

Das älteste Wasser der Erde. Die Erdkruste ist normalerweise ein eher unruhiger Ort: Die ständige Drift der Kontinente schiebt die Kruste an einigen Orten in die Höhe, drückt sie an anderen in die Tiefe.
Dadurch öffnen sich Risse im Untergrund, Spalten entstehen und schließen sich wieder. Unter anderem deshalb nahm man bisher an, dass es in den Tiefen des Gesteins eigentlich keine Hohlräume geben kann, in denen Wasser über Milliarden Jahre ungestört überdauern konnte. Als das bisher älteste urzeitliche Nass galt ein Reservoir unter der Witwatersrand-Mine in Südafrika. "Isotope von Edelgasen in diesen tiefen Bruchspalten deuten darauf hin, dass das Wasser dort 25 Millionen Jahre alt ist", erklären Greg Holland von der Lancaster University und seine Kollegen.
In diesem urzeitlichen Wasser wurde sogar Leben gefunden - Mikroben, die ohne Licht nur auf Basis chemischer Reaktionen überdauern. Edelgase verraten Alter des Untergrund-Wassers Uraltes Wasser und Leben auch im Untergrund des Mars? Chronology of the universe. Illustration of evolution of the universe from the Big Bang (left).
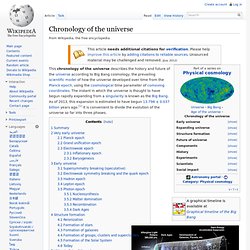
In this diagram, the universe is represented in two dimensions and the third (horizontal) dimension is time, increasing to the right. Summary[edit] The very earliest universe was so hot, or energetic, that initially no particles existed or could exist (except perhaps in the most fleeting sense), and the forces we see around us today were believed to be merged into one unified force. Space-time itself expanded during an inflationary epoch due to the immensity of the energies involved. Gradually the immense energies cooled – still to a temperature inconceivably hot compared to any we see around us now, but sufficiently to allow forces to gradually undergo symmetry breaking, a kind of repeated condensation from one status quo to another, leading finally to the separation of the strong force from the electroweak force and the first particles.
Logarithmic timeline. A logarithmic timeline is a timeline laid out according to a logarithmic scale.
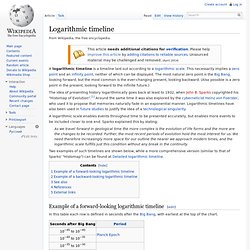
This necessarily implies a zero point and an infinity point, neither of which can be displayed. The most natural zero point is the Big Bang, looking forward, but the most common is the ever-changing present, looking backward. (Also possible is a zero point in the present, looking forward to the infinite future.) The idea of presenting history logarithmically goes back at least to 1932, when John B. Sparks copyrighted his "Histomap of Evolution".[1] Around the same time it was also explored by the cyberneticist Heinz von Foerster, who used it to propose that memories naturally fade in an exponential manner.
A logarithmic scale enables events throughout time to be presented accurately, but enables more events to be included closer to one end. As we travel forward in geological time the more complex is the evolution of life forms and the more are the changes to be recorded. See also[edit] References[edit] Datei:Carte Neandertaliens anciens-de.svg. Summary[edit] Licensing[edit] Original upload log[edit] This image is a derivative work of the following images: File:Carte_Neandertaliens_anciens.jpg licensed with Cc-by-sa-2.5,2.0,1.0, Cc-by-sa-3.0-migrated, GFDL 2006-04-17T12:59:10Z 120 924x600 (285390 Bytes) map of main sites where pre-Neandertal or ancient Neandertal fossil where found [[Category:Homo neanderthalensis]]File:Cyan_pog.svg licensed with PD-self 2011-10-19T10:59:52Z Antonsusi 64x64 (608 Bytes) valid SVG2009-09-08T14:10:19Z Davide101 64x64 (607 Bytes) {{Information |Description={{en|1=Shiny cyan button/marker widget.
Used to mark the location of something such as a tourist attraction.}} Uploaded with derivativeFX Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time. Geologic time scale. The geologic time scale (GTS) is a system of chronological measurement that relates stratigraphy to time, and is used by geologists, paleontologists, and other earth scientists to describe the timing and relationships between events that have occurred throughout Earth's history.
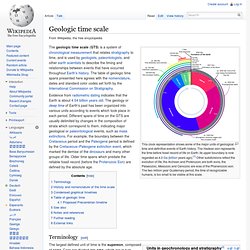
The table of geologic time spans presented here agrees with the nomenclature, dates and standard color codes set forth by the International Commission on Stratigraphy. Evidence from radiometric dating indicates that the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The geology or deep time of Earth's past has been organized into various units according to events which took place in each period. Different spans of time on the GTS are usually delimited by changes in the composition of strata which correspond to them, indicating major geological or paleontological events, such as mass extinctions.
Terminology[edit] Timeline of evolutionary history of life.