

The Story of Fidgity Phillip by Heinrich Hoffman. THE STORY OF FIDGITY PHILLIP The First Description of ADHD The very first written description of ADHD was in 1845 by a German psychiatrist, Dr.
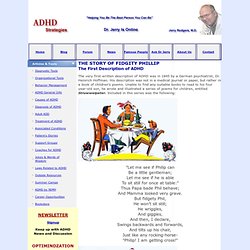
Heinrich Hoffman. His description was not in a medical journal or paper, but rather in a book of children's poems. Unable to find any suitable books to read to his four year-old son, he wrote and illustrated a series of poems for children, entitled Struwwelpeter. Included in this series was the following: "Let me see if Philip can Be a little gentleman; Let me see if he is able To sit still for once at table:" Thus Papa bade Phil behave; And Mamma looked very grave.
See the naughty, restless child Growing still more rude and wild, Till his chair falls over quite. Where is Philip, where is he? So........there you have a perfect description of what we now know as ADHD--in 1845. His lectures and papers started an avalanche of studies and papers on ADHD, providing information on the symptoms, diagnosis, cause, and treatments. Neurology of ADHD. History.
ADD/ADHD RESOURCES. Read ADD/ADHD MATERIAL. ADHD, Data and Statistics - NCBDDD. New Data: Medication and Behavior Treatment [Read summary( The data from a national sample of children with special health care needs, ages 4-17 years, collected in 2009-10, showed that most children with ADHD received either medication treatment or behavioral therapy; however, many were not receiving treatment as described in the best practice guidelines from 2011.
DSM-IV Definition. DSM-IV (Text Revision) Definition Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Essential features: A.

Persistent pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that is more frequently displayed and is more severe than is typically observed in individuals at comparable level of development. B. Some hyperactive-impulsive or inattentive symptoms must have been present before seven years of age. C. Disruptive Behavior Disorders. Disruptive behavior disorders are among the easiest to identify of all coexisting conditions because they involve behaviors that are readily seen such as temper tantrums, physical aggression such as attacking other children, excessive argumentativeness, stealing, and other forms of defiance or resistance to authority.
These disorders, which include ODD and CD, often first attract notice when they interfere with school performance or family and peer relationships, and frequently intensify over time. Disruptive Behavior Disorders - Behavior Disorder. Disruptive Behavior Disorders are often diagnosed during early childhood and associated with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder.

This article defines disruptive behavior disorders such as ADHD, Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD), and conduct disorders. Get information on treatment of these disorders as well. What Is a Disruptive Behavior Disorder? Disruptive Behavior Disorder is a technical term that refers to a specific portion of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th Edition, Text Revision, abbreviated as DSM-IV-TR. The section is a subset of the Disorders Usually First Diagnosed in Infancy, Childhood, or Adolescence, with the subcategory name of Attention-Deficit and Disruptive Behavior Disorders. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD, similar to hyperkinetic disorder in the ICD-10) is a psychiatric disorder[1][2] of the neurodevelopmental type[3][4] in which there are significant problems of attention, hyperactivity, or acting impulsively that are not appropriate for a person's age.[5] These symptoms must begin by age six to twelve and be present for more than six months for a diagnosis to be made.[6][7] In school-aged individuals the lack of focus may result in poor school performance.
Despite being the most commonly studied and diagnosed psychiatric disorder in children and adolescents, the cause in the majority of cases is unknown. ADHD management usually involves some combination of counseling, lifestyle changes, and medications. ADHD and its diagnosis and treatment have been considered controversial since the 1970s.[16] The controversies have involved clinicians, teachers, policymakers, parents and the media.
Adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (also referred to as adult ADHD or simply ADHD in adults, formerly AADD) is the neurobiological condition of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults.
About one-third[1]p. 44 to two-thirds[2]p. 87 of children with symptoms from early childhood continue to demonstrate notable ADHD symptoms throughout life. Three subtypes of ADHD are identified in the DSM-IV: Predominantly Inattentive (ADHD-PI)Predominantly Hyperactive (ADHD-PH)Combined type (ADHD-C). In later life, the hyperactive/impulsive subtype manifests more frequently[1]p. 44, although with age the hyperactivity symptoms tend to turn more into "inner restlessness" in teens and adults with ADHD.[3] Diagnosis of the condition includes assessment interviews by clinicians with: examination of personal historyobservational evidence from family members or close friendsacademic reports, often going back to school yearsetc.,[7][8]
Slideshow: ADHD/ADD in Adults. Who Can Diagnose ADHD? Causes of ADD and ADHD. By Dr Kenny Handelman - 2008-11-20 While many people consider ADD or ADHD to be caused by many social factors, i.e. bad parenting, video games, poor schools, etc., research is clear that the social causes have no merit with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder.

The first place to start with the cause of ADD or ADHD is genetics. It is a very genetic disorder. There is term called 'heritability', which refers to how genetic a disorder is. As an example - breast cancer is 30% heritable - meaning that about 30% of the possible causes of breast cancer can be attributed to genetics. That means that ADHD is highly genetic. Now if genes cause 80 percent that means there is about 20 percent that is not caused by genetics. The Prenatal Causes of ADHD: These are the acquired causes of Attention Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder that occur during the pregnancy. * Mother drinking alcohol during pregnancy: With alcohol during pregnancy, there is the same increased risk - 2.5 times. * Brain tumours. Causes of Attention Deficit Disorder (ADHD)