

Science is awesome. Artist Puts a Human Face on DNA. When Heather Dewey-Hagborg walks down the street, she notices all the bits of genetic information left behind by other unsuspecting pedestrians — everything from strands of hair to fingernails to discarded cigarette butts.
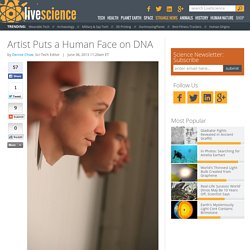
For an artist and doctoral student, these objects were a chance to investigate a compelling question: How much can be learned about a person from a stray hair? "The question really stuck in my head, and I became obsessed with trying to get an answer," Dewey-Hagborg, who studies electronic art at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Troy, N.Y., told LiveScience. "The more I walked around the city, the more I saw these genetic artifacts everywhere I looked. " She started collecting samples: A wad of chewing gum outside a grocery store, strands of hair from Penn Station in Manhattan, and cigarette butts along two major thoroughfares in Brooklyn. Hair Dryer. Mountain Populations Offer Clues to Human Evolution. Photo In the hearts of evolutionary biologists, mountains occupy a special place.
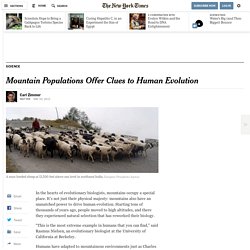
It’s not just their physical majesty: mountains also have an unmatched power to drive human evolution. Starting tens of thousands of years ago, people moved to high altitudes, and there they experienced natural selection that has reworked their biology. Fun Video: Pink Light Doesn't Exist. The laws list: K. Brief Answers to Cosmic Questions. Structure of the Universe Does the Universe have an edge, beyond which there is nothing?

Epigenetics_primer.jpg (JPEG Image, 1980 × 1223 pixels) Dynamic Periodic Table. Electromagnetic theories of consciousness. The electromagnetic theories of consciousness propose that consciousness can be understood as an electromagnetic phenomenon.
Overview[edit] Theorists differ in how they relate consciousness to electromagnetism. Electromagnetic field theories (or "EM field theories") of consciousness propose that consciousness results when a brain produces an electromagnetic field with specific characteristics. Science Space Photo of the Day. When the lamp is shattered, The light in the dust lies dead.
The Aviator: Science Fiction of the Post Global Warming World. How can you go wrong with blimps?
The Aviator. Physics Flash Animations. We have been increasingly using Flash animations for illustrating Physics content. This page provides access to those animations which may be of general interest. The animations will appear in a separate window. The animations are sorted by category, and the file size of each animation is included in the listing. Also included is the minimum version of the Flash player that is required; the player is available free from The categories are: In addition, I have prepared a small tutorial in using Flash to do Physics animations. LInks to versions of these animations in other languages, other links, and license information appear towards the bottom of this page. The Animations There are 99 animations listed below. Other Languages and Links. Accelerating Human Evolution. Your Brain on Pot: Watch a handy, 2-minute explanation from ASAP Science. (VIDEO) Science Documentary Films.
Home : Scientific Reports. Search" BSA Image Collection. General Biology Video Lecture Course. Geologic Time: Graphical Representation of Geologic Time. Free Medical Books. 15 Current Technologies My Newborn Son Won't Use. I was surprised when a 23-year-old co-worker told me she didn't remember a time before broadband Internet.
At some point, her parents must have had dial-up, but she was so young that she doesn't even remember back that far. Wireless broadband won't dominate the home market until he's 8 to 10, but my son won't remember a world where consumers pay for wired Internet connections. Even today, 4G LTE provides comparable download speeds and better upload speeds than cable Internet, but the cost of using mobile broadband all the time is prohibitive. Delivery of subunit influenza vaccine to skin with microneedles improves immunogenicity and long-lived protection : Scientific Reports. Top Ten Infrared Space Pictures. Image courtesy J.
Hora, HSCfA, W. Runner's High Hardwired in People—And Dogs. People are wired to run, according to a new study that looked at the roots of the pleasurable sensation known as runner's high.
Experienced during moderate to intense aerobic exercise, runner's high occurs when natural chemicals called endocannabinoids activate the part of the brain associated with "feeling good," said study co-author Greg Gerdeman. "Endocannabinoids are molecules that are often referred to as the body's own marijuana-like substances, because they activate similar cellular receptors," said Gerdeman, a biologist at Eckerd College in St. Petersburg, Florida. To test if running—and its feel-good effect—is hardwired in more active animals, Gerdeman and colleagues set up an experiment with two species of natural athletes, humans and dogs, and one species that doesn't run, the ferret. (See National Geographic Adventure's running guide.) The team, led by the University of Arizona's David Raichlen, recruited ten humans to run and walk on a treadmill.
How to Read Body Language to Reveal the Underlying Truth in Almost Any Situation.
Science & Nature - Human Body and Mind - Mind. Visually Channel. 100 - The Mapping of Humanity's Family Tree. MIT researchers produce miracle LED: puts out twice as much power as it takes in.