

Change Management Learning Center - Prosci. Managing Change Guide. If you would like to download a word version of the managing change guide click here: Part 1 - Managing Change (word) Part 2 - Worst Practice Guide (in Energy & Environmental Management) (word) Part 3 - Influencing Senior Management - Getting It Wrong (word) Written by Phil Harding (philharding.net) and John Pooley (The John Pooley Consultancy) this guide was first produced by the Government Office for the South West (Sustainability & Environmental Technologies Team) in partnership with Envirowise (now part of WRAP) in 2004 and re-published as a paperback in 2007 for its 4th print run.

It is also endorsed by the Carbon Trust, ESTA (the Energy Services and Technology Association), and Climate SouthWest. © Government Office for the South West, 2004 - 2007. Special workshops or conference presentations from the authors. Organisational Change Management. Organisational Change Management. PDCA. PDCA (plan–do–check–act or plan–do–check–adjust) is an iterative four-step management method used in business for the control and continuous improvement of processes and products.
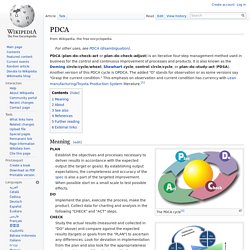
It is also known as the Deming circle/cycle/wheel, Shewhart cycle, control circle/cycle, or plan–do–study–act (PDSA). Another version of this PDCA cycle is OPDCA. The added "O" stands for observation or as some versions say "Grasp the current condition. " This emphasis on observation and current condition has currency with Lean manufacturing/Toyota Production System literature.[1] Meaning[edit] Continuous quality improvement with PDCA Establish the objectives and processes necessary to deliver results in accordance with the expected output (the target or goals). Implement the plan, execute the process, make the product. Study the actual results (measured and collected in "DO" above) and compare against the expected results (targets or goals from the "PLAN") to ascertain any differences.
About[edit] See also[edit] Online Diagram Software to draw Flowcharts, UML & more. Organisational Change Management. Project Management. Streamline Productivity with the "Minimum Effective Dose” for Tasks.
Timeline Creation. Improving Business Processes - Problem Solving Tools From Mind Tools. Streamlining Tasks to Improve Efficiency Map processes carefully before making changes. © iStockphoto/s_john79 You probably use dozens of business processes every day.
For example, you may go through the same steps each time you generate a report, resolve a customer complaint, contact a new client, or manufacture a new product. You've likely come across the results of inefficient processes, too. That's why it's so important to improve processes when they are not working well. About Business Processes Processes can be formal or informal. For example, you might have procedures for receiving and submitting invoices, or for establishing relationships with new clients. Informal processes are more likely to be ones that you have created yourself, and you may not have written them down. The Importance of Efficient Processes These different kinds of processes have one thing in common: they're all designed to streamline the way that you and your team work.
Improving Your Team's Processes Key Points.
Complexity map castellani map of complexity science. 10 Principles of Leading Change Management. Since the mid-2000s, organizational change management and transformation have become permanent features of the business landscape.

Vast new markets and labor pools have opened up, innovative technologies have put once-powerful business models on the chopping block, and capital flows and investor demand have become less predictable. To meet these challenges, firms have become more sophisticated in the best practices for organizational change management.
They are far more sensitive to and more keenly aware of the role that culture plays. They’ve also had to get much better on their follow-through. Yet according to a 2013 Strategy&/Katzenbach Center survey of global senior executives on culture and change management, the success rate of major change initiatives is only 54 percent. How to Lead Change Management DeAnne Aguirre, senior partner with Strategy&, discusses techniques that can help companies transform quickly and effectively. 1. ADKAR Change Management Model Overview - Change Management Learning Center.
Overview This tutorial presents an overview of the ADKAR model for change management.

ADKAR is a goal-oriented change management model that allows change management teams to focus their activities on specific business results. The model was initially used as a tool for determining if change management activities like communications and training were having the desired results during organizational change. The model has its origins in aligning traditional change management activities to a given result or goal. For example, Awareness of the business reasons for change is a goal of early communications related to a business change. The goals or outcomes defined by ADKAR are sequential and cumulative. As a manager, you can use this model to identify gaps in your change management process and to provide effective coaching for your employees. The ADKAR model has the ability to identify why changes are not working and help you take the necessary steps to make the change successful.
Exercise 1. 10 Principles of Leading Change Management.