation. History[edit] Design[edit] Intelligenceanalysistraining.com.
Links. SystemsThinking. Free PEST market analysis template and method, free pest market analysis examples. Pest variations The PEST model, like most very good simple concepts, has prompted several variations on the theme.

For example, the PEST acronym is sometimes shown as STEP, which obviously represents the same factors. Stick with PEST - nearly everyone else does. More confusingly (and some would say unnecessarily) PEST is also extended to seven or even more factors, by adding Ecological (or Environmental), Legislative (or Legal), and Industry Analysis, which produces the PESTELI model. Other variations on the theme include STEEP and PESTLE, which allow for a dedicated Ethical section.
It's a matter of personal choice, but for most situations the original PEST analysis model arguably covers all of the 'additional' factors within the original four main sections. Analysis - Table of Contents. PEST Analysis - Problem-Solving Training from MindTools. Identifying "Big Picture" Opportunities and Threats (Also Known as PESTLE, PESTEL, PESTLIED, STEEPLE, SLEPT and LONGPESTLE) Learn how to use PEST Analysis to identify the threats and opportunities in your business environment.
Changes in your business environment can create great opportunities for your organization – and cause significant threats. For example, opportunities can come from new technologies that help you reach new customers, from new funding streams that allow you to invest in better equipment, and from changed government policies that open up new markets. Threats can include deregulation that exposes you to intensified competition; a shrinking market; or increases to interest rates, which can cause problems if your company is burdened by debt. PEST Analysis is a simple and widely used tool that helps you analyze the Political, Economic, Socio-Cultural, and Technological changes in your business environment. About the Tool. Risk Analysis Techniques - Problem-Solving Training from MindTools. Evaluating and Managing Risks Find out how to do a risk analysis, with James Manktelow and Amy Carlson.
Whatever your role, it's likely that you'll need to make a decision that involves an element of risk at some point. Risk is made up of two parts: the probability of something going wrong, and the negative consequences if it does. Risk can be hard to spot, however, let alone prepare for and manage. And, if you're hit by a consequence that you hadn't planned for, costs, time, and reputations could be on the line. Free SWOT analysis template and method, free swot analysis examples.
As a more general guide, here is a free SWOT analysis template worksheet (doc file), and the same free SWOT analysis tool (pdf format).
If you have difficulty opening the above doc file here are two other formats: Geospatial Analysis - spatial and GIS analysis techniques and GIS software. Competitor analysis. Competitor analysis is an essential component of corporate strategy.[2] It is argued that most firms do not conduct this type of analysis systematically enough.
Instead, many enterprises operate on what is called “informal impressions, conjectures, and intuition gained through the tidbits of information about competitors every manager continually receives.” As a result, traditional environmental scanning places many firms at risk of dangerous competitive blindspots due to a lack of robust competitor analysis.[3] Competitor array[edit] Analytical Methods for Accident Investigation. SWOT Analysis - Strategy Tools from MindTools. Discover New Opportunities, Manage and Eliminate Threats Find out more about SWOT, with James Manktelow & Amy Carlson.
SWOT Analysis is a useful technique for understanding your Strengths and Weaknesses, and for identifying both the Opportunities open to you and the Threats you face. Used in a business context, it helps you carve a sustainable niche in your market. Used in a personal context , it helps you develop your career in a way that takes best advantage of your talents, abilities and opportunities. This article looks at how to use SWOT in a business context.
OODA loop. Diagram of a decision cycle known as the Boyd cycle, or the OODA loop Overview[edit] The OODA loop has become an important concept in litigation,[1] business[2] and military strategy.
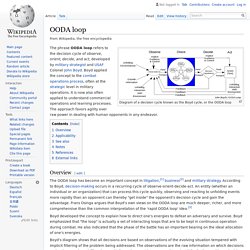
According to Boyd, decision-making occurs in a recurring cycle of observe-orient-decide-act. An entity (whether an individual or an organization) that can process this cycle quickly, observing and reacting to unfolding events more rapidly than an opponent can thereby "get inside" the opponent's decision cycle and gain the advantage. Frans Osinga argues that Boyd's own views on the OODA loop are much deeper, richer, and more comprehensive than the common interpretation of the 'rapid OODA loop' idea.[3] Boyd developed the concept to explain how to direct one's energies to defeat an adversary and survive. Boyd’s diagram shows that all decisions are based on observations of the evolving situation tempered with implicit filtering of the problem being addressed.