

Edge : Conversations on the edge of human knowledge. Neil deGrasse Tyson. Neil deGrasse Tyson (/ˈniːəl dəˈɡræs ˈtaɪsən/; born October 5, 1958) is an American astrophysicist, author, and science communicator.
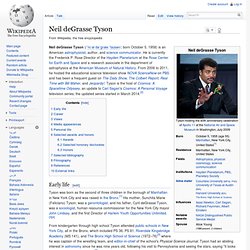
He is currently the Frederick P. Rose Director of the Hayden Planetarium at the Rose Center for Earth and Space and a research associate in the department of astrophysics at the American Museum of Natural History. From 2006 to 2011, he hosted the educational science television show NOVA ScienceNow on PBS and has been a frequent guest on The Daily Show, The Colbert Report, Real Time with Bill Maher, and Jeopardy!. Tyson is the host of Cosmos: A Spacetime Odyssey, an update to Carl Sagan's Cosmos: A Personal Voyage television series; the updated series started in March 2014.[2] Early life[edit] Astronomer Carl Sagan, who was a faculty member at Cornell University, tried to recruit Tyson to Cornell for undergraduate studies.[3] In an interview with writer Daniel Simone,[8] Tyson said: Promoting Cosmos TV series in Australia for National Geographic Career[edit] Our Universe as a Dodecahedron Natural Language Toolkit. Imagining the Tenth Dimension.
NASA Sun Earth Media Viewer: Live Solar Images. Erik Verlinde. Erik Peter Verlinde (born 21 January 1962) is a Dutch theoretical physicist and string theorist.
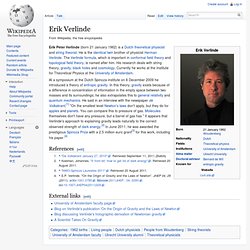
He is the identical twin brother of physicist Herman Verlinde. The Verlinde formula, which is important in conformal field theory and topological field theory, is named after him. His research deals with string theory, gravity, black holes and cosmology. Currently he works at the Institute for Theoretical Physics at the University of Amsterdam. At a symposium at the Dutch Spinoza-institute on 8 December 2009 he introduced a theory of entropic gravity. Hyper-Lexikon: Spencer-Brown. Spencer-Brown, George: Laws of Form - Gesetze der Form.

Bohmeier-Verlag, Lübeck 1997 S.194: "When we die the self-boundary eventually disappears. Before it did so, we ascribed a huge value to what we called 'inside' of ourselves, and comparativeley little value to what we called 'outside'. The death experience is thus ultimatley the loss of the selective blindness to see both sides of every distinction equally. "Form Call the space cloven by any distinction, together with the entire content of the space, the form of distinction. "Content Call it the first distinction. "An observer, since he distinguishes the space he occupies, is also a mark. " (76) [] The story about getting Russell to endorse the book is in the Preface to the Fifth English Edition (I just got hold of my sister's signed copy!
Anyway, on the back, there's these endorsements: "He is by far the best pupil I have ever taught. " Eu Yan Sang : Caring For Mankind. Philsci-archive.pitt.edu/4007/1/ConsciousnessPrimaryArt2.pdf. Wow I Had NO Idea G00GLE Could Do This! Machu Picchu 360. iNveridux - Devil's Lane Inscription - Canyonlands National Park. Spectacular footage from above the volcanic crater Softology. Labyrinths and Mazes. Beautiful_ammolite.jpg (550×600) Richard E. Bellman. Richard Ernest Bellman (August 26, 1920 – March 19, 1984) was an American applied mathematician, celebrated for his invention of dynamic programming in 1953, and important contributions in other fields of mathematics.
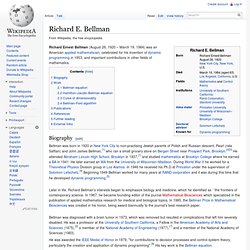
Biography[edit] Later in life, Richard Bellman's interests began to emphasize biology and medicine, which he identified as ``the frontiers of contemporary science. In 1967, he became founding editor of the journal Mathematical Biosciences which specialized in the publication of applied mathematics research for medical and biological topics. In 1985, the Bellman Prize in Mathematical Biosciences was created in his honor, being award biannually to the journal's best research paper. Bellman was diagnosed with a brain tumor in 1973, which was removed but resulted in complications that left him severely disabled. Work[edit] Bellman equation[edit] Hamilton–Jacobi–Bellman equation[edit] Curse of dimensionality[edit] Bellman–Ford algorithm[edit] Publications[edit] 1957. References[edit] DSC_1400.JPG (1395×1302)