

Kid Care - from St. Louis Children's Hospital. Mobile App for Nutrition. On the go learning works Continuous learning is needed Time and schedule hurts Need-to-know basis learning Learn a lot from each other.

SciPak, Stretchable Electronic "Skin" Personalized Medicine Getting Closer: the LPL DNA Chip. Group Wants Implantable Device Software to be Open Source. In Share The Software Freedom Law Center, an open source advocacy legal group, has issues a paper claiming that the closed nature of the software running most implantable devices is a health risk. Unsurprisingly, they then claim that the best way to address this problem, in terms of safety and security, is by making the code open source, or at least auditable. From the abstract: The FDA has issued 23 recalls of defective devices during the first half of 2010, all of which are categorized as “Class I,” meaning there is “reasonable probability that use of these products will cause serious adverse health consequences or death.” At least six of the recalls were likely caused by software defects. Despite the crucial importance of these devices and the absence of comprehensive federal oversight, medical device software is considered the exclusive property of its manufacturers, meaning neither patients nor their doctors are permitted to access their IMD’s source code or test its security.
iPhone / iPad App for Better Burn Injury Management. Boston Scientific’s SpyGlass System Proves Safe and Effective - Peroral Cholangioscopists Throughout The World Rejoice! Researchers develop electronic nose that can sniff tuberculosis - Health. Similar to the alcohol breath analyser used by police, the device will use sensors developed in California to track biomarkers.
Cellnovo Mobile Diabetes Management System Receives CE Approval. 4inShare Cellnovo has received CE Mark approval for its mobile diabetes management system.
The system includes an insulin patch pump, a wireless touch screen handset with a built-in blood glucose monitor, and an extendable applications set. Smiths Medical Unveils PharmGuard Anesthesia Software Service (P.A.S.S.) 0inShare For its popular Medfusion 3500 syringe infusion pump, Smiths Medical (St.
Paul, Minn.) has announced a new service, specifically aimed at anesthesia and critical care market. Dubbed PharmGuard Anesthesia Software Service (P.A.S.S.), the offering provides “anesthesiologists and pharmacists with the convenience of a customer-specific drug library entered into their Medfusion® 3500 syringe infusion pumps prior to shipping the pumps to them,” according to the company. Engineers Use Wireless Network to Monitor Breathing. 7inShare A couple years ago, a team of researchers from the University of Utah managed to create a wireless network made from standard home automation devices to “see” through walls.
Now, the engineers are using the same technology to monitor breathing in patients with sleep apnea, post surgery, and babies at risk for SIDS. The system consists of a network of 20 off-the-shelf wireless transceivers placed on the edge of a bed, which allows for a total of 380 individual measurements. Ultrasonix To Present New Positional Tracking Technology for Peripheral Nerve Blocks. 2inShare SonixGPS from Ultrasonix Medical Corporation is an interesting technology that might make peripheral nerve blocks quicker and easier.
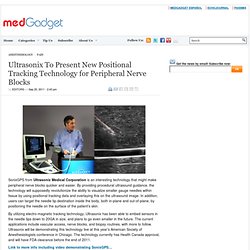
By providing procedural ultrasound guidance, the technology will supposedly revolutionize the ability to visualize smaller gauge needles within tissue by using positional tracking data and overlaying this on the ultrasound image. In addition, users can target the needle tip destination inside the body, both in-plane and out-of-plane, by positioning the needle on the surface of the patient’s skin. By utilizing electro-magnetic tracking technology, Ultrasonix has been able to embed sensors in the needle tips down to 20GA in size, and plans to go even smaller in the future. The current applications include vascular access, nerve blocks, and biopsy routines, with more to follow. Wireless Pacemaker Programming Device Unveiled at USC Body Computing Conference. 6inShare At the Body Computing Conference held on September 23 at the University of Southern California, Karten Design (Los Angeles, CA) introduced a wireless, cloud-connected device designed to simplify the programming of pacemakers.
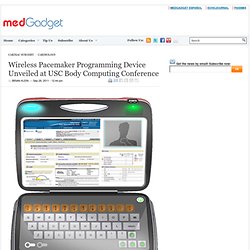
The conceptual device is said to facilitate access to electronic medical records during pacemaker procedures. In addition, it enables nurses to operate equipment with real-time remote support from doctors and technicians. The device is a result of a collaboration between Karten Design and the USC Center for Body Computing (CBC). Check out the press release: Today, health care facilities must store and maintain up to five distinct programming systems, which are all operated by off-site manufacturers’ representatives. Images: (Top) Healthcare profressionals can update a patient’s electronic medical record directly on the device. Flashback: Exclusive: Interview with Medical Design Innovator Stuart Karten; Innovative Hearing Aid from Starkey Labs Takes Awards.
Scientists use brain imaging to reveal the movies in our mind. BERKELEY — Imagine tapping into the mind of a coma patient, or watching one’s own dream on YouTube.
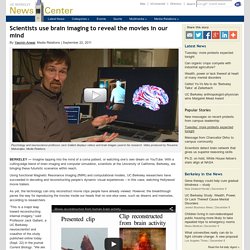
With a cutting-edge blend of brain imaging and computer simulation, scientists at the University of California, Berkeley, are bringing these futuristic scenarios within reach. Using functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) and computational models, UC Berkeley researchers have succeeded in decoding and reconstructing people’s dynamic visual experiences – in this case, watching Hollywood movie trailers.