

Caroline Jensen
Cobblestone, 77 King Street North, Dublin. Bars & pubs - Time Out Dublin. Loft Market, Powerscourt Townhouse Centre, Dublin. Shops - Time Out Dublin. Music - Search results - Time Out Dublin. 651 results, sorted alphabetically Music The Point Theatre, Dublin's largest indoor music venue, closed its doors in the summer of 2007 to undergo a complete overhaul and rebranding as The O2,... 101 Talbot Restaurants & cafés Casual, but serious about its vegetarian customers, this long-running restaurant nourishes wise locals who pay little attention to food fads.
20 great things to do in Dublin - Time Out Dublin. By Time Out editors and Sulakshana Gupta 1.
Experience Dublin as the locals do Despite its unsavoury reputation in past years, Temple Bar is one of the city's most charming neighbourhoods and residents are trying hard to keep it that way. Cobblestone streets, bars, cafés, art galleries and architectural splendour harmoniously blend with old streetscapes and eco-friendly schemes. Among the cultural attractions are Dublin's only art-house cinema at the Irish Film Institute, the Gallery of Photography and the Project Arts Centre. 2. If all you came to Dublin for is the Guinness, then camp out at Kehoe's. An Error Occurred Setting Your User Cookie.
Three-dimensional structure of aspartyl protease from human immunodeficiency virus HIV-1. Three-dimensional structure of aspartyl protease from human immunodeficiency virus HIV-1 Manuel A.
Navia*, Paula M. D. Fitzgerald*, Brian M. McKeever*, Chih-Tai Leu†, Jill C. *Department of Biophysical Chemistry, Merck Sharp and Dohme Research Laboratories, PO Box 2000 (RY80M-203), Rahway, New Jersey 07065, USA †Department of Molecular Biology, Merck Sharp and Dohme Research Laboratories, Sumneytown Pike (WP16-101), West Point, Pennsylvania 19486, USA ‡Sadly, Dr Irving S. The crystal structure of the protease of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), which releases structural proteins and enzymes from viral polyprotein products, has been determined to 3 Å resolution.
References. An Error Occurred Setting Your User Cookie. An Error Occurred Setting Your User Cookie. This site uses cookies to improve performance. If your browser does not accept cookies, you cannot view this site. Setting Your Browser to Accept Cookies There are many reasons why a cookie could not be set correctly. Below are the most common reasons: You have cookies disabled in your browser.
Human immunodeficiency virus has an aspartic-type protease that can be inhibited by pepstatin A. Science Magazine: Sign In. PIN domain. In molecular biology the PIN domain is a protein domain that is about 130 amino acids in length.
The PIN domain was named after its identification in the N-terminus of the PilT protein (PilT N terminus). PIN domains function as nuclease enzymes that cleave single stranded RNA in a sequence dependent manner.[1] PIN domains contain three nearly invariant acidic residues. Crystal structures show these residues clustered together in the putative active site. Celebrating macromolecular crystallography: A personal perspective. From crystallography to structural biology, a century of discoveries. Directory of Open Access Journals. Celebrating macromolecular crystallography: A personal perspectiveAbad-Zapatero, CelerinoArbor: Ciencia, Pensamiento y Cultura. 2015;191(772):a215 DOI 10.3989/arbor.2015.772n2001Abstract | Full Text The twentieth century has seen an enormous advance in the knowledge of the atomic structures that surround us.

The discovery of the first crystal structures of simple inorganic salts by the Braggs in 1914, using the diffraction of X-rays by crystals, provided the critical elements to unveil the atomic structure of matter. Subsequent developments in the field leading to macromolecular crystallography are presented with a personal perspective, related to the cultural milieu of Spain in the late 1950’s. A VapBC Toxin-Antitoxin Module Is a Posttranscriptional Regulator of Metabolic Flux in Mycobacteria. + Author Affiliations The largest family of toxin-antitoxin (TA) modules are encoded by the vapBC operons, but their roles in bacterial physiology remain enigmatic.

Microarray analysis in Mycobacterium smegmatis overexpressing VapC/VapBC revealed a high percentage of downregulated genes with annotated roles in carbon transport and metabolism, suggesting that VapC was targeting specific metabolic mRNA transcripts. To validate this hypothesis, purified VapC was used to identify the RNA cleavage site in vitro. The Biochemistry of VapBC Toxin-Antitoxins. Shigella flexneri. Shigella flexneri is a species of Gram-negative bacteria in the genus Shigella that can cause diarrhea in humans.
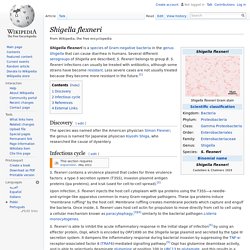
Several different serogroups of Shigella are described; S. flexneri belongs to group B. S. flexneri infections can usually be treated with antibiotics, although some strains have become resistant. VapBC. First discovered in 1992, vapBC loci are now thought make up around 37–42% of all type II toxin-antitoxin systems.[3][4] Discovery[edit] Distribution[edit] VapBC operons have been found in distantly related prokaryotes, including the pathogens Leptospira interrogans,[9] Mycobacterium tuberculosis[10] and Piscirickettsia salmonis.[11] The loci have been described as "surprisingly abundant, especially in Archaea"[12]—vapBC family members made up 37% of all TA families identified by one bioinformatics search[3] and 42% of those found by another.[4] Bioinformatics searches have discovered vapBC homologues on both chromosomes and plasmids, and often in high copy number per cell.
RCSB PDB-101. <div style="padding-left:8px;font-weight:bold;color:#FF0000;font-size:16px"><p>This browser is either not Javascript enabled or has it turned off.
<br />This site will not function correctly without Javascript. </p></div> Lysozyme Keywords: cytolysis, defense response to bacterium, hydrolase activity acting on glycosyl bonds, antibiotic, peptidoglycan catabolic process Attacking Bacteria Lysozyme protects us from the ever-present danger of bacterial infection. The First Antibiotic Alexander Fleming discovered lysozyme during a deliberate search for medical antibiotics. A Cellular Guardian.