

Yossi Gofman
Actively investing in Social Media Start-ups
Funny Pics. An Awkward Moment Post de Rohan Aurora. Serendip - The Sound of NOW. Sagee Ben-Zedeff (sageeb) TapintoU. Alisha Outridge. Yael Tamar. CHART OF THE DAY: How Much Apple Is Making On The App Store. Yael Tamar Greenberg (yaeltamar) Daps'em. Hamutal Meridor. Hamutal Meridor (hamutalm) Benny Vaksendiser. Apple. iOS 5 - 200+ new features for iPad, iPhone, and iPod touch.
Apple TV Bluetooth support discovered in iOS 5. Apple's incoming iOS 5 update could enable the Apple TV's latent Bluetooth connectivity, it's reported, with mention of various pairing options being discovered in the pre-release beta code.
The new software will allow the STB to connect to Apple's Bluetooth keyboard, 9 to 5 Mac's tipster spotted, though there's also speculation that it might permit direct pairings with the iPhone, iPad and other peripherals. That functionality could open the door to Bluetooth game controllers, potentially, or using an iPod touch or iPhone as a remote control for apps running on the Apple TV. Apple has long been expected to enable App Store access on the streamer, turning it into a casual gaming console of sorts as well as increasing the number of internet media sources the Apple TV could play.
Inside Apple's iOS 5: Assistive Touch allows accessible gesture commands. Feature By AppleInsider Staff Available in Apple's latest beta build of iOS 5 is Assistive Touch, a new feature that will allow for quick gestures to be replicated for those who may be at a physical disadvantage.
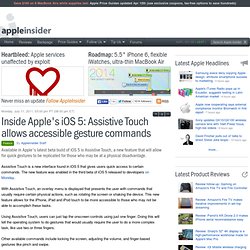
Assistive Touch is a new interface found in iOS 5 that gives users quick access to certain commands. The new feature was enabled in the third beta of iOS 5 released to developers on Monday. OS X Lion - The world’s most advanced desktop operating system. ROAR! Apple Puts Out The Call For Devs To Submit OS X Lion Apps. A Lion is quickly approaching.
OS X Lion — aka OS X 10.7. Some are saying it will hit this week. Other signs point to next week. Either way, it’s coming very soon. How do we know? The email message (pasted below) notes: OS X Lion, the eighth major release of the world’s most advanced operating system, will soon be available to millions of Mac users around the world. A GM build of Lion was released to developers last week. One key feature of OS X Lion is the Mac App Store. You’d think Apple will need at least a few days to start reviewing these Lion-specific apps from developers. Apple iPad Will Go Higher-Resolution Display: Reports - Desktops and Notebooks.
Help. Ray Kurzweil. Are you ready for robots with sensitive skin? Robots have just taken another (slightly weird) step toward becoming our overlords.
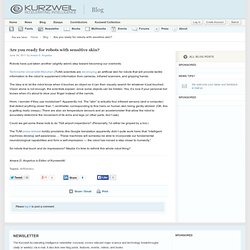
Technische Universität München (TUM) scientists are developing an artificial skin for robots that will provide tactile information to the robot to supplement information from cameras, infrared scanners, and gripping hands. The idea is to let the robot know when it touches an object so it can then visually search for whatever it just touched. Vision alone is not enough, the scientists explain, since some objects can be hidden.
Yes, it’s nice if your personal bot knows when it’s about to slice your finger instead of the carrots. Hmm, I wonder if they use moisturizer? The future of chip manufacturing. Scientists use optogenetics to control reward-seeking behavior. Nerve cells in the nucleus accumbens (red) receive input from amygdala fibers (green).
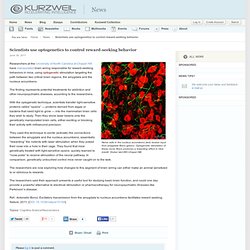
Optogenetic stimulation of these nerve fibers produces a rewarding effect in mice (credit: Stuber lab/UNC-Chapel Hill) Researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill have manipulated brain wiring responsible for reward-seeking behaviors in mice, using optogenetic stimulation targeting the path between two critical brain regions, the amygdala and the nucleus accumbens. The finding represents potential treatments for addiction and other neuropsychiatric diseases, according to the researchers. With the optogenetic technique, scientists transfer light-sensitive proteins called “opsins” — proteins derived from algae or bacteria that need light to grow — into the mammalian brain cells they wish to study.
Then they shine laser beams onto the genetically manipulated brain cells, either exciting or blocking their activity with millisecond precision. Genetic ‘conductor’ involved with new brain cell production in adults. A team of North Carolina State University researchers has discovered more about how the Foxj1 gene — connected to the production of new brain cells in adults — does its job.
The team had previously discovered that the gene was an “off switch” that told neuronal stem cells to stop reproducing and triggered the development of a stem cell “niche” in the olfactory bulbs. However, further experiments with newly developed genetically modified mice unexpectedly revealed that a fraction of Foxj1-expressing cells actually functioned as stem cells until the mouse reached the age equivalent of a human toddler, not throughout adulthood.
‘Lovotics’: the new science of engineering human, robot love. Segway – The leader in personal, green transportation. Segway PT. Computers and motors in the base of the device keep the Segway PT upright when powered on with balancing enabled.
A user commands the Segway to go forward by shifting their weight forward on the platform, and backward by shifting their weight backward. The Segway detects, as it balances, the change in its center of mass, and first establishes and then maintains a corresponding speed, forward or backward. Gyroscopic sensors and fluid-based leveling sensors detect the weight shift. Wikipedia. Chicory. "Chicory" is also the common name in the United States for curly endive (Cichorium endivia); these two closely related species are often confused.[6] Names[edit] Common chicory is also known as blue daisy, blue dandelion, blue sailors, blue weed, bunk, coffeeweed, cornflower, hendibeh, horseweed, ragged sailors, succory, wild bachelor's buttons, and wild endive.[7] (Note: "Cornflower", is more commonly applied to Centaurea cyanus.)
Common names for varieties of var. foliosum include endive, radicchio, Belgian endive, French endive, red endive, sugarloaf and witloof (or witlof). Description[edit] Doctor Who. Dalek. The Daleks i/ˈdɑːlɛks/ are a fictional extraterrestrial race of mutants principally portrayed in the British science fiction television programme Doctor Who.
The Daleks were conceived by science-fiction writer Terry Nation and first appeared in the 1963 Doctor Who serial The Daleks, in the shells designed by Raymond Cusick. Creation[edit] The Daleks were created by writer Terry Nation and designed by BBC designer Raymond Cusick.[1] They were introduced in December 1963 in the second Doctor Who serial, colloquially known as The Daleks.[2] They became an immediate and huge hit with viewers, featuring in many subsequent serials and two 1960s motion pictures. They have become as synonymous with Doctor Who as the Doctor himself, and their behaviour and catchphrases are now part of British popular culture.
Entry into popular culture[edit] WebTools. The Colbert Report. Home. Yossi Gofman (YGofman) Yossi Gofman.